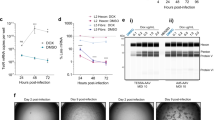
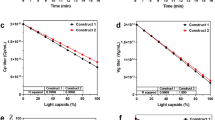
Abstract
Adenovirus (Ad) and Adeno-associated virus (AAV) are efficient gene delivery systems; manipulation of the wild-type genome allows their use as vectors for the overexpression of desirable transgenes. Generation and purification of such viral vectors can be labour intensive, costly and require specialized equipment, but a new generation of membrane-mediated ion exchange kits for purification of recombinant virus may facilitate this process. Here, we examine the yields, transgene expression and purity of preparations of Ad and AAV purified using commercially available kits in comparison to other established techniques for purification of recombinant viral vectors. We demonstrate comparable results for Ad and AAV respectively in all parameters investigated, with a substantial reduction in purification time for the kit-based technology. Such approaches are attractive methods for small-scale purification of recombinant Ad and AAV viral vectors.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hacein-Bey-Abina S et al. LMO2-associated clonal T cell proliferation in two patients after gene therapy for SCID-X1. Science 2003; 302: 415–419.
Lehrman S . Virus treatment questioned after gene therapy death. Nature 1999; 401: 517–518.
Huyghe BG et al. Purification of a type 5 recombinant adenovirus encoding human p53 by column chromatography. Hum Gene Ther 1995; 6: 1403–1416.
Blanche F et al. An improved anion-exchange HPLC method for the detection and purification of adenoviral particles. Gene Therapy 2000; 7: 1055–1062.
Shabram PW et al. Analytical anion-exchange HPLC of recombinant type-5 adenoviral particles. Hum Gene Ther 1997; 8: 453–465.
Klyushnichenko V, Bernier A, Kamen A, Harmsen E . Improved high-performance liquid chromatographic method in the analysis of adenoviral particles. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl 2001; 755: 27–36.
Vellekamp G et al. Empty capsids in column-purified recombinant adenovirus preparations. Hum Gene Ther 2001; 12: 1923–1936.
Adenopure Instruction Manual www.puresyn.com.
Graham FL, Smiley J, Russel WC, Narin R . Characteristics of a human cell line transformed by DNA from human adenovirus type 5. J Gen Virol 1997; 36: 59–72.
Zhang WW, Koch PE, Roth JA . Detection of wild-type contamination in a recombinant adenoviral preparation by PCR. Biotechniques 1995; 18: 444–447.
Clark KR, Liu X, McGrath JP, Johnson PR . Highly purified recombinant adeno-associated virus vectors are biologically active and free of detectable helper and wild type viruses. Hum Gene Ther 1999; 10: 1031–1039.
Zolotukhin S et al. Recombinant adeno-associated virus purification using novel methods improves infectious titer and yield. Gene Therapy 1999; 6: 973–985.
Auricchio A et al. Isolation of highly infectious and pure adeno-associated virus type 2 vectors with a single-step gravity-flow column. Hum Gene Ther 2001; 12: 71–76.
Brument N et al. A versatile and scalable two-step ion-exchange chromatography process for the purification of recombinant adeno-associated virus serotypes-2 and -5. Mol Ther 2002; 6: 678–686.
Green AP et al. A new scalable method for the purification of recombinant adenovirus vectors. Hum Gene Ther 2002; 13: 1921–1934.
McIntyre, 2001-Adenovirus Reference Material Working Group is a consortium of industry, government and academic researchers to manufacture adenovirus reference standards and codify analytical methods under the auspices of the FDA. Information is available at www.wilbio.com.
Zhu J et al. Characterization of replication-competent adenovirus isolates from large-scale production of a recombinant adenoviral vector. Hum Gene Ther 1999; 10: 113–121.
Summerford C, Samulski RJ . Membrane-associated heparan sulfate proteoglycan is a receptor for adeno-associated virus type 2 virions. J Virol 1998; 72: 1438–1445.
Gao G et al. Purification of recombinant adeno-associated virus vectors by column chromatography and its performance in vivo. Hum Gene Ther 2000; 11: 2079–2091.
Smith RH, Ding C, Kotin RM . Serum-free production and column purification of adeno-associated virus type 5. J Virol Methods 2003; 114: 115–124.
Grimm D, Kern A, Rittner K, Kleinschmidt JA . Novel tools for production and purification of recombinant adeno-associated virus vectors. Hum Gene Ther 1998; 9: 2745–2760.
Rabinowitz JE et al. Cross-dressing the virion: the transcapsidation of adeno-associated virus serotypes functionally defines subgroups. J Virol 2004; 78: 4421–4432.
Kaludov N et al. Adeno-associated virus serotype 4 (AAV4) and AAV5 both require sialic acid binding for hemagglutination and efficient transduction but differ in sialic acid linkage specificity. J Virol 2001; 75: 6884–6893.
Walters RW et al. Binding of adeno-associated virus type 5 to 2, 3-linked sialic acid is required for gene transfer. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 20610–20616.
Davidoff AM et al. Purification of recombinant adeno-associated virus type 8 vectors by ion exchange chromatography generates clinical grade vector stock. J Virol Methods 2004; 121: 209–215.
Harris JD, Beattie SG, Dickson JG . Novel tools for production and purification of recombinant adeno-associated viral vectors. Methods Mol Med 2003; 76: 255–267.
Maizel Jr JV, White DO, Scharff MD . The polypeptides of adenovirus. I. Evidence for multiple protein components in the virion and a comparison of types 2, 7A, and 12. Virology 1968; 36: 126–136.
Acknowledgements
We thank Science Foundation Ireland (SFI), Health Research Board Ireland and Higher Education Authority for their financial support and also Martina Harte (NUIG) and Vecteurotrain, for their guidance in establishing the adenoviral purification protocol. We thank Dr T Athanasopoulos, Dr J Harris and Dr G Dickson for guidance and advice with iodixanol gradient and heparin column purification of AAV, Dr D Grimm and Dr J Kleinschmidt for plasmid pDG and Dr N Madigan for cloning of PON1. We also thank Dr D Draganov for anti-hPON1 antibody.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duffy, A., O'Doherty, A., O'Brien, T. et al. Purification of adenovirus and adeno-associated virus: comparison of novel membrane-based technology to conventional techniques. Gene Ther 12 (Suppl 1), S62–S72 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302616
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302616
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Evaluating the stability of host-reference gene expression and simultaneously quantifying parasite burden and host immune responses in murine malaria
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Virus purification by CsCl density gradient using general centrifugation
Archives of Virology (2017)
-
Purification of recombinant baculoviruses for gene therapy using membrane processes
Gene Therapy (2009)