Abstract
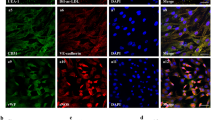
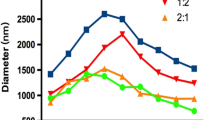
Myocardial angiogenesis mediated by human vascular endothelial growth factor 165 (hVEGF165) cDNA was promoted in rat myocardium using an in vivo-targeted gene delivery system known as ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction (UTMD). Microbubbles carrying plasmids encoding hVEGF165, or control solutions were infused intravenously during ultrasonic destruction of the microbubbles within the myocardium. Biochemical and histological assessment of gene expression and angiogenesis were performed 5, 10, and 30 days after UTMD. UTMD-treated myocardium contained hVEGF165 protein and mRNA. The myocardium of UTMD-treated animals showed hypercellular foci associated with hVEGF165 expression and endothelial cell markers. Capillary density in UTMD-treated rats increased 18% at 5 days and 33% at 10 days, returning to control levels at 30 days (P<0.0001). Similarly, arteriolar density increased 22% at 5 days, 86% at 10 days, and 31% at 30 days (P<0.0001). Thus, noninvasive delivery of hVEGF165 to rat myocardium by UTMD resulted in significant increases in myocardial capillary and arteriolar density.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hammond HK, McKirnan MD . Angiogenic gene therapy for heart disease: a review of animal studies and clinical trials. Cardiovasc Res 2001; 49: 561–567.
Simons M et al. Clinical trials in coronary angiogenesis: issues, problems, consensus: an expert panel summary. Circulation 2000; 102: E73–E86.
Pecher P, Schumacher BA . Angiogenesis in ischemic human myocardium: clinical results after 3 years. Ann Thorac Surg 2000; 69: 1414–1419.
Simons M, Ware JA . Therapeutic angiogenesis in cardiovascular disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2003; 2: 863–871.
Rosengart TK et al. Six-month assessment of a Phase I trial of angiogenic gene therapy for the treatment of coronary artery disease using direct intramyocardial administration of an adenovirus vector expressing the VEGF121 cDNA. Ann Surg 1999; 230: 466–472.
Udelson JE et al. Therapeutic angiogenesis with recombinant fibroblast growth factor-2 improves stress and rest myocardial perfusion abnormalities in patients with severe symptomatic chronic coronary artery disease. Circulation 2000; 102: 1605–1610.
Henry TD et al. The VIVA trial: vascular endothelial growth factor in ischemia for vascular angiogenesis. Circulation 2003; 107: 1359–1365.
Simons M et al. Pharmacological treatment of coronary artery disease with recombinant fibroblast growth factor-2: double-blind, randomized, controlled clinical trial. Circulation 2002; 105: 788–793.
Laham RJ et al. Local perivascular delivery of basic fibroblast growth factor in patients undergoing coronary bypass surgery: results of a phase I randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Circulation 1999; 100: 1865–1871.
Ruel M et al. Long-term effects of surgical angiogenic therapy with fibroblast growth factor 2 protein. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2002; 124: 28–34.
Lederman RJ et al. Therapeutic angiogenesis with recombinant fibroblast growth factor-2 for intermittent claudication (the TRAFFIC study): a randomised trial. Lancet 2002; 359: 2053–2058.
Grines CL et al. Angiogenic gene therapy (AGENT) trial in patients with stable angina pectoris. Circulation 2002; 105: 1291–1297.
Losordo DW et al. Phase 1/2 placebo-controlled, double-blind, dose-escalating trial of myocardial vascular endothelial growth factor 2 gene transfer by catheter delivery in patients with chronic myocardial ischemia. Circulation 2002; 105: 2012–2018.
Hedman M et al. Safety and feasibility of catheter-based local intracoronary vascular endothelial growth factor gene transfer in the prevention of postangioplasty and in-stent restenosis and in the treatment of chronic myocardial ischemia: phase II results of the Kuopio Angiogenesis Trial (KAT). Circulation 2003; 107: 2677–2683.
Shohet RV et al. Echocardiographic destruction of albumin microbubbles directs gene delivery to the myocardium. Circulation 2000; 101: 2554–2556.
Chen SY et al. Optimization of ultrasound parameters for cardiac gene delivery of adenoviral or plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid by ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction. J Am Coll Cardiol 2003; 42: 301–308.
Bekeredjian R et al. Ultrasound targeted microbubble destruction can repeatedly direct highly specific plasmid expression to the heart. Circulation 2003; 108: 1022–1026.
Dor Y et al. Conditional switching of VEGF provides new insights into adult neovascularization and pro-angiogenic therapy. EMBO J 2002; 21: 1939–1947.
D'Amore PA . Capillary growth: a two-cell system. Semin Cancer Biol 1992; 3: 49–56.
Carmeliet P, Collen D . Genetic analysis of blood vessel formation. Role of endothelial versus smooth muscle cells. Trends Cardiovasc Med 1997; 7: 271–281.
Grosskreutz CL et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor-induced migration of vascular smooth muscle cells in vitro. Microvasc Res 1999; 58: 128–136.
Carmeliet P . Mechanisms of angiogenesis and arteriogenesis. Nat Med 2000; 6: 389–395.
Song J, Ming QI, Kaul S, Price RJ . Stimulation of arteriogenesis in skeletal muscle by Microbubbles destruction with ultrasound. Circulation 2002; 106: 1550–1555.
Greenleaf WJ et al. Artificial cavitation nuclei significantly enhance acoustically induced cell transfection. Ultrasound Med Biol 1998; 24: 587–595.
Miller DL, Gies RA . The interaction of ultrasonic heating and cavitation in vascular bioeffects on mouse intestine. Ultrasound Med Biol 1998; 24: 123–128.
Wu J, Ross JP, Chiu JF . Reparable sonoporation generated by microstreaming. J Acoust Soc Am 2002; 111: 1460–1464.
Kondo T, Misik V, Riesz P . Effect of gas-containing microspheres and echo contrast agents on free radical formation by ultrasound. Free Radic Biol Med 1998; 25: 605–612.
Skyba DM et al. Direct in vivo visualization of intravascular destruction of microbubbles by ultrasound and its local effects on tissue. Circulation 1998; 98: 290–293.
Price RJ, Skyba DM, Kaul S, Skalak TC . Delivery of colloidal particles and red blood cells to tissue through microvessel ruptures created by targeted microbubble destruction with ultrasound. Circulation 1998; 98: 1264–1267.
Croll SD et al. VEGF-mediated inflammation precedes angiogenesis in adult brain. Exp Neurol 2004; 187: 388–402.
Mor F, Quintana FJ, Cohen IR . Angiogenesis-inflammation cross-talk: vascular endothelial growth factor is secreted by activated T cells and induces Th1 polarization. J Immunol 2004; 172: 4618–4623.
Chavakis T et al. Regulation of neovascularization by human neutrophil peptides (alpha-defensins): a link between inflammation and angiogenesis. FASEB J 2004; epub ahead of print.
Chen SY et al. Bioeffects of myocardial contrast microbubble destruction by echocardiography. Echocardiography 2002; 19: 495–500.
Bekeredjian R et al. Effects of ultrasound targeted microbubble destruction on cardiac gene expression. J Ultrasound Med Biol 2004; 30: 539–543.
Hershey JC et al. Revascularization in the rabbit hindlimb: dissociation between capillary sprouting and arteriogenesis. Cardiovasc Res 2001; 49: 618–625.
Helisch A, Schaper W . Arteriogenesis: the development and growth of collateral arteries. Microcirculation 2003; 10: 83–97.
Ware JA, Simons M . Angiogenesis in ischemic heart disease. Nat Med 1997; 3: 158–164.
Losordo DW, Dimmeler S . Therapeutic angiogenesis and vasculogenesis for ischemic disease. Part I. Angiogenic cytokines. Circulation 2004; 109: 2487–2491.
Moulton KS et al. Inhibition of plaque neovascularization reduces macrophage accumulation and progression of advanced atherosclerosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100: 4736–4741.
Belgore F et al. Localisation of members of the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) family and their receptors in human atherosclerotic arteries. J Clin Pathol 2004; 57: 266–272.
Khurana R et al. Angiogenesis-dependent and independent phases of intimal hyperplasia. Circulation 2004; 110: 2436–2443.
Templeton NS et al. Improved DNA: liposome complexes for increased systemic delivery and gene expression. Nat Biotechnol 1997; 15: 647–652.
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J . Extraction and Purification of plasmid DNA. In: Sambrook J (ed). Molecular Cloning Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, 1989, pp 1.38–1.39.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the American Heart Association (Texas Affiliate) 0265186Y (Frenkel), National Institutes of Health K24 HL03890 (Grayburn), American Heart Association (National) 0150586N (Shohet).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Korpanty, G., Chen, S., Shohet, R. et al. Targeting of VEGF-mediated angiogenesis to rat myocardium using ultrasonic destruction of microbubbles. Gene Ther 12, 1305–1312 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302532
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302532
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The partitioning of nanoparticles to endothelium or interstitium during ultrasound-microbubble-targeted delivery depends on peak-negative pressure
Journal of Nanoparticle Research (2015)
-
miR-29b as a Therapeutic Agent for Angiotensin II-induced Cardiac Fibrosis by Targeting TGF-β/Smad3 signaling
Molecular Therapy (2014)
-
Stimulation of adult resident cardiac progenitor cells by durable myocardial expression of thymosin beta 4 with ultrasound-targeted microbubble delivery
Gene Therapy (2013)
-
Ultrasound-mediated targeted microbubbles: a new vehicle for cancer therapy
Frontiers of Chemical Science and Engineering (2013)
-
The angiogenic response is dependent on ultrasound contrast agent concentration
Vascular Cell (2012)