Abstract
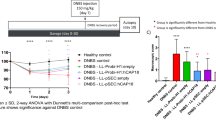
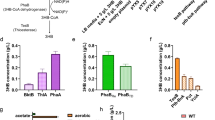
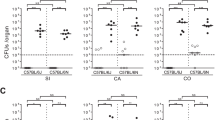
Taking advantage of the proximity of bowel mucosa to luminal bacteria, we have attempetd to deliver a therapeutic gene to the colonic mucosa by oral administration of an invasive and non-pathogenic Escherichia coli. E. coli diamenopimelate (dap) auxotroph, harboring plasmid pGB2Ωinv-hly, express the inv gene from Yersinia pseudotubercolosis that confers the ability to invade nonprofessional phagocytic cells and the hly gene from Listeria monocytogenes that allows expression of lystreriolysin O, a perforin cytolysin able to perfore phagosomal membranes. This bacterial vector invades and transfers functional DNA to epithelial cells in vitro. We have shown that this strain carrying a therapeutic gene (pC1ΩTGF-β1) can significantly reduce the severity of experimental colitis in mice. However, as a consequence of mucosal barrier disruption during colitis, vector-specific mRNA transcripts could be recovered from the colon and also from extra-colonic tissues. We therefore replaced the constitutive CMV promoter in pC1ΩTGF-β1 by the inflammation-inducible interleukin-8 promoter generating plasmid pC1ΩTGF-β1IND. Plasmid-specific TGF-β1 mRNA transcripts were detectable in mouse CMT-93 epithelial cells incubated with E. coli BM2710/pGB2Ωinv-hly carrying pC1ΩTGF-β1IND following exposure to inflammatory cytokines. Furthermore, the transcripts were detectable only within inflamed tissues and the therapeutic effects were comparable to those in animals treated with E. coli BM2710/pGB2Ωinv-hly+pC1ΩTGF-β1. In summary, engineered enteric bacteria can efficiently deliver in vivo therapeutic genes to the intact intestinal mucosa and regulation expression of the therapeutic gene by an inflammation-inducible promoter prevents its dissemination during colitis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sands BE . Therapy of inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 2000; 118: S68–S82.
Ribbson KA, Thomson JH, Liu X . Anti-inflammatory properties of interleukin-10 administration in hapten-induced colitis. Eur J Pharmacol 1997; 323: 245–254.
Arnott ID, McNeill G, Satsangi J . An analysis of factors influencing short-term and sustained response to infliximab treatment for Crohn's disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2003; 17: 1451–1457.
Kitani A et al. Treatment of experimental (trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid) colitis by intranasal administration of transforming growth factor (TGF-β1 plasmid: TGF-β1 mediated suppression of T-helper cell type 1 response occurs by interleukin (IL)-10 induction and IL-12 receptor β2 chain downregulation. J Exp Med 2000; 192: 41–52.
Barbara G et al. Interleukin-10 gene transfer prevents experimental colitis in rats. Gut 2000; 46: 344–349.
Piccirillo CA, Chang Y, Prud'homme GJ . TGF-β1 somatic gene therapy prevents autoimmune disease in nonobese diabetic mice. J Immunol 1998; 161: 3950–3956.
Chun S et al. Distribution, fate and mechanism of immune modulation following mucosal delivery of plasmid DNA encoding IL-10. J Immunol 1999; 10: 1915–1922.
Sanderson N et al. Hepatic expression of mature trasforming growth factor β1 in transgenic mice results in multiple tissue lesion. Cell Biol 1995; 110: 975–984.
Sime PJ, Xing Z, Graham FL, Gauldie J . Adenovector-mediated gene transfer of active transforming factor-β induces prolonged severe fibrosis in rat lungs. J Clin Invest 1997; 100: 768–776.
Grillot-Courvalin C, Goussard S, Courvalin P . Bacteria as gene delivery vectors for mammalian cells. Curr Opin Biotechnol 1999; 10: 477–481.
Weiss S, Chakraborty T . Transfer of eukaryotic expression plasmids to mammalian host cells by bacterial carriers. Curr Opin Biotech 2001; 12: 467–472.
Sizemore DR, Branstrom AA, Sadoff JC . Attenuated Shigella as a DNA delivery vehicle for DNA-mediated immunization. Science 1995; 270: 299–302.
Courvalin P, Goussard S, Grillot-Courvalin C . Gene transfer from bacteria to mammalian cells. C. R. Acad. Sci. 1995; 318: 1207–1212.
Grillot-Courvalin C et al. Functional gene transfer from intracellular bacteria to mammalian cells. Nature Biotechnol 1998; 16: 862–866.
Darji A et al. Oral somatic transgene vaccination using attenuated S. typhimurium. Cell 1997; 91: 765–775.
Dietrich G et al. Delivery of antigen-encoding plasmid DNA into the cytosol of macrophages by attenuated suicide Listeria monocytogenes. Nat Biotechnol 1998; 16: 181–185.
Takeuchi M, Alard P, Streilein JW . TGF-β1 promotes immune deviation by altering accessory signals of antigen-presenting cells. J Immunol 1998; 160: 1589–1597.
Babyatsky MW, Rossiter G, Podolsky DK . Expression of transforming growth factors α and β in colonic mucosa in inflamamtory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 1996; 110: 975–984.
Kulkarni AB et al. Transforming growth factor b1 null mutation in mice causes excessive inflamamtory response and early death. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1993; 90: 770–774.
Gardiner KR et al. Colonic bacteria and bacterial translocation in experimental colitis. Br J Surg 1993; 80: 512–516.
Roebick KA . Regulation of interleukin-8 gene expression.J Interferon Cytokine Res 1999; 19: 429–438.
Parhar K et al. The p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase regulates interleukin-1beta-induced IL-8 expression via an effect on the IL-8 promoter in intestinal epithelial cells. Immunology 2003; 108: 502–512.
Bouma G, Strober W . The immunological and genetic basis of inflammatory bowel disease. Nat Rev 2003; 3: 521–533.
Tilg H et al. Treatment of Crohn's disease with recombinant human interleukin 10 induces the proinflammatory cytokine interferon gamma. Gut 2000; 50: 191–195.
Van Deventer SJH, Elson CO, Fedorack RN . Multiple doses of intravenous interleukin-10 in steroid refractory Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology 1997; 113: 383–389.
Kruis W et al. Double-blind comparison of an oral Escherichia coli preparation and mesalazine in maintaining remission of ulcerative colitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 1997; 11: 853–858.
Fabia R et al. The effect of exogenous administration of Lactobacillus reuteri R2LC and oat fiber on acetic acid-induced colitis in the rat. Scand J Gastroenterol 1993; 28: 155–162.
Madsen KL et al. Lactobacillus species prevents colitis in interleukin-10 gene-deficient mice. Gastroenterology 1999; 116: 1107–1114.
Shata MT et al. Recent advances with recombinant bacterial vaccine vectors. Mol Med Today 2000; 6: 66–70.
Pereira CM, Guth BE, Sbrogio-Almeida ME, Castilho BA . Antibody response against Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin expressed as fusion to flagellin. Microbiology 2001; 147: 861–867.
Steidler L et al. Treatment of murine colitis by Lactococcus lactis secreting interleukin-10. Science 2000; 289: 1352–1355.
Paglia P et al. Gene transfer in dendritic cells, induced by oral DNA vaccination with Salmonella typhimurium, results in protective immunity against a murine fibrosarcoma. Blood 1998; 92: 3172–3176.
Paglia P et al. In vivo correction of genetic defects of monocyte/macrophages using attenuated Salmonella as oral vectors for targeted gene delivery. Gene Therapy 2000; 7: 1725–1730.
Thomas CE, Ehrhardt A, Kay MA . Progress and problems with the use of viral vectors for gene therapy. Nat Rev Genet 2003; 4: 346–358.
Castagliuolo I, Brun P, Tormen D, Palù G . Lymphocytes endowed with colon selective homing and engineered to produce TGF-β1 prevent the development of dinitro benzen sulfonic acid colitis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2003; 15: 1257–1265.
Liu Q, Muruve DA . Molecular basis of the inflammatory response to adenovirus vectors. Gene Therapy 2003; 10: 935–940.
Tousignant JD et al. Comprehensive analysis of the acute toxicities induced by systemic administration of cationic lipid:plasmid DNA complexes in mice. Hum Gene Ther 2000; 11: 2493–2513.
Hense M et al. Eukaryotic expression plasmid transfer from the intracellular bacterium Listeria monocytogenes to host cells. Cell Microbiol 2001; 3: 599–609.
Grillot-Courvalin C, Goussard S, Courvalin P . Wild-type intracellular bacteria deliver DNA into mammalian cells. Cell Microbiol 2002; 4: 177–186.
Critchley RJ et al. Potential therapeuthic applications of recombinant, invasive E. coli. Gene Ther 2004; 11: 1224–1233.
Buning H et al. Receptor targeting of adeno-associated virus vectors. Gene Therapy 2003; 10: 1142–1151.
Gosselin MA, Lee RJ . Folate receptor-targeted liposomes as vectors for therapeutic agents. Biotechnol Annu Rev 2002; 8: 103–131.
Kluth DC, Erwing LP, Pearce WP, Rees AJ . Gene transfer into inflamed glomeruli using macrophages transfected with adenovirus. Gene Therapy 2000; 7: 263–270.
Hansen G et al. CD4+ T helper cells engineered to produce latent TGF-β1 reverse allergen-induced airway hyper reactivity and inflammation. J Clin Invest 2000; 105: 61–70.
van Montfrans C et al. Prevention of colitis by interleukin-10 transduced T lymphocytes in SCID mice transfer model. Gastroenterology 2002; 123: 1865–1876.
Harrington KJ, Linardakis E, Vile RG . Transcriptional control: an essential component of cancer gene therapy strategies? Adv Drug Del Rev 2000; 44: 167–184.
Barzon L et al. Transcriptionally-targeted retroviral vector for combined suicide and immunomodulating gene therapy of thyroid cancer. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2002; 87: 5304–5311.
Berg RD . Translocation of enteric bacteria in health and disease. Curr Stud Hematol Blood Transfus 1992; 59: 44–65.
Sartor RB . Cytokines in intestinal inflammation: pathophysiological and clinical considerations. Gastroenterology 1994; 106: 533–544.
During MJ et al. Peroral gene therapy of lactose intolerance using an adeno-associated virus vector. Nat Med 1998; 4: 1131–1135.
Roy K, Mao HQ, Huang SK, Leong KW . Oral gene delivery with chitosan-DNA nanoparticles generates immunologic protection in a murine model of peanut allergy. Nat Med 1999; 5: 387–391.
Keates AC et al. Interleukin 16 is up-regulated in Crohn's disease and participates in TNBS colitis in mice. Gastroenterology 2000; 119: 972–982.
Castagliuolo I et al. Neurokinin-1 (NK-1) receptor is required in Clostridium difficile-induced enteritis. J Clin Invest 1998; 101: 1547–1550.
Barzon L et al. Gene therapy of thyroid cancer via retrovirally-driven combined expression of human interleukin-2 and Herpes Simplex Virus thymidine kinase. Eur J Endocrinol 2003; 148: 73–80.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by grants from the University of Padua to IC, MIUR to GP, and ‘Vaincre la Mucoviscidose’ to CGC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Castagliuolo, I., Beggiao, E., Brun, P. et al. Engineered E. coli delivers therapeutic genes to the colonic mucosa. Gene Ther 12, 1070–1078 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302493
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302493
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Development of bacteria as diagnostics and therapeutics by genetic engineering
Journal of Microbiology (2019)
-
Recent trends and advances in microbe-based drug delivery systems
DARU Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences (2019)
-
Cyclooxygenase-2 Silencing for the Treatment of Colitis: A Combined In Vivo Strategy Based on RNA Interference and Engineered Escherichia Coli
Molecular Therapy (2015)
-
Engineered retroviral virus-like particles for receptor targeting
Archives of Virology (2014)
-
Gene therapy for cancer: bacteria-mediated anti-angiogenesis therapy
Gene Therapy (2011)