Abstract
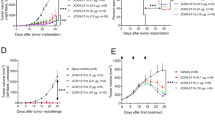
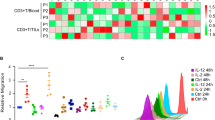
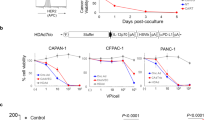
Interleukin-13 receptor (IL-13R) α2 chain plays a key role in ligand binding and internalization. We have recently demonstrated that this cytokine receptor chain has unique characteristics in tumor biology: it inhibits tumorigenicity of breast and pancreatic cancer in animal models. In this study, we have exploited IL-13Rα2 chain and established a novel approach for pancreatic cancer therapy. For this, a plasmid encoding the IL-13Rα2 chain gene was mixed with liposomes and injected into subcutaneously or orthotopically xenografted human pancreatic tumors in immunodeficient mice, followed by systemic or local therapy by a recombinant IL-13 cytotoxin. Only tumors forced to express IL-13Rα2 chain acquired extreme susceptibility to the antitumor effect of IL-13 cytotoxin. There was a dominant infiltration of cells including macrophages and natural killer cells in the regressing tumors. Since macrophages were found to produce nitric oxide, IL-13Rα2-targeted cancer therapy involved not only a direct tumor cell killing by IL-13 cytotoxin but also activation of innate immune response at the tumor site. Therefore, this approach may be a new powerful tool for pancreatic cancer or other localized cancer therapy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Thomas A, Murray T, Thun M . Cancer statistics 2002. CA Cancer J Clin 2002; 52: 23–47.
Lillemoe KD . Current management of pancreatic carcinoma. Ann Surg 1995; 221: 133–148.
Giantonio BJ et al. Superantigen-based immunotherapy: a phase I trial of PNU-214565, a monoclonal antibody-staphylococcal enterotoxin A recombinant fusion protein, in advanced pancreatic and colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 1997; 15: 1994–2007.
Mulvihill S et al. Safety and feasibility of injection with an E1B-55 kDa gene-deleted, replication selective adenovirus (ONYX-015) into primary carcinomas of the pancreas: a phase I trial. Gene Ther 2001; 8: 308–315.
Löhr M et al. Microencapsulated cell-mediated treatment of inoperable pancreatic carcinoma. Lancet 2001; 357: 1591–1592.
Minty A et al. Interleukin-13 is a new human lymphokine regulating inflammatory and immune responses. Nature 1993; 36: 248–251.
Serve H et al. Inhibition of proliferation and clonal growth of human breast cancer cells by interleukin 13. Cancer Res 1996; 56: 3583–3588.
Lebel-Binay S et al. Experimental gene therapy of cancer using tumor cells engineered to secrete interleukin-13. Eur J Immunol 1995; 25: 2340–2348.
Kawakami M, Leland P, Kawakami K, Puri RK . Mutation and functional analysis of IL-13 receptors in human malignant glioma cells. Oncol Res 2001; 12: 459–467.
Obiri NI, Debinski W, Leonard WJ, Puri RK . Receptor for interleukin 13: interaction with interleukin 4 by a mechanism that does not involve the common γ chain shared by receptors for interleukins 2, 4, 7, 9 and 15. J Biol Chem 1995; 270: 8797–8804.
Murata T, Obiri NI, Debinski W, Puri RK . Human ovarian carcinoma cell lines express IL-4 and IL-13 receptors: comparison between IL-4- and IL-13-induced signal transduction. Int J Cancer 1997; 70: 230–240.
Obiri NI et al. The IL-13 receptor structure differs on various cell types and may share more than one component with IL-4 receptor. J Immunol 1997; 158: 756–764.
Obiri NI, Murata T, Debinski W, Puri RK . Modulation of interleukin (IL)-13 binding and signaling by the γc chain of the IL-2 receptor. J Biol Chem 1997; 272: 20251–20258.
Murata T, Obiri NI, Puri RK . Structure of and signal transduction through interleukin-4 and interleukin-13 receptors. Int J Mol Med 1998; 1: 551–557.
Joshi BH, Plautz GE, Puri RK . IL-13 receptor α chain: a novel tumor associated transmembrane protein in primary explants of human malignant gliomas. Cancer Res 2000; 60: 1168–1172.
Aman MJ et al. cDNA cloning and characterization of the human interleukin 13 receptor α chain. J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 29265–29270.
Hilton DJ et al. Cloning and characterization of a binding subunit of the interleukin-13 receptor that is a component of the interleukin-4 receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1996; 93: 497–501.
Miloux B et al. Cloning of the human IL-13Rα1 chain and reconstitution with the IL-4Rα of a functional IL-4/IL-13 receptor complex. FEBS Lett 1997; 401: 163–166.
Nelms K et al. The IL-4 receptor: signaling mechanisms and biologic functions. Annu Rev Immunol 1999; 17: 701–738.
Caput D et al. Cloning and characterization of a specific interleukin (IL)-13 binding protein structurally related to the IL-5 receptor α chain. J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 16921–16926.
Donaldson DD et al. The murine IL-13 receptor α2: molecular cloning, characterization, and comparison with murine IL-13 receptor α1. J Immunol 1998; 161: 2317–2324.
Kawakami K, Taguchi J, Murata T, Puri RK . The interleukin-13 receptor α2 chain: an essential component for binding and internalization but not for IL-13 induced signal transduction through STAT6 pathway. Blood 2001; 97: 2673–2679.
Kawakami K, Takeshita F, Puri RK . Identification of distinct roles for a dileucine and a tyrosine internalization motif in the interleukin-13 binding component IL-13 receptor α2 chain. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 25114–25120.
Murata T, Obiri NI, Debinski W, Puri RK . Structure of IL-13 receptor: analysis of composition in cancer and immune cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1997; 238: 90–94.
Husain SR, Puri RK . Interleukin-13 fusion cytotoxin as a potent targeted agent for AIDS-Kaposi's sarcoma xenograft. Blood 2000; 95: 3506–3513.
Joshi BH, Kawakami K, Leland P, Puri RK . Heterogeneity of interleukin-13 receptor expression and subunit structure in squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck: differential sensitivity to a chimeric fusion protein comprised of interleukin-13 and a mutated form of Pseudomonas exotoxin. Clin Cancer Res 2002; 8: 1948–1956.
Kawakami K, Kawakami M, Joshi BH, Puri RK . Interleukin-13 receptor-targeted cancer therapy in an immunodeficient animal model of human head and neck cancer. Cancer Res 2001; 61: 6194–6200.
Murata T, Husain SR, Mohri H, Puri RK . Two different IL-13 receptor chains are expressed in normal human skin fibroblasts, and IL-4 and IL-13 mediate signal transduction through a common pathway. Int Immunol 1998; 10: 1103–1110.
Maini A et al. Interleukin-13 receptors on human prostate carcinoma cell lines represent a novel target for a chimeric protein composed of IL-13 and a mutated form of Pseudomonas exotoxin. J Urol 1997; 158: 948–953.
Kawakami K, Husain SR, Bright RK, Puri RK . Gene transfer of interleukin-13 receptor α2 chain dramatically enhances the antitumor effect of IL-13 receptor-targeted cytotoxin in human prostate cancer xenografts. Cancer Gene Ther 2001; 8: 861–868.
Leland P et al. Human breast carcinoma cells express type II IL-4 receptors and are sensitive to antitumor activity of a chimeric IL-4-Pseudomonas exotoxin fusion protein in vitro and in vivo. Mol Med 2000; 6: 165–178.
Debinski W, Obiri NI, Pastan I, Puri RK . A novel chimeric protein composed of interleukin 13 and Pseudomonas exotoxin is highly cytotoxic to human carcinoma cells expressing receptors for interleukin 13 and interleukin 4. J Biol Chem 1995; 270: 16775–16780.
Puri RK et al. Targeting of interleukin-13 receptor on human renal cell carcinoma cells by a recombinant chimeric protein composed of interleukin-13 and a truncated form of Pseudomonas exotoxin A (PE38QQR). Blood 1996; 87: 4333–4339.
Husain SR, Joshi BH, Puri RK . Interleulin-13 receptor as a unique target for anti-glioblastoma therapy. Int J Cancer 2001; 92: 168–175.
Kawakami K, Joshi BH, Puri RK . Sensitization of cancer cells to interleukin 13-Pseudomonas exotoxin-induced cell death by gene transfer of interleukin 13 receptor α chain. Hum Gene Ther 2000; 11: 1829–1835.
Puri RK et al. In vitro and in vivo suppression of interleukin-2-activated killer cell activity by chimeric proteins between interleukin-2 and Pseudomonas exotoxin. Cell Immunol 1992; 143: 324–334.
Kawakami K, Kawakami M, Husain SR, Puri RK . Targeting interleukin-4 receptors for effective pancreatic cancer therapy. Cancer Res 2002; 62: 3575–3580.
Terabe M et al. NKT cell-mediated repression of tumor immunosurveillance by IL-13 and the IL-4R-STAT6 pathway. Nat Immunol 2000; 1: 515–520.
Kawakami K et al. In vivo over-expression of IL-13 receptor α2 chain inhibits tumorigenicity of human breast and pancreatic tumors in immunodeficient mice. J Exp Med 2001; 194: 1743–1754.
Kawakami M, Kawakami K, Puri RK . Apoptotic pathways of cell death induced by an interleukin-13 receptor-targeted recombinant cytotoxin in head and neck cancer cells. Cancer Immunol Immunother 2002; 50: 691–700.
Kawakami M, Kawakami K, Puri RK . Intratumoral administration of interleukin 13 receptor-targeted cytotoxin induces apoptotic cell death in human malignant glioma tumor xenografts. Mol Cancer Ther 2002; 1: 999–1007.
Gold DV, Alisauskas R, Sharkey RM . Targeting of xenografted pancreatic cancer with a new monoclonal antibody, PAM4. Cancer Res 1995; 55: 1105–1110.
Frankel AE, Kreitman RJ, Sausville EA . Targeted toxins. Clin Cancer Res 2000; 6: 326–334.
Oshima Y, Joshi BH, Puri RK . Conversion of interleukin-13 into a high affinity agonist by a single amino acid substitution. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 14375–14380.
Sanchez GI et al. Immunogenicity and protective efficacy of a Plasmodium yoelii Hsp60 DNA vaccine in BALB/c mice. Infect Immun 2001; 69: 3897–3905.
Obiri NI et al. Expression of high affinity interleukin-4 receptors on human renal carcinoma cells and inhibition of tumor growth in vitro by interleukin-4. J Clin Invest 1993; 91: 88–93.
Puri RK et al. Expression of high affinity IL4 receptors on murine sarcoma cells and receptor mediated cytotoxicity of tumor cells to chimeric protein between IL-4 and Pseudomonas exotoxin. Cancer Res 1991; 51: 3011–3017.
Templeton NS et al. Improved DNA:liposome complexes for increased systemic derivery and gene expression. Nat Biotechnol 1997; 15: 647–652.
Bastian NR et al. Induction of iron-derived EPR signals in murine cancers by nitric oxide. J Biol Chem 1994; 269: 5127–5131.
Yim C-Y et al. Nitric oxide synthesis contributes to IL-2-induced antitumor responses against intraperitoneal Meth A tumor. J Immunol 1995; 155: 4382–4390.
Acknowledgements
We thank Ms P Dover for the procurement of reagents and laboratory supplies, and Dr RH Zaugg, Vical Inc. for kindly providing VR-1020 vector. We also thank Drs R Aksamit and N Markovitz of CBER/FDA for critical reading of this manuscript. These studies were conducted as part of a collaboration between the FDA and Neopharm Inc. under a Cooperative Research and Development Agreement (CRADA).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kawakami, K., Kawakami, M., Husain, S. et al. Potent antitumor activity of IL-13 cytotoxin in human pancreatic tumors engineered to express IL-13 receptor α2 chain in vivo. Gene Ther 10, 1116–1128 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3301956
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3301956
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Targeting of interleukin-13 receptor α2 for treatment of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma induced by conditional deletion of TGF-β and PTEN signaling
Journal of Translational Medicine (2013)
-
Histone modification enhances the effectiveness of IL-13 receptor targeted immunotoxin in murine models of human pancreatic cancer
Journal of Translational Medicine (2011)
-
Interleukin-13 exerts autocrine growth-promoting effects on human pancreatic cancer, and its expression correlates with a propensity for lymph node metastases
International Journal of Colorectal Disease (2009)