Abstract
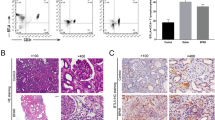
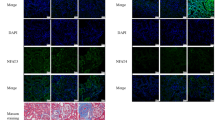
Acute rejection and graft arteriopathy in cardiac transplantation limit the long-term survival of recipients; these processes are enhanced by several cytokines and adhesion molecules. Nuclear factor-kappa B (NFκB) is critical in the transcription of multiple genes involved in inflammation and cell proliferation. To test the hypothesis that NFκB decoy can attenuate acute rejection and arteriopathy, we performed single intraluminal delivery of NFκB decoy into murine cardiac allografts using a hemagglutinating virus of Japan (HVJ)-artificial viral envelope (AVE)-liposome method. No decoy or scrambled decoy transfer was performed for control. Hearts were heterotopically transplanted from BALB/c to C3H/He mice (major mismatch group) and from DBA/2 to B10.D2 mice (minor mismatch group). Nontreated or scrambled decoy transfected allografts of the major mismatch group were acutely rejected, while NFκB decoy prolonged their survival. While severe cell infiltration and intimal thickening with enhancement of inflammatory factors were observed in untreated or scrambled decoy-treated allografts of minor mismatch group at day 28, NFκB decoy attenuated these changes. We conclude that NFκB is critically involved in the development of acute as well as chronic rejection of the transplanted hearts. NFκB decoy attenuates both acute rejection and graft arteriopathy by blocking the activation of several genes.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hosenpud JD et al. The registry of the international society for heart and lung transplantation: sixteenth official report--1999 J Heart Lung Transplant 1999 17: 611–626
Johnson DE et al. Transplant coronary artery disease: histopathologic correlations with angiographic morphology J Am Coll Cardiol 1991 17: 449–457
Suzuki J et al. Nonmuscle and smooth muscle myosin heavy chain expression in rejected cardiac allograft. A study in rat and monkey models Circulation 1996 94: 1118–1124
Hosenpud JD . Immune mechanism of cardiac allograft vasculopathy: an update Transplant Immunol 1993 1: 237–249
Morishita R et al. Intimal hyperplasia after vascular injury is inhibited by antisense cdk2 kinase oligonucleotides J Clin Invest 1994 93: 1458–1464
Morishita R et al. A gene strategy using a transcription factor decoy of the E2F binding site inhibits smooth muscle proliferation in vivo Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1995 92: 5855–5859
Suzuki J et al. Prevention of graft coronary arteriosclerosis by antisense cdk2 kinase oligonucleotide Nature Med 1997 3: 900–903
May MJ, Ghosh S . Signal transduction through NF-kappa B Immunol Today 1998 19: 80–88
Sha WC . Regulation of immune responses by NF-kappa B/Rel transcription factor J Exp Med 1998 187: 143–146
Barnes PJ, Karin M . Nuclear factor-kappaB: a pivotal transcription factor in chronic inflammatory diseases New Engl J Med 1997 336: 1066–1071
Morishita R et al. In vivo transfection of cis element ‘decoy’ against nuclear factor-κB binding site prevents myocardial infarction Nature Med 1997 3: 894–899
Saeki Y et al. Development and characterization of cationic liposomes conjugated with HVJ (Sendai virus); reciprocal effect of cationic lipid for in vitro and in vivo gene transfer Hum Gene Ther 1997 8: 2133–2141
Isobe M, Yagita H, Okumura K, Ihara A . Specific acceptance of cardiac allograft after treatment with antibodies to ICAM-1 and LFA-1 Science 1992 255: 1125–1127
Furukawa Y, Matsumori A, Hirozane T, Sasayama S . Angiotensin II receptor antagonist TCV-116 reduces graft coronary artery disease and preserves graft status in a murine model. A comparative study with captopril Circulation 1996 93: 333–339
Isobe M et al. Immunosuppression to cardiac allografts and soluble antigens by anti-vascular cellular adhesion molecule-1 and anti-very late antigen-4 monoclonal antibodies J Immunol 1994 153: 5810–5818
Suzuki J et al. Inhibition of accelerated coronary atherosclerosis with short-term blockade of ICAM-1 and LFA-1 in a heterotopic murine model of cardiac transplantation J Heart Lung Transplant 1997 16: 1141–1148
Akai Y et al. Intraglomerular expressions of IL-1 alpha and platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF-B) mRNA in experimental immune complex-mediated glomerulonephritis Clin Exp Immunol 1994 95: 29–34
Patel GV et al. Detection of epidermal growth factor receptor mRNA in tissue sections from biopsy specimens using in situ polymerase chain reaction Am J Pathol 1994 144: 7–14
Nuovo GJ, Gallery F, MacConnell P, Braun A . In situ detection of polymerase chain reaction-amplified HIV-1 nucleic acid and tumor necrosis factor-alpha RNA in the central nervous system Am J Pathol 1994 144: 659–666
Sawa Y et al. Efficiency of in vivo gene transfection into transplanted rat heart by coronary infusion of HVJ liposome Circulation 1995 92: (Suppl. II) 479–482
Morishita R et al. Pharmacokinetics of antisense oligodeoxyrebonucleotides (cyclin B1 and CDC2 kinase) in the vessel wall in vivo: enhanced therapeutic utility for restenosis by HVJ-liposome delivery Gene 1994 149: 13–19
Miura N . Okada Y. Use of the deoxyinosine-containing probe to isolate and sequence cDNA encoding the fusion (F) glycoprotein of Sendai virus (HVJ) Gene 1985 38: 271–274
Miura N et al. Molecular cloning of a full-length cDNA encoding the hemagglutinin-neuraminidase glycoprotein of Sendai virus FEBS Lett 1985 188: 112–116
Lenardo MJ, Fan CM, Maniatis T, Baltimore D . The involvement of NF-kappa B in beta-interferon gene regulation reveals its role as widely inducible mediator of signal transduction Cell 1989 57: 287–294
Cooper JA Jr et al. Attenuation of interleukin-8 production by inhibiting nuclear factor-kappaB translocation using decoy oligonucleotides Biochem Pharmacol 2000 59: 605–613
Vos IH et al. NFkappaB decoy oligodeoxynucleotides reduce monocyte infiltration in renal allografts FASEB J 2000 14: 815–822
Uretsky BF et al. Development of coronary artery disease in cardiac transplanted patients receiving immunosuppressive therapy with cyclosporine and predonisolone Circulation 1987 76: 827–834
Pollak R, Fabrega AJ . Diltazem in the prevention of coronary artery disease in heart-transplant recipients New Engl J Med 1993 328: 1851–1852
Okada Y, Tadokoro J . Analysis of giant polynuclear cell formation caused by HVJ virus from Ehrlich ascites tumor cells Exp Cell Res 1962 26: 106–118
Hwang HC et al. Gene therapy using adenovirus carrying the herpes simplex-thymidine kinase gene to treat in vivo models of human malignant mesothelioma and lung cancer Am J Resp Cell Mol Biol 1995 13: 7–16
Morishita R et al. Novel strategy of gene therapy in cardiovascular disease with HVJ-liposome method. In: Koide H, Ichikawa I (eds). Progression of Chronic Renal Diseases. Contrib Nephrol Karger: Basel, 1996 118: 254–264
Okada Y et al. Modification of cell membranes with viral envelopes during fusion of cells with HVJ (Sendai virus) Exp Cell Res 1975 93: 368–378
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants from Grant-in-Aid from the Ministry of Education, Science and Culture, Grant-in-Aid from Ministry of Health and Welfare, Research Grant for Immunology, Allergy and Organ Transplant, Japan Heart Foundation Research Grant and Grant-in-Aid from the Kanae Foundation for Life and Socio-Medical Science. We would like to thank Midori Oike and Rie Shiohara for excellent technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suzuki, J., Morishita, R., Amano, J. et al. Decoy against nuclear factor-kappa B attenuates myocardial cell infiltration and arterial neointimal formation in murine cardiac allografts. Gene Ther 7, 1847–1852 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3301316
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3301316
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Apoptotic exosome-like vesicles regulate endothelial gene expression, inflammatory signaling, and function through the NF-κB signaling pathway
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
A new approach to transfect NF-κB decoy oligodeoxynucleotides into the periodontal tissue using the ultrasound-microbubble method
International Journal of Oral Science (2017)
-
Dilated cardiomyopathy update: infectious-immune theory revisited
Heart Failure Reviews (2013)
-
Protosappanin A induces immunosuppression of rats heart transplantation targeting T cells in grafts via NF-κB pathway
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology (2010)
-
Neointimal hyperplasia associated with synthetic hemodialysis grafts
Kidney International (2008)