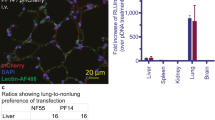
Abstract
Intravenous administration could become a delivery route of choice for prophylactic and curative gene therapies on condition that genes cross the capillary barrier and reach target tissues without being degraded. We investigated the kinetics and process of transgene delivery through mouse lung capillaries following DNA complexation with linear polyethylenimine (L-PEI) and intravenous injection. Using digoxin-labeled DNA we followed the cellular localization of DNA at different times after injection and correlated these findings with cell markers and transgene expression. At 2 h after injection some DNA was still localized on the interior of the capillary lumen, but other complexes had already crossed the barrier and resulted in gene expression. At 24 h after injection most labeled DNA was localised in pulmonary cells, as was transgene expression. Only rarely was transgene expression found in endothelial cells, suggesting that the complexes cross the capillary barrier rapidly. Levels of caspase-1-like activity did not increase following transfection implying that L-PEI/DNA complexes are transported across cellular barriers by a non-damaging, physiological process, without causing inflammation. The high levels of expression of different transgenes in pneumocytes indicates that transport of L-PEI/DNA complexes through the endothelial barrier does not affect their transfection capacity. These findings open up new possibilities for gene delivery and its application to the lung.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Croce CM, Sozzi G, Huebner K . Role of FHIT in human cancer J Clin Oncol 1999 17: 1618–1624
Sozzi GS et al. Absence of Fhit protein in primary lung tumors and cell lines with FHIT gene abnormalities Cancer Res 1997 57: 5207–5212
Sozzi G et al. Loss of FHIT functions in lung cancer and preinvasive bronchial lesions Cancer Res 1998 58: 5032–5037
Griesenbach U et al. Comparison between intrathracheal and intravenous administration of liposome–DNA complexes for cystic fibrosis lung gene therapy Gene Therapy 1998 5: 181–188
Li S, Huang L . In vivo gene transfer via intravenous administration of cationic lipid-protamine–DNA (LPD) complexes Gene Therapy 1997 4: 891–900
McLean JW et al. Organ-specific endothelial cell uptake of cationic liposome^DNA complexes in mice Am J Physiol 1997 273: H387–H404
Rodman DM et al. In vivo gene delivery to the pulmonary circulation in rats: transgene distribution and vascular inflammatory response Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 1997 16: 640–649
Goula D et al. Polyethylenimine-based intravenous delivery of transgenes to mouse lung Gene Therapy 1998 5: 1291–1295
Renkin EM . Cellular and intercellular transport pathways in exchange vessels Am Rev Respir Dis 1992 146: S28–S31
William R et al. The IL-1 beta-converting enzyme (caspase-1) inhibits apoptosis of inflammatory neutrophils through activation of IL-1 beta J Immunol 1998 161: 957–962
Wong WW . ICE family proteases in inflammation and apoptosis Agents Actions Suppl 1998 49: 5–13
Chao DT, Korsmeyer SJ . BCL-2 family: regulators of cell death Annu Rev Immunol 1998 16: 395–419
Dietrich JB . Apoptosis and anti-apoptosis genes in the Bcl-2 family Arch Physiol Biochem 1997 105: 125–135
Liu F, Qi H, Huang L, Liu D . Factors controlling the efficiency of cationic lipid-mediated transfection in vivo via intravenous administration Gene Therapy 1997 4: 517–523
Goula D et al. Size, diffusibility and transfection performance of linear PEI/DNA complexes in the mouse central nervous system Gene Therapy 1998 5: 712–717
Boussif O et al. A novel, versatile vector for gene and oligonucleotide transfer into cells in culture and in vivo: polyethylenimine Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1995 92: 7297–7303
Behr JP . Gene transfer with synthetic cationic amphiphiles: prospects for gene therapy Bioconj Chem 1994 5: 382–389
Zou SM, Behr JP, Goula D, Demeneix BA . Gene delivery with polyethylenimine. In: Templeton NS, Lasic DD (eds). Gene Therapy: Therapeutic Mechanisms and Strategies Marcel Dekker: NY 1999 (in press)
Suh J, Paik H-J, Hwang BK . Ionization of polyethylenimine and polyallylamine at various pHs Bioorg Chem 1994 22: 318–327
Schnitzer JE, Oh P, Jacobson BS, Dvorak AM . Caveolae from luminal plasmalemma of rat lung endothelium: microdomains enriched in caveolin, Ca(2+)-ATPase, and inositol trisphosphate receptor Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1995 92: 1759–1763
Zanta MA, Boussif O, Adib A, Behr JP . In vitro gene delivery to hepatocytes with galactosylated polyethylenimine Bioconjug Chem 1997 8: 839–844
Coll JL et al. In vitro targeting and specific transfection of human neuroblastoma cells by chCE7 antibody-mediated gene transfer Gene Therapy 1997 4: 156–161
Kircheis R et al. Coupling of cell-binding ligands to polyethylenimine for targeted gene delivery Gene Therapy 1997 4: 409–418
Erbacher P, Remy JS, Behr JP . Gene transfer with synthetic virus-like particles via the integrin-mediated endocytosis pathway Gene Therapy 1999 6: 138–145
Guissouma H et al. Physiological regulation of hypothalamic TRH transcription in vivo is T3 receptor isoform specific FASEB J 1998 12: 1755–1764
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the Association Française pour la Lutte contre la Mucoviscidose (AFLM) the Association Française contre les Myopathies (AFM) and ARC for support. GL was supported by ARSEP, AISM and Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche (Progetto Finalizzato ‘Biotecnologie’). The support from Telethon (Italy) for the project: ‘Use of transgenic mutant mice as a model to study the molecular control of bone development and peripheral myelination and to develop new gene therapy strategies in the embryo’ (Project D76) is gratefully acknowledged. Dr M Post (Toronto) kindly provided the anti-surfactant antibody. Daniel Goula is a recipient of a graduate fellowship from the French government (MRE).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goula, D., Becker, N., Lemkine, G. et al. Rapid crossing of the pulmonary endothelial barrier by polyethylenimine/DNA complexes. Gene Ther 7, 499–504 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3301113
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3301113
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Nanoengineered strategies for siRNA delivery: from target assessment to cancer therapeutic efficacy
Drug Delivery and Translational Research (2017)
-
Cationic nanocarriers induce cell necrosis through impairment of Na+/K+-ATPase and cause subsequent inflammatory response
Cell Research (2015)
-
Optimizing the transient transfection process of HEK-293 suspension cells for protein production by nucleotide ratio monitoring
Cytotechnology (2014)
-
Aerosol delivery of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E-binding protein 1 effectively suppresses lung tumorigenesis in K-rasLA1 mice
Cancer Gene Therapy (2013)
-
Effect of fractalkine-Fc delivery in experimental lung metastasis using DNA/704 nanospheres
Cancer Gene Therapy (2011)