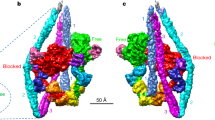
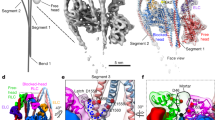
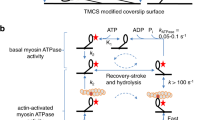
Abstract
Both ATP hydrolysis by myosin and the accompanying cyclic association–dissociation of actin and myosin are essential for muscle contraction. It is important for understanding the molecular mechanism of contraction to know the three-dimensional locations of the two major functional sites of myosin: the ATPase site1 and the actin-binding site2,3. We have determined the position of the ATPase site of myosin using three-dimensional image reconstruction from electron micrographs and site-specific labelling with the avidin–biotin system1. The ATPase site is about 5 nm from the tip of the myosin head and is about 4 nm away from the actin-binding site of myosin. This is the first report of the three-dimensional location of an enzyme active site by electron microscopy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sutoh, K., Yamamoto, K. & Wakabayashi, T. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 83, 212–216 (1986).
Toyoshima, C. & Wakabayashi, T. J. Biochem., Tokyo 97, 245–263 (1985).
Tomioka, A., Tokunaga, M. & Wakabayashi, T. Proc. China-Japan Bilateral Symposium on Biophysics 505–509 (China Academic, 1985).
DeRosier, D. J. & Klug, A. Nature 217, 130–134 (1968).
Moore, P. B., Huxley, H. E. & DeRosier, D. J. J. molec. Biol. 50, 279–295 (1970).
Toyoshima, C. & Wakabayashi, T. J. Biochem., Tokyo 86, 1887–1890 (1979).
Wakabayashi, T. & Toyoshima, C. J. Biochem., Tokyo 90, 683–701 (1981).
Taylor, K. A. & Amos, L. A. J. molec. Biol. 147, 297–324 (1981).
Amos, L. A., Huxley, H. E., Holmes, K. C., Goody, R. S. & Taylor, K. A. Nature 299, 467–469 (1982).
Vibert, P. & Craig, R. J. molec. Biol. 157, 299–319 (1982).
Toyoshima, C. & Wakabayashi, T. J. Biochem., Tokyo 97, 219–243 (1985).
Sutoh, K., Yamamoto, K. & Wakabayashi, T. J. molec. Biol. 178, 323–339 (1984).
Toyoshima, C., Yamamoto, K., Sutoh, K., Sekine, T. & Wakabayashi, T. 11th YAMADA Conference, Abstr. p. 38 (1985).
Holtzman, E., Wise, D., Wall, J. & Karlin, A. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 79, 310–314 (1982).
Sutoh, K. Biochemistry (in the press).
Okamoto, Y. & Yount, R. G. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 82, 1575–1579 (1985).
Bayer, E. & Wilchek, M. Meth. Enzym. 34, 265–267 (1974).
Green, N. M., Konieczny, L., Toms, E. J. & Valentine, R. C. Biochem. J. 125, 781–791 (1971).
Elliott, A. & Offer, G. J. molec. Biol. 123, 505–519 (1978).
Takahashi, K. J. Biochem., Tokyo 83, 905–908 (1978).
Walker, M., Knight, P. & Trinick, J. J. molec. Biol. 184, 535–542 (1985).
Tao, T. & Lamkin, M. Biochemistry 20, 5051–5055 (1981).
Huxley, H. E. Science 164, 1356–1366 (1969).
Huxley, A. F. J. Physiol., Land. 243, 1–43 (1974).
Yagi, N., O'Brien, E. J. & Matsubara, I. Biophys. J. 33, 121–138 (1981).
Huxley, H. E., Faruqi, A. R., Kress, M., Bordas, J. & Koch, M. H. J. J. molec. Biol. 158, 637–684 (1982).
Yanagida, T. J. molec. Biol. 146, 539–560 (1981).
Cooke, R., Crowder, M. S. & Thomas, D. D. Nature 300, 776–778 (1982).
Borejdo, J., Assulin, O., Ando, T. & Putnam, S. J. molec. Biol. 158, 391–414 (1982).
Crowder, M., Wilkie, M. & Cooke, R. Biophys. J. 47, 381a (1985).
Weeds, A. G. & Taylor, R. S. Nature 257, 54–56 (1975).
DeRosier, D. J. & Moore, P. B. J. molec. Biol. 52, 355–369 (1970).
Amos, L. A. & Klug, A. J. molec. Biol. 99, 51–73 (1975).
Wakabayashi, T., Huxley, H. E., Amos, L. A. & Klug, A. J. molec. Biol. 93, 477–497 (1975).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tokunaga, M., Sutoh, K., Toyoshima, C. et al. Location of the ATPase site of myosin determined by three-dimensional electron microscopy. Nature 329, 635–638 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1038/329635a0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/329635a0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.