Abstract
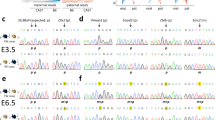
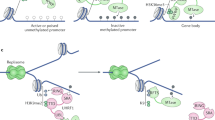
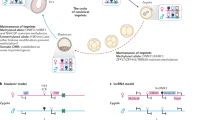
Mouse embryogenesis relies on the presence of both the maternal and the paternal genome for development to term1,2. It has been proposed that specific modifications are imprinted onto the chromosomes during gametogenesis3; these modifications are stably propagated4, and their expression results in distinct and complementary contributions of the two parental genomes to the development of the embryo and the extraembryonic membranes5,6. Genetic data further suggest that a substantial proportion of the genome could be subject to chromosomal imprinting7, the molecular nature of which is unknown. We used random DNA insertions in transgenic mice to probe the genome for modified regions. The DNA methylation patterns of transgenic alleles were compared after transmission from mother or father in seven mouse strains carrying autosomal insertions of the same transgenic marker. One of these loci showed a clear difference in DNA methylation specific for its parental origin, with the paternally inherited copy being relatively undermethylated. This difference was observed in embryos on day 10 of gestation, but not in their extraembryonic membranes. Moreover, the methylation pattern was faithfully reversed upon each germline transmission to the opposite sex. Our findings provide evidence for heritable molecular differences between maternally and paternally derived alleles on mouse chromosomes.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
1. Surani, M. A. H., Barton, S. C. & Norris, M. L. Nature 308, 548–550 (1984). 2. McGrath, J. & Solter, D. Cell 37, 179–183 (1984). 3. Surani, M. A. H., Reik, W., Norris, M. L. & Barton, S. C. J. Embryoi exp. Morph. 97 (Suppl.) 123–136 (1986). 4. Surani, M. A. H., Barton, S. C. & Norris, M. L. Cell 45, 127–136 (1986). 5. Barton, S. C., Surani, M. A. H. & Norris, M. L. Nature 311, 374–376 (1984). 6. Surani, M. A. H., Barton, S. C. & Norris, M. L. Nature 326, 395–397 (1987). 7. Searle, A. G. & Beechey, C. V. in Aneuploidy: Etiology and Mechanisms (eds Dellarco, V. L., Voytele, P. E. & Hollaender, A.) 363–376 (Plenum, New York, 1985). 8. Reik, W. et al. Eur. J. Immun. 17, 465–469 (1987). 9. Chapman, V., Forrester, L., Sansford, J., Hastie, N. & Rossant, J. Nature 307,284–286 (1984). 10. Rossant, J., Sanford, J. P., Chapman, V. M. & Andrews, G. K. Devl Biol. 117,567–573 (1986). 11. Rahe, B., Erickson, R. P. & Quinto, M. Nucleic Acids Res. 11, 7947–7959 (1983). 12. Jahner, D. & Jaenisch, R. Molec. cell. Biol. 5, 2212–2220 (1985). 13. Bird, A. P. Nature 321, 209–213 (1986). 14. Cattanach, B. M. & Kirk, M. Nature 315, 496–498 (1985). 15. Sanford, J., Forrester, W., Chapman, V., Chandley, A. & Hastie, N. Nucleic Acids Res. 12, 2823–2936(1984). 16. Ponzetto–Zimmerman, C. & Wolgemuth, D. J. Nucleic Acids Res. 12, 2807–2822 (1984). 17. Monk, M., Boubelik, M. & Lehnert, S. Development 99, 371–382 (1987). 18. Lock, L. F., Takagi, N. & Martin, G. R. Cell 48, 39–46 (1987). 19. Surani, M. A. H. in Experimental Approaches to Mammalian Embryonic Development (eds Rossant, J. & Pedersen, R. A.) 401–435 (Cambridge University Press, 1986). 20. Myers, R. H., Madden, J. J., league, J. L. & Falek, A. Am. J. hum. Genet. 34,481–488 (1982). 21. Klar, A. J. S. Nature 326, 466–470 (1987). 22. Feinberg, A. P. & Vogelstein, B. Analyt. Biochem. 137, 266–267 (1984). 23. Hecht, N. B., Liem, H., Kleene, K. C., Distel, R. J. & Ho, S. M. Devl Biol. 102,452–461 (1984). 24. Swain, J. L., Stewart, T. & Leder, P. Clin. Res. 35, 419A (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reik, W., Collick, A., Norris, M. et al. Genomic imprinting determines methylation of parental alleles in transgenic mice. Nature 328, 248–251 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1038/328248a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/328248a0
This article is cited by
-
Epigenetic regulation in the tumor microenvironment: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic targets
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2023)
-
Emerging evidence that the mammalian sperm epigenome serves as a template for embryo development
Nature Communications (2023)
-
PIWI-Interacting RNA (piRNA) and Epigenetic Editing in Environmental Health Sciences
Current Environmental Health Reports (2022)
-
Role of genomic imprinting in mammalian development
Journal of Biosciences (2020)
-
Functions and mechanisms of epigenetic inheritance in animals
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2018)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.