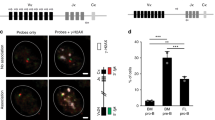
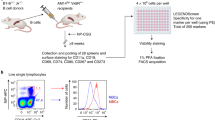
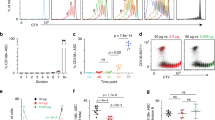
Abstract
B cells and their antibody-secreting progeny represent one of several differentiation pathways that haematopoietic stem cells (HSC) may enter1,2. Cells representing intermediate stages between HSC and B cells have been identified in mammalian haematopoietic tissues3,4 and studied intensively over the past decade. This population of early B-lineage cells, termed pre-B, is characterized by cellular proliferation and an orderly cascade of immunoglobulin gene rearrangements5–7, a combination of events leading to the generation of clonally diverse B cells which then migrate to peripheral lymphoid tissues. It remains to be determined what elements determine the polyclonal growth of pre-B cells, how immunoglobulin gene rearrangements are regulated, and what happens to pre-B cells undergoing ‘non-productive’ immunoglobulin gene rearrangements. These issues could be resolved more easily if early B-lineage cells could be identified precisely and isolated. Here, we describe a cell surface glycoprotein that is selectively expressed by pre-B and newly formed B cells in murine haematopoietic tissues. The molecule, a homodimer formed by disulphide-linked chains of relative molecular mass (Mr) 140,000, is identified by a mouse monoclonal alloantibody called BP-1.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cooper, M. D., Peterson, R. D. A., South, M. A. & Good, R. A. J. exp. Med. 123, 75–102 (1966).
Moore, M. A. S. & Owen, J. T. T. Lancet ii, 658–659 (1967).
Osmond, D. G. & Nossal, G. J. V. Cell. Immun. 13, 117–131 (1974).
Owen, J. J. T., Cooper, M. D. & Raff, M. C. Nature 249, 361–363 (1974).
Kincade, P. W. Adv. Immun. 31, 177–245 (1981).
Cooper, M. D., Velardi, A., Calvert, J. E., Gathings, W. E. & Kubagawa, H. in Progress in Immunology V (ed. Tada, T.) 603–612 (Academic, Tokyo, 1983).
Alt, F. W., Blackwell, T. K., DePinho, R. A., Reth, M. G. & Yancopoulos, G. D. Immun. Rev. 89, 5–30 (1986).
Coffman, R. L. & Weissman, I. L. Nature 289, 681–683 (1981).
Kincade, P. W., Lee, G., Watanabe, T., Sun, L. & Scheid, M. P. J. Immun. 127, 2261–2268 (1981).
McKearn, J. P., Baum, C. & Davie, J. M. J. Immun. 132, 332–339 (1984).
Paige, C. J., Skarvalt, H. & Sauter, H. J. Immun. 134, 3699–3704 (1985).
Pillemer, E., Whitlock, C. & Weissman, I. L. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 81, 4434–4438 (1984).
Bonhomme, F. et al. Biochem. Genet. 22, 275–303 (1984).
Alt, F., Rosenberg, N., Lewis, S., Thomas, E. & Baltimore, D. Cell 27, 381–390 (1981).
Shulman, M., Wilde, C. D. & Kohler, G. Nature 276, 269–270 (1978).
Gathings, W. E., Lawton, A. R. & Cooper, M. D. Eur. J. Immun. 7, 804–810 (1977).
Williams, A. F. Nature 314, 579–580 (1985).
Springer, T. G., Galfre, G., Secher, D. S. & Milstein, C. Eur. J. Immun. 9, 301–304 (1979).
Bergman, Y., Haimovich, J. & Melchers, F., Eur. J. Immun. 8, 574–579 (1977).
Knapp, M. R. et al. J. Immun. 123, 992–999 (1979).
Maki, R., Kearney, J., Paige, C. & Tonegawa, S. Science 209, 1366–1369 (1980).
Perry, R. P., Kelley, D. E., Coleclough, C. & Kearney, J. F. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 78, 247–251 (1981).
Burrows, P. D., LeJeune, M. & Kearney, J. F. Nature 20, 838–841 (1979).
Burrows, P. D., Beck-Engeser, G. B. and Wabl, M. R. Nature 306, 243–246 (1983).
Goding, J. W. J. Immun. 124, 2082–2088 (1980).
Chen, C. H., Chanh, T. C. & Cooper, M. D. Eur. J. Immun. 14, 385–391 (1984).
Weber, K. & Osborn, M. J. biol. Chem. 244, 4406–4412 (1969).
Bordier, C. J. biol. Chem. 256, 1604–1607 (1981).
Elder, J. H. & Alexander, S. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 79, 4540–4544 (1982).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cooper, M., Mulvaney, D., Coutinho, A. et al. A novel cell surface molecule on early B-lineage cells. Nature 321, 616–618 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1038/321616a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/321616a0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.