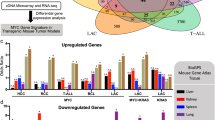
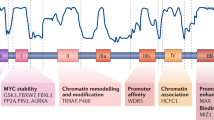
Abstract
N-myc, a cellular gene related to the c-myc proto-oncogene1–4, was originally identified on the basis of its very frequent amplification and overexpression in a restricted set of tumours, most notably human neuroblastomas1,2. That N-myc may have a causal role in the genesis of these tumours is suggested by the observation that in the rat embryo fibroblast co-transformation assay5,6 it has a transforming potential similar to that of c-myc7,8. The apparent structural and functional homology of N-myc and c-myc suggests that they may be members of the same proto-oncogene family. However, despite these apparent similarities, expression of the two genes appears to be dramatically different with respect to tumour specificity, as well as tissue and developmental stage specificity9,10. To further elucidate the common and unique aspects of N-myc and c-myc gene structure and function in normal and transformed cells, we have determined the organization of human N-myc and the nucleotide sequence of its messenger product, and we report here that N-myc and c-myc have a similar intron/exon structure and that their protein products share regions of significant homology.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kohl, N. E. et al. Cell 35, 359–367 (1983).
Schwab, M. et al. Nature 305, 245–248 (1983).
Michitsch, R. W., Montgomery, K. T. & Melera, P. W. Molec. cell. Biol. 4, 2370–2380 (1984).
Michitsch, R. W. & Melera, P. W. Nucleic Acids Res. 13, 2545–2558 (1985).
Land, H., Parada, L. F. & Weinberg, R. A. Nature 304, 596–602 (1983).
Ruley, H. E. Nature 304, 602–606 (1983).
Yancopoulos, G. D. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 82, 5455–5459 (1985).
Schwab, M., Varmus, H. E. & Bishop, J. M. Nature 316, 160–162 (1985).
Kohl, N. E., Gee, C. E. & Alt, F. W. Science 226, 1335–1337 (1984).
Zimmerman, K. A. et al. Nature (in the press).
Mount, S. M. Nucleic Acids Res. 10, 459–472 (1982).
Colby, W. W. et al. Nature 301, 722–725 (1983).
Battey, J. et al. Cell 34, 779–787 (1983).
Watt, R. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 80, 6307–6311 (1983).
Saito, H. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 80, 7476–7480 (1983).
Bernard, O. et al. EMBO J. 2, 2375–2383 (1983).
DePinho, R. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. (in the press).
Ralston, R. & Bishop, J. M. Nature 306, 803–806 (1983).
Persson, H. & Leder, P. Science 225, 718–721 (1984).
van Straaten, F. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 80, 3183–3187 (1983).
Cochran, B. et al. Science 226, 1080–1082 (1984).
Curran, T. et al. Cell 36, 259–268 (1984).
Westin, E. H. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 79, 2490–2494 (1982).
Reitsma, P. H. et al. Nature 306, 492–494 (1983).
Campisi, J. et al. Cell 36, 241–247 (1984).
Thiele, C. J., Reynolds, C. P. & Israel, M. A. Nature 313, 404–406 (1985).
Gonda, T. J., Sheiness, D. K. & Bishop, J. M. Molec. cell Biol. 2, 617–624 (1982).
Kelly, K. et al. Cell 35, 603–610 (1983).
Makino, R., Hayashi, K. & Sugimura, T. Nature 310, 697–698 (1984).
Pfeifer-Ohlsson, S. et al. Cell 38, 585–596 (1984).
Leder, P. Science 222, 765–771 (1983).
Collins, S. & Groudine, M. Nature 298, 679–681 (1982).
Dalla Favera, R., Wong-Staal, F. & Gallo, R. C. Nature 299, 61–63 (1982).
Alitalo, K. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 80, 1707–1711 (1983).
Little, C. D. et al. Nature 36, 194–196 (1983).
McGrogan, M. et al. J. biol. Chem. 260, 2307–2314 (1985).
Reynolds, G. A. et al. Cell 38, 275–285 (1984).
Ghosh, P. K. & Lebowitz, P. J. Virol. 40, 224–240 (1981).
Ghosh, P. K. et al. J. molec. Biol. 126, 813–846 (1978).
Everett, R. D., Baty, D. & Chambon, P. Nucleic Acids Res. 11, 2447–2464 (1983).
Baty, D. et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 12, 915–932 (1984).
Vigneron, M. et al. EMBO J. 3, 2373–2382 (1984).
McKnight, S. L. & Kingsbury, R. Science 217, 316–324 (1982).
DePinho, R. et al. Molec. cell. Biol. 4, 2905–2910 (1984).
Seeger, R. C. et al. J. Immun. 128, 983–989 (1982).
Yancopoulos, G. D. & Alt, F. W. Cell 40, 271–281 (1985).
Tumilowicz, J. J. et al. Cancer Res. 30, 2110–2118 (1970).
Gilbert, F. et al. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 7, 33–42 (1982).
Reth, M. G. & Alt, F. W. Nature 312, 418–423 (1984).
Gubler, U. & Hoffman, B. J. Gene 25, 263–269 (1983).
Biggin, M., Farrell, P. J. & Barrell, B. G. EMBO J. 3, 1083–1090 (1984).
Zinn, K., DiMaio, D. & Maniatis, T. Cell 34, 865–879 (1983).
Maxam, A. M. & Gilbert, W. Meth. Enzym. 65, 499–560 (1980).
Proodfoot, N. J. & Brownlee, G. G. Nature 263, 211–214 (1976).
Tinoco, I. Jr. et al. Nature new Biol. 246, 40–41 (1973).
McLachlan, A. D. J. molec. Biol. 61, 409–424 (1971).
Alitalo, K. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 80, 100–104 (1983).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kohl, N., Legouy, E., DePinho, R. et al. Human N-myc is closely related in organization and nucleotide sequence to c-myc. Nature 319, 73–77 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1038/319073a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/319073a0
This article is cited by
-
MYC transcription activation mediated by OCT4 as a mechanism of resistance to 13-cisRA-mediated differentiation in neuroblastoma
Cell Death & Disease (2020)
-
Mitochondrial AKAP1 supports mTOR pathway and tumor growth
Cell Death & Disease (2017)
-
Tumour-suppressor microRNAs let-7 and mir-101 target the proto-oncogene MYCN and inhibit cell proliferation in MYCN-amplified neuroblastoma
British Journal of Cancer (2011)
-
Activation of anaplastic lymphoma kinase is responsible for hyperphosphorylation of ShcC in neuroblastoma cell lines
Oncogene (2002)
-
Bcl-2 and N-Myc Coexpression Increases IGF-IR and Features of Malignant Growth in Neuroblastoma Cell Lines
Neoplasia (2001)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.