Abstract
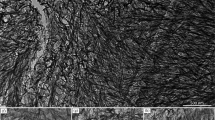
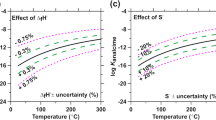
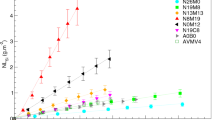
The long-term stability of nuclear waste form borosilicate glasses must be predicted from extrapolations of short-term laboratory data and then verified, which is only possible by comparing the glasses with their natural analogues of geological age. Here, we suggest that basalt glasses are useful analogues for predicting the long-term behaviour of nuclear waste form borosilicate glasses. Previous workers1–11 have considered the possibility of using natural glasses as analogues, but our study is a direct comparison of the experimentally studied corrosion products of basalt glasses, their natural long-term corrosion products and those of borosilicate glasses. Observations on the alteration processes for natural basalt glasses are combined with the experimental data on the alteration of basalt glasses and borosilicate glasses and are used to generate radioactivity release curves for nuclear waste form borosilicate glasses using the QTERM computer code12–15. Our data on natural glasses place significant constraints on the anticipated fraction of activity released; major differences between our two release curves do not occur until after 1,000 years.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ewing, R. C. Scientific Basis for Nuclear Waste Management Vol. 1 (ed. McCarthy, G.) 57–68 (Plenum, New York, 1979).
Ewing, R. C. & Haaker, R. F. Naturally Occurring Glasses: Analogues for Radioactive Waste Forms (Battelle Rep. PNL-2776/UC-70, 1979).
Adams, P. B. Int. Symp. Ceramics in Nuclear Waste Management (eds Chikalla, T. D. & Mendel, J. E.) 233–237 (American Ceramic Society, 1979).
Malow, G. & Ewing, R. C. Scientific Basis for Nuclear Waste Management Vol. 3 (ed. Moore, J. G.) 315–322 (Plenum, New York, 1981).
Dickin, A. P. Nature 294, 342–345 (1981).
Melling, P. J., Vemparti, C. S., Allnatt, A. R. & Jacobs, P. W. M. Physics and Chemistry of Glasses 22, 49–54 (1981).
Bates, J. K., Jardine, L. J. & Steindler, M. J. Science 218, 51–53 (1982).
Allen, C. C. Scientific Basis for Nuclear Waste Management-V (ed. Lutze, W.) 37–44 (Elsevier, New York 1982).
Barkatt, A. et al. Geochim. cosmochim. Acta 48, 361–372 (1984).
Plodinec, M. J., Jantzen, C. M. & Wicks, G. G. 2nd Int. Symp. Ceramics in Nuclear Waste Management (eds Wicks, G. G. & Ross, W.) 491–495 (American Ceramic Society, 1984).
Malow, G., Lutze, W. and Ewing, R. C. J. non-crystalline Solids 67, 305–321 (1984).
Altenhein, F. K., Lutze, W. & Ewing, R. C. Scientific Basis for Nuclear Waste Management-V (ed. Lutze, W.) 45–56 (Elsevier, New York, 1982).
Altenhein, F. K., Lutze, W. & Ewing, R. C. Scientific Basis for Nuclear Waste Management-VI (ed. Brookins, D.) 269–280 (Elsevier, New York, 1983).
Altenhein, F. K., Lutze, W. & Ewing, R. C. 2nd Int. Symp. Ceramics in Nuclear Waste Management. (eds Wicks, G. G. & Ross, W.) 636–644 (American Ceramic Society, 1984).
Freude, E., Grambow, B., Lutze, W., Rabe, H. & Ewing, R. C. Scientific Basis for Nuclear Waste Management-VIII (eds Jantzen, C. M., Stone, J. A. & Ewing, R. C.) (Elsevier, New York, in the press).
Staudigel, H. & Hart, S. R. Geochim. cosmochim. Acta 47, 337–350 (1983).
Allen, C. C., Gooding, J. L., Jercinovic, M. J. & Keil, K. Icarus 45, 347–369 (1981).
Jercinovic, M. J. thesis, Univ. New Mexico (1984).
Ailin-Pyzik, I. B. & Sommer, S. E. J. geophys. Res. 86, 9503–9510 (1981).
Melson, W. G. Trans. Am. geophys. Un. 54, 1011–1014 (1973).
Melson, W. G. & Thompson, G. Bull. geol. Soc. Am. 84, 703–716 (1973).
Schmincke, H.-U. Init. Rep. DSDP LXV, 477–483 (1983).
Honnorez, J. The Sea (ed. Emiliani, C.) 525–587 (Wiley, New York, 1981).
Hermansson, H.-P., Bjorner, I.-K., Christensen, H. & Yokoyama, H. Studsvik Rep. NW-84/653 (1984).
MCC-1P, Static Leach Test Method Nuclear Waste Materials Handbk (US Department of Energy, DOE/TIC-11400, 1981).
Wicks, G. G. & Wallace, R. M. DOE Rep. DP-82-18, 1982).
Wicks, G. G. & Wallace, R. M. Scientific Basis for Nuclear Waste Management-VI (ed.Brookins, D.) 23–28 (Elsevier, New York, 1983).
Friedman, I., Smith, R. L. & Long, W. D. Bull. geol. Soc. Am. 77, 323–328 (1966).
Morgenstein, M. & Riley, T. J. Asian Perspectives 17, 145–159 (1974).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lutze, W., Malow, G., Ewing, R. et al. Alteration of basalt glasses: implications for modelling the long-term stability of nuclear waste glasses. Nature 314, 252–255 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1038/314252a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/314252a0
This article is cited by
-
Natural glass from Deccan volcanic province: an analogue for radioactive waste form
International Journal of Earth Sciences (2015)
-
Insight into silicate-glass corrosion mechanisms
Nature Materials (2008)
-
The corrosion of glass on the sea bed
Journal of Materials Science (1989)
-
Mechanism of aqueous dissolution of silicate glasses yielded by fission tracks
Nature (1986)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.