Abstract
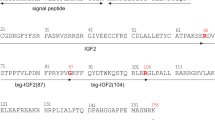
Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) and IGF-II are mitogenic polypeptides of relative molecular mass (Mr) ∼7,500 isolated from human plasma1,2 each containing four peptide domains in a single chain and identical at more than 60% of their amino acid loci. The B- and A-domains of the IGFs are ∼40% identical to the B-and A-chains of human insulin1,2. IGF-I and IGF-II have similar in vitro biological activities2 and receptor reactivity3, but are immunologically distinct4,5. IGF-I appears to mediate the effects of growth hormone on cartilage to promote skeletal growth5,6, whereas IGF-II may have a special role in fetal development7,8 and in the central nervous system9. To investigate the in vivo role of IGF-II, we have studied IGF-II biosynthesis in the BRL-3A rat liver cell line10. BRL-3A cells synthesize and secrete a 7,484 Mr protein 93% identical to human IGF-II and representing rat IGF-II (rIGF-II)11. Rat IGF-II is synthesized as a ∼22,000 Mr prepro-rIGF-II (ref. 12) from 12 S poly(A)+mRNA13. In addition, ∼20,000 Mr pro-rIGF-II has been identified in lysates of biosynthetically labelled intact BRL-3A cells14. We report here the isolation of an almost complete cDNA clone for rIGF-II. Our results indicate that pro-rIGF-II is synthesized as a 156 amino acid peptide precursor (17,619 Mr) containing mature rIGF-II 1–67 at its amino-terminus and an 89-residue carboxy-terminal peptide extension.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rinderknecht, E. & Humbel, R. E. J. biol. Chem. 253, 2769–2776 (1978).
Zapf, J., Froesch, E. R. & Humbel, R. E. Curr. Topics cell. Regul. 19, 257–309 (1981).
Rechler, M. M. et al. in Insulin-like Growth Factors/Somatomedins: Basic Chemistry, Biology and Clinical Importance (ed. Spencer, E. M.) 459–490 (de Gruyter, New York, 1983).
Van Wyk, J. J., Svoboda, M. E. & Underwood, L. E. J. clin. Endocr. Metab. 50, 206–208 (1980).
Zapf, J., Walter, H. & Froesch, E. R. J. clin. Invest. 68, 1321–1330 (1981).
Schoenle, E., Zapf, J., Humbel, R. E. & Froesch, E. R. Nature 296, 252–253 (1982).
Moses, A. C. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 77, 3649–3653 (1980).
Adams, S. O., Nissley, S. P., Handwerger, S. & Rechler, M. M. Nature 302, 150–153 (1983).
Haselbacher, G. K., Schwab, M. E., Pasi, A. & Humbel, R. E. Symposium Insulin-like Growth Factors/Somatomedins, Nairobi, Kenya, 13-15 November, p. 75 (abstract) (1982).
Nissley, S. P. et al. in Insulin-like Growth Factors/Somatomedins: Basic Chemistry, Biology, and Clinical Importance (ed. Spencer, E. M.) 31–48 (de Gruyter, New York, 1983).
Marquardt, H., Todaro, G. J., Henderson, L. E. & Oroszlan, S. J. biol. Chem. 256, 6859–6865 (1981).
Acquaviva, A. M., Bruni, C. B., Nissley, S. P. & Rechler, M. M. Diabetes 31, 656–658 (1982).
Yang, Y. W.-H. et al. in Insulin-like Growth Factor/Somatomedins: Basic Chemistry, Biology, and Clinical Importance (ed. Spencer, E. M.) 603–610 (de Gruyter, New York, 1983).
Yang, Y. W.-H., Romanus, J. A., Liu, T.-Y., Nissley, S. P. & Rechler, M. M. J. biol. Chem. (in the press).
Berget, S. M. Nature 309, 179–182 (1984).
Yang, Y. W.-H., Rechler, M. M., Nissley, S. P. & Coligan, J. E. J. biol. Chem. (in the press).
Jansen, M. et al. Nature 306, 609–611 (1983).
Land, H., Grez, M., Hauser, H., Lindenmaier, W. & Schutz, G. Meth. Enzym. 100, 285–292 (1983).
Maniatis, T., Fritsch, E. F. & Sambrook, J. Molecular Cloning (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York, 1982).
Michelson, A. M. & Orkin, S. H. J. biol. Chem. 257, 14773–14782 (1982).
Casadaban, M. J. & Cohen, S. N. J. molec. Biol. 138, 179–207 (1980).
Mandel, M. & Higa, A. J. molec. Biol. 53, 159–162 (1970).
Hanahan, D. & Meselson, M. Meth. Enzym. 100, 333–342 (1983).
Suggs, S. V. et al. in Developmental Biology Using Purified Genes (eds Brown, D. D. & Fox, C. F.) 683–693 (Academic, New York, 1981).
Clewell, D. B. & Helinski, D. R. Biochemistry 9, 4428–4440 (1970).
Maxam, A. M. & Gilbert, W. Meth. Enzym. 65, 499–560 (1980).
Wickens, M. P., Buell, G. N. & Schimke, R. T. J. biol. Chem. 253, 2483–2495 (1975).
Rechler, M. M. et al. Cancer Cells 3 (in the press).
Bell, G. I. et al. Nature 310, 775–777 (1984).
Dull, T. J., Gray, A., Hayflick, J. S. & Ullrich, A. Nature 310, 777–781 (1984).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Whitfield, H., Bruni, C., Frunzio, R. et al. Isolation of a cDNA clone encoding rat insulin-like growth factor-II precursor. Nature 312, 277–280 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1038/312277a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/312277a0
This article is cited by
-
Expression of insulin-like growth factors during bone induction in rat
Calcified Tissue International (1993)
-
Molecular biology of the insulin-like growth factors
Molecular Neurobiology (1990)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.