Abstract
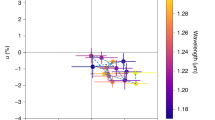
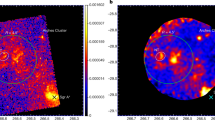
Although most of the luminosity of Seyfert galaxy nuclei is emitted in the IR, the relative amounts of thermal dust and non-thermal emission are uncertain. Seyfert galaxies generally have smooth and featureless IR spectra, in contrast to the prominent dust emission features seen in galaxies whose nuclei resemble giant H II regions—the star burst nuclei1,2. Nevertheless, in type 2 Seyferts, the general form of the energy distribution and lack of marked variability suggest that here too thermal dust emission is dominant3–5, and in NGC1068 this supposition is supported by the resolved size of its nucleus6. Dust is observed in absorption at 10 µm (refs 7,8) and in emission near 20 µm (ref. 9). Polarization has been detected from the UV to 10 µm, and attributed to scattering and absorption at short wavelengths10 with a possible non-thermal component11,12, to scattering and non-thermal radiation in the near IR9, and to either absorption or non-thermal emission in the 10 µm region13. We present here spectropolarimetric measurements of NGC1068, between 8 and 13 µm, which show that the polarized flux at these wavelengths is intrinsic to the emission mechanism and not due to absorption by aligned grains.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Phillips, M. M., Aitken, D. K. & Roche, P. F. Mon. Not. R. astr. Soc. 207, 25–34 (1984).
Roche, P. F., Aitken, D. K., Phillips, M. M., & Whitmore, B. Mon. Not. R. astr. Soc. 207, 35–46 (1984).
Soifer, B. T. & Neugebauer, G. Infrared Astronomy, IAU Symp No. 96 329 (1981).
Smith, M. G. 16th Symp. Galactic and Extragalactic Infrared Spectroscopy, 369 (1982).
Stein, W. A. & Soifer, B. T. A. Rev. Astr. Astrophys. 21, 177 (1983).
Becklin, E. E., Mathews, K., Neugebauer, G. & Wynn-Williams, C. G. Astrophys. J. Lett. 186, L69–L72 (1973).
Kleinman, D. E., Gillett, F. C. & Wright, E. L. Astrophys. J. 208, 42 (1976).
Cutri, R. M. et al. Astrophys. J. 245, 818–828 (1981).
Lebofsky, M. J., Rieke, G. H. & Kemp, J. C. Astrophys. J. 222, 95–99 (1978).
Angel, J. R. P., Stockman, H. S., Woolf, N. J., Beaver, A. E. & Martin, P. G. Astrophys. J. Lett. 206, L5–L10 (1976).
McClean, I. S., Aspin, C., Heathcote, S. R. & McCaughrean, M. J. Nature 304, 609–611 (1983).
Miller, J. S. & Antonucci, R. R. J. Astrophys. J. Lett. 271, L7–L11 (1983).
Knacke, R. F. & Capps, R. W. Astrophys. J. Lett. 192, L19–L22 (1974).
Dyck, H. M., Capps, R. W., Forrest, W. J. & Gillett, F. C. Astrophys. J. Lett. 183, L99–L102 (1973).
Dyck, H. M. & Beichman, C. A. Astrophys. J. 194, 57–64 (1974).
Capps, R. W., Gillett, F. C. & Knacke, R. F. Astrophys. J. 226, 863–868 (1978).
Davis, L. & Greenstein, J. L. Astrophys. J. 114, 206 (1951).
Dennison, B. Astrophys. J. 215, 529–532 (1977).
Martin, P. G. Astrophys. J. 202, 393–399 (1975).
Dyck, H. M. & Lonsdale, C. J. Infrared Astronomy, IAU Symp. 96 223–236 (1981).
McCarthy, D. W., Low, F. J., Kleinman, S. G. & Gillett, F. C. Astrophys. J. Lett. 257, L7–L11 (1982).
van de Hulst, J. M., Hummel, E. & Dickey, J. M. Astrophys. J. 261, 159–163 (1982).
Meaburn, J., Morgan, R. L., Vine, H., Pedlar, A. & Spencer, R. Nature 296, 331–333 (1982).
Jones, T. W., Leung, C. M., Gould, R. J. & Stein, W. A. Astrophys. J. 212, 52–59 (1977).
Martin, P. G. Mon. Not. R. astr. Soc. 158, 63–78 (1972).
Purcell, E. M. & Spitzer, L. Astrophys. J. 167, 31–62 (1971).
Purcell, E. M. Physica 41, 100–133 (1969).
Gold, T. Nature 169, 322 (1952).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aitken, D., Bailey, J., Briggs, G. et al. Infrared spectropolarimetry of Seyfert galaxy NGC1068. Nature 310, 660–662 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1038/310660a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/310660a0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.