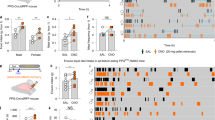
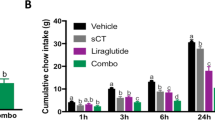
Abstract
Cholecystokinin (CCK) acts acutely to inhibit food consumption in fasted rats1–4, mice5–7, sheep8, pigs9, monkeys10 and humans11–13. CCK has been proposed as a satiety signal, inducing the behavioural sequence of satiety2, or as an aversive internal stimulus, which inhibits food intake by inducing malaise4. Reductions in food intake and related exploratory behaviours are initiated by CCK at its peripheral receptor in the gut, which appears to transmit sensory feedback via the vagus nerve to brain regions mediating appetitive behaviours15–17. The therapeutic potential of CCK as an appetite suppressant in obesity syndromes rests on the demonstration of significant, long-lasting body weight reduction. Chronic CCK administration by repeated injections is problematic, since this peptide is rapidly degraded in vivo. We chose the Alzet constant infusion osmotic minipump to investigate possible alterations in body weight and food intake during continuous infusion of CCK. We now report that no change was detected in either body weight or total daily food consumption at any time point during 2 weeks of intraperitoneally (i.p.) infused CCK. The mechanism underlying the lack of chronic CCK effects appears to be a rapid development of behavioural tolerance. Acute challenge doses of CCK which induced satiety-related behaviours in saline-infused rats were ineffective in CCK-infused rats. The behavioural tolerance was apparent within a few hours of minipump implantation. These results provide the first evidence that rapid and reversible tolerance develops to the actions of a gut peptide.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gibbs, R. A., Young, C. & Smith, G. P. J. comp. Physiol. Psychol. 84, 488–495 (1973).
Antin, J., Gibbs, J., Holt, J., Young, R. C. & Smith, G. P. J. comp. Physiol. Psychol. 89, 784–790 (1975).
Hsiao, S., Wang, C. H. & Schallert, T. Physiol. Behav. 23, 909–914 (1979).
McLaughlin, C. & Baile, C. A. Physiol. Behav. 25, 543–548 (1980).
Crawley, J. N., Hays, S. E., Paul, S. M. & Goodwin, F. K. Physiol. Behav. 27, 407–411 (1981).
Koopmans, H. S., Deutch, J. A. & Branson, P. J. Behav. Biol. 7, 441–444 (1972).
Parrott, R. F. & Batt, R. A. L. Physiol. Behav. 24, 751–753 (1980).
Della-Fera, M. A. & Baile, C. A. Science 206, 471–473 (1979).
Parrott, R. F. & Baldwin, B. A. Physiol. Behav. 24, 419–422 (1980).
Falasco, J. D., Smith, G. P. & Gibbs, J. Physiol. Behav. 23, 887–890 (1979).
Stacher, G., Bauer, H. & Steinringer, H. Physiol. Behav. 23, 325–331 (1979).
Sturdevant, R. A. L. & Goetz, H. Nature 261, 713–715 (1976).
Kissileff, H. R., Pi-Sunyer, F. X., Thornton, J. & Smith, G. P. Am. J. clin. Nutr. 34, 154–160 (1981).
Deutsch, J. A. & Hardy, W. T. Nature 266, 196 (1977).
Smith, G. P., Jerome, C., Cushin, B. J., Eterno, R. & Simansky, K. J. Science 213, 1036–1037 (1981).
Crawley, J. N., Hays, S. E. & Paul, S. M. Eur. J. Pharmac. 73, 379–380 (1981).
Morley, J. E., Levine, A. S., Kneip, J. & Grace, M. Life Sci. 30, 1943–1947 (1982).
Beinfeld, M. C. Neuropeptides 1, 203–209 (1981).
Beinfeld, M. C., Meyer, D. K., Eskay, R. L., Jensen, R. T. & Brownstein, M. J. Brain Res. 212, 51–57 (1981).
Crawley, J. N., Hays, S. E., O'Donohue, T. L. & Goodwin, F. K. Peptides 2, Suppl. 1, 123–129 (1981).
Crawley, J. N., Rojas-Ramirez, J. A. & Mendelson, W. B. Peptides 3, 535–538 (1982).
Crawley, J. N., Szara, S., Pryor, G. T., Creveling, C. R. & Bernard, B. K. J. Neurosci. Meth. 5, 235–247 (1982).
Mineka, S. & Snowdon, C. T. Physiol. Behav. 21, 65–72 (1978).
Moran, T. & McHugh, P. R. Am. J. Physiol. 242, R491–R497 (1982).
Booth, D. A. J. comp. Physiol. Psychol. 81, 457–471 (1972).
McLaughlin, C. L., Peikin, S. R. & Baile, C. A. Am. J. Physiol. (in press).
Wolfe, B. B., Harden, T. K., Sporn, J. R. & Molinoff, P. B. J. Pharmac. exp. Ther. 207, 446–457 (1978).
Mukherjee, C., Caro, J. G. & Lefkowitz, R. J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 72, 1945–1949 (1975).
Ehlert, F. J., Kokka, N. & Fairhurst, A. S. Molec. Pharmac. 17, 24–30 (1980).
Rosenberg, H. C. & Chui, T. H. Life Sci. 24, 803–808 (1979).
Crawley, J. N., Marangos, P. J., Stivers, J. & Goodwin, F. K. Neuropharmacology 21, 85–90 (1982).
Lippa, A. S. et al. Pharmac. Biochem. Behav. 9, 853–856 (1978).
Fagni, L., Gaudry, M. & Lynch, G. Soc. Neurosci. 8 (1982).
Lesniak, M. A. & Roth, J. J. biol. Chem. 251, 3720–3729 (1981).
Davis, M. E., Akera, T. & Brody, T. M. J. Pharmac. exp. Ther. 211, 112–119 (1979).
Elazar, Z., Motles, E., Fly, Y. & Simantov, R. Life Sci. 24, 541–548 (1979).
Zarbin, M. A., Walmsley, J. K., Innis, R. B. & Kuhar, M. J. Life Sci. 29, 697–705 (1981).
Gardner, J. D., Abdelmoumene, S., Lee, P. C., Collins, S. M. & Jensen, R. T. in Biology of Normal and Cancerous Exocrine Pancreatic Cells (eds Ribet, A., Pradayrol, L. & Susini, C.) 165–169 (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1980).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Crawley, J., Beinfeld, M. Rapid development of tolerance to the behavioural actions of cholecystokinin. Nature 302, 703–706 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1038/302703a0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/302703a0
This article is cited by
-
The regulation of food intake by the gut-brain axis: implications for obesity
International Journal of Obesity (2013)
-
Comparison of the metabolic effects of sustained CCK1 receptor activation alone and in combination with upregulated leptin signalling in high-fat-fed mice
Diabetologia (2013)
-
Appetite regulation and weight control: the role of gut hormones
Nutrition & Diabetes (2012)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.