Abstract
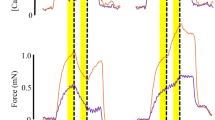
Muscle force is generated by cycling cross-bridges between actin and myosin filaments. In smooth muscle, cyclic attachment and detachment of cross-bridges is thought to be induced by a Ca2+- and calmodulin-dependent myosin light chain kinase which phosphorylates myosin. The relaxation that occurs after Ca2+ removal is usually ascribed to dephosphorylation of myosin by a phosphatase as non-phosphorylated myosin is unable to form force-generating criss-bridges1. Recently, Dillon et al.2 claimed, however, that dephosphorylation of attached cross-bridges may impede cross-bridge detachment, thus forming so-called ‘latch bridges’. Here we present evidence that after a Ca2+- and calmodulin-induced contraction of chemically skinned guinea pig Taenia coli3, the rapid removal of Ca2+ impedes the detachment of the myosin cross-bridges from the actin filament; force can then be maintained without energy consumption. The extremely slowly detaching cross-bridges which maintain the force after Ca2+ removal may indeed correspond to the ‘latch bridges’ mentioned above.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adelstein, R. S. & Eisenberg, E. A. Rev. Biochem. 49, 921–956 (1980).
Dillon, P. F., Aksoy, M. O., Driska, S. P. & Murphy, R. A. Science 211, 495–497 (1981).
Sparrow, M. P., Mrwa, U., Hofmann, F. & Rüegg, J. C. FEBS Lett. 125, 141–145 (1981).
Moisescu, D. G. Nature 262, 610–613 (1976).
Murphy, R. A., Driska, S. P. & Cohen, D. M. in Excitation–Contraction Coupling in Smooth Muscle (eds Casteels, R., Godfraind, T. & Rüegg, J. C.) 417–424 (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1977).
Stein, L. A., Schwarz, R. P. Jr, Chock, P. B. & Eisenberg, E. Biochemistry 18, 3895–3909 (1979).
Schneider, M., Sparrow, M. & Rüegg, J. C. Experientia 37, 980–982 (1981).
Rüegg, J. C. Physiol. Rev. 51, 201–248 (1971).
Siegman, M. J., Butler, T. M., Mooers, S. U. & Davies, R. E. J. gen. Physiol. 76, 609–629 (1980).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Güth, K., Junge, J. Low Ca2+ impedes cross-bridge detachment in chemically skinned Taenia coli. Nature 300, 775–776 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1038/300775a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/300775a0
This article is cited by
-
Comparison of the effects of 2,3-butanedione monoxime on force production, myosin light chain phosphorylation and chemical energy usage in intact and permeabilized smooth and skeletal muscles
Journal of Muscle Research and Cell Motility (1994)
-
Influence of 2,3-butanedione monoxime on heart energy metabolism
Basic Research in Cardiology (1993)
-
Flash photolysis studies of relaxation and cross-bridge detachment: higher sensitivity of tonic than phasic smooth muscle to MgADP
Journal of Muscle Research and Cell Motility (1993)
-
Complex stiffness of smooth muscle cytoplasm in the presence of Ca-activated brevin
Journal of Muscle Research and Cell Motility (1991)
-
The action of brevin, an F-actin severing protein, on the mechanical properties and ATPase activity of skinned smooth muscle
Journal of Muscle Research and Cell Motility (1990)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.