Abstract
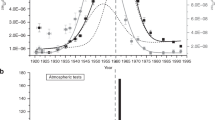
Radionuclides produced by atmospheric testing of nuclear weapons have been used as environmental tracers for the past 30 years. 185W and 90Sr have proved valuable in monitoring atmospheric circulation1, 14C has been applied to oceanic mixing2, and 3H has been routinely used as a tracer in the hydrologic system. Tandem accelerator mass spectrometry4 has made possible measurements of several long-lived radionuclides that were previously virtually undetectable. One of the potentially most valuable of these for studying the movement and mixing of groundwater and surface water is 36Cl. 36Cl is produced continuously in the terrestrial environment in very small amounts by spallation of argon by cosmic radiation and by the capture of naturally produced neutrons by 35Cl. It was also produced in much larger amounts by neutron activation of seawater and released into the environment during atmospheric thermonuclear tests. This 36Cl pulse has many potential applications as a tracer in natural water systems. Here, numerical modelling and analyses of water samples indicate that in the mid-latitudes the fallout peak was 3 orders of magnitude above the natural background, and that the period of enhanced 36Cl fallout was 1953 to about 1964.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lockhardt, L. B. Jr, Baus, R. A., Patterson, R. L. Jr & Sanders, A. W. Jr Science 130, 161–162 (1959).
Münnich, K. O. & Roether, W. Proc. Symp. on Radioactive Dating Methods of Low Level Counting, 93–104 (IAEA, Vienna, 1967).
Vogel, J. C., Thilo, L. & Van Dijken, M. J. Hydrol. 23, 131–140 (1974).
Elmore, D. et al. Nature 277, 22–25 (1979).
Carter, M. W. & Moghissi, A. A. Hlth Phys. 33, 55–71 (1977).
Zander, I. & Araskog, R. Nuclear Explosions 1945-1972; Basic Data, FOA-4, Rep. A-4505-A (1973).
Dyrssen, D. & Nyman, P. O. Acta radiol. 43, 421–427 (1955).
Glasstone, S. (ed.) The Effects of Nuclear Weapons, Appendix B (U.S. Atomic Energy Commission, 1964).
Peterson, K. R. Hlth Phys. 18, 357–378 (1970).
Krey, P. W. & Krajewski, B. J. geophys. Res. 75, 2901–2908 (1970).
Schaeffer, O. A., Thompson, S. O. & Lark, N. L. J. geophys. Res. 65, 4013–4016 (1960).
Bentley, H. W. & Davis, S. N. 2nd A. Symp. on Accelerator Mass Spectrometry (ed. Kutchera, M.) (Argonne National Laboratories, 1982).
MacFarlane, D. S., Cherry, J. A., Gillham, R. W. & Sudicky, E. A. J. Hydrol. (in the press).
Cherry, J. A., Gillham, R. W., Anderson, E. G. & Johnson, P. E. J. Hydrol. (in the press).
Sudicky, E. A., Cherry, J. A. & Frind, E. O. J. Hydrol. (in the press).
Egboka, B. C. E., Cherry, J. A., Farvolden, R. N. & Frind, E. O. J. Hydrol. (in the press).
Egboka, B. C. E. thesis, Univ. Waterloo (1980).
Elmore, D. et al. Nature 300, 735–737 (1982).
Finkel, R. C., Nishiizumi, K., Ferraro, R. D. & Gove, H. E. Geophys. Res. Lett. 7, 983–986 (1980).
Bonner, F. T., Roth, E., Schaeffer, O. A. & Thompson, S. O. Geochim. cosmochim. Acta 25, 261–266 (1962).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bentley, H., Phillips, F., Davis, S. et al. Thermonuclear 36Cl pulse in natural water. Nature 300, 737–740 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1038/300737a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/300737a0
This article is cited by
-
36Cl, a new tool to assess soil carbon dynamics
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Water transit time and active recharge in the Sahel inferred by bomb-produced 36Cl
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Application of the chlorine-36 method for the delineation of groundwater infiltration of large river systems: example of the Danube River in western Hungary (Szigetk�z area)
Environmental Geology (2004)
-
36Cl bomb pulse measured in a shallow ice core from Dye 3, Greenland
Nature (1982)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.