Abstract
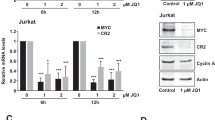
Malignant transformation of cells by acute transforming RNA tumour viruses is mediated by the expression of certain specific pro viral DNA sequences (‘oncogenes’). These sequences have been well characterized and, in many cases, molecularly cloned1–8. These viral oncogenes are related to similar genes found in normal uninfected cells9,10. Moreover, these particular sequences are highly conserved in evolution4,11, suggesting that these genes have an important, albeit unknown, role in normal cell function. It has been suggested that an increased dosage of products of such endogenous oncogenes may be responsible for malignant transformation10,12,13. For example, increased expression of the endogenous chick c-myc oncogene has been observed in avian leukosis virus-induced transformation of chick bursal lymphocytes12. Here we demonstrate that sequences in normal human DNA homologous to the avian myc oncogene are present in multiple copies in the chromosomal DNA of the human leukaemia cell line HL-60. Other transformation-specific genes derived from the Abelson leukaemia virus4 and feline sarcoma virus6 are not amplified in HL-60. This myc-related gene amplification is not present in other cultured human myeloid leukaemia cells, including K-56214 and KG-115.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Czermlofsky, A. P. et al., Nature 287, 198–203 (1980).
Lautenberger, J. A., Schulz, R. A., Garon, C. F., Tsichlio, P. N. & Papas, T. S. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 78, 1518–1522 (1981).
Vennstrom, B., Moscovici, C., Goodman, H. M. & Bishop, J. M. J. Virol. 39, 625–631 (1981).
Goff, S. P., Gilboa, E., Witte, O. N. & Baltimore, D. Cell 22, 777–785 (1980).
Vande Woude, G. F. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 76, 4464–4468 (1979).
Sherr, C. J., Fedele, L. A., Oskarsson, M., Maizel, J. & Vande Woude, G. F. J. Virol. 34, 200–212 (1980).
Gelmann, E. P., Wong-Staal, F., Kramer, R. & Gallo, R. C. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 78, 3373–3377 (1981).
Robbins, K. C., Devare, S. G. & Aaronson, S. A. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 78, 2918–2922 (1981).
Stehelin, D., Varmus, H. E., Bishop, J. M. & Vogt, P. K. Nature 260, 170–173 (1976).
Bishop, J. M. Cell 23, 5–6 (1981).
Wong-Staal, F., Dalla-Favera, R., Franchini, G., Gelmann, E. & Gallo, R. C. Science 213, 226–228 (1981).
Hayward, W. S., Neel, B. G. & Astrin, S. M. Nature 290, 475–479 (1981).
Klein, G. Nature 294, 313–318 (1981).
Lozzio, C. B. & Lozzio, B. B. Blood 45, 321–334 (1975).
Koeffler, H. P. & Golde, D. W. Science 200, 1153–1154 (1978).
Collins, S. J., Gallo, R. C. & Gallagher, R. E. Nature 270, 347–349 (1977).
Graf, T. & Beug, H. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 516, 269–299 (1978).
Roussel, M. et al. Nature 281, 452–455 (1979).
Eva, A. et al. Nature 295, 116–119 (1982).
Kafatos, F. C., Jones, C. W. & Efstratiadis, A. Nucleic Acids Res. 7, 1541–1552 (1979).
de Saint Vincent, B. et al. Cell 27, 267–277 (1981).
Nunberg, J. H., Kaufman, R. J., Chang, A. C. Y., Cohen, S. N. & Schimke, R. T. Cell 19, 355–364 (1980).
Gallagher, R. et al. Blood 54, 713–733 (1979).
Noori-Daloii, M. R., Swift, R. A., Kung, H. J., Crittenden, L. B. & Witter, R. L. Nature 294, 574–576 (1981).
Collins, S. J., Ruscetti, F. W., Gallagher, R. E. & Gallo, R. C. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 75, 2458–2462 (1978).
Southern, E. M. J. molec. Biol. 98, 503–517 (1975).
Rigby, P. W., Dieckmann, M., Rhodes, C. & Berg, P. J. molec. Biol. 113, 237–258 (1977).
Robins, T., Bister, K., Garon, C., Papas, T. & Duesberg, P. J. Virol. 41, 635–642 (1982).
Fritsch, E. F., Lawn, R. M. & Maniatis, T. Nature 279, 598–603 (1979).
Westin, E. H. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 79, 2490–2494 (1982).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Collins, S., Groudine, M. Amplification of endogenous myc-related DNA sequences in a human myeloid leukaemia cell line. Nature 298, 679–681 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1038/298679a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/298679a0
This article is cited by
-
FIT links c-Myc and P53 acetylation by recruiting RBBP7 during colorectal carcinogenesis
Cancer Gene Therapy (2023)
-
Glutamine stabilizes myc via alpha-ketoglutarate and regulates paclitaxel sensitivity
Medical Oncology (2022)
-
Regulation of cancer cell metabolism: oncogenic MYC in the driver’s seat
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2020)
-
Mode of action and pharmacogenomic biomarkers for exceptional responders to didemnin B
Nature Chemical Biology (2015)
-
Two sides of the Myc-induced DNA damage response: from tumor suppression to tumor maintenance
Cell Division (2012)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.