Abstract
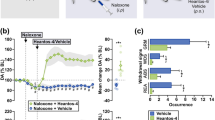
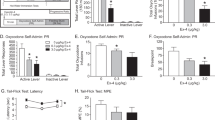
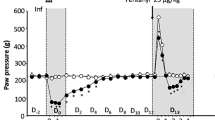
There is both theoretical and therapeutic interest in establishing whether the signals conveyed by the enkephalins are turned off under the action of a specific peptidase which might, in this case, represent a target for a new class of psychoactive agents. Enkephalinase, a dipeptidyl carboxypeptidase cleaving the Gly3-Phe4 bond of enkephalins1,2 and distinct from angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE)3–6, might be selectively involved in enke-phalinergic transmission. It is a membrane-bound enzyme1,7,8 whose localization in the vicinity of opiate receptors in the central nervous system is suggested by parallel regional1,7,9 and subcellular10 distributions as well as by the effects of lesions9. Such a role is further supported by the ontogenetic development of enkephalinase11,12, its substrate specificity accounting for the increased biological activity of several enkephalin analogues13 and its adaptive increase following chronic treatment with morphine1,14. To investigate the functional role of this enzyme further, we have designed a potent and specific enkephalinase inhibitor. We report here that this compound, thiorphan [(DL-3-mercapto-2-benzylpropanoyl)-glycine; patent no. 8008601] protects the enkephalins from the action of enkephalinase in vitro in nanomolar concentration and in vivo after either intracerebroventricular or systemic administration. In addition, thiorphan itself displays antinociceptive activity which is blocked by naloxone, an antagonist of opiate receptors.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Malfroy, B., Swerts, J. P., Guyon, A., Roques, B. P. & Schwartz, J-C. Nature 276, 523–526 (1978).
Guyon, A. et al. Life Sci. 25, 1605–1612 (1979).
Swerts, J. P., Perdrisot, R., Malfroy, B. & Schwartz, J-C. Eur. J. Pharmac. 53, 209–210 (1979).
Swerts, J. P., Perdrisot, R., Patey, G., De La Baume, S. & Schwartz, J-C. Eur. J. Pharmac. 57, 279–281 (1979).
Sullivan, S., Akil, H., Blacker, D. & Barchas, J. D. in Endogenous and Exogenous Opiate Agonists and Antagonists (ed. Way, E. L.) 357–360 (Pergamon, New York, 1980).
Gorenstein, C. & Snyder, S. H. Life Sci. 25, 2065–2070 (1979).
Sullivan, S., Akil, H. & Barchas, J. D. Commun. Psychopharmac. 2, 525–531 (1979).
Vogel, Z. & Altstein, M. in Endogenous and Exogenous Opiate Agonists and Antagonists (ed. Way, E. L.) 353–356 (Pergamon, New York, 1980).
Malfroy, B., Swerts, J. P., Llorens, C. & Schwartz, J-C. Neurosci. Lett. 11, 329–334 (1979).
De La Baume, S., Patey, G. & Schwartz, J-C. Neuroscience (in the press).
De La Baume, S., Patey, G., Gros, C. & Schwartz, J-C. in Endogenous and Exogenous Opiate Agonists and Antagonists (ed. Way, E. L.) 179–182 (Pergamon, New York, 1980).
Patey, G., De La Baume, S., Gros, C. & Schwartz, J-C. Life Sci. 27, 245–252 (1980).
Fournie-Zaluski, M. C. et al. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 91, 130–135 (1979).
Schwartz, J-C. et al. Adv. Biochem. Psychopharmac. 22, 219–235 (1980).
Quiocho, F. A. & Lipscomb, W. N. Adv. Protein Chem. 15, 1–48 (1971).
Ondetti, M. A., Rubin, B. & Cushman, D. W. Science 196, 441–444 (1977).
Ondetti, M. A. et al. Biochemistry 18, 1427–1430 (1979).
Yang, H. Y. T. & Neff, N. H. J. Neurochem. 19, 2443–2450 (1972).
Erdos, E. G., Johnson, A. R. & Boyden, N. T. Biochem. Pharmac. 27, 843–848 (1978).
Hambrook, J. M., Morgan, B. A., Rance, M. J. & Smith, C. F. Nature 262, 782–783 (1976).
Lane, A. C., Ranee, M. J. & Walter, D. S. Nature 269, 75–76 (1977).
Marks, N., Grynbaum, A. & Neidle, A. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 74, 1552–1559 (1977).
Meek, J. L., Yang, H. Y. T. & Costa, E. Neuropharmacology 16, 151–154 (1977).
Vogel, Z. & Alstein, M. FEBS Lett. 80, 332–336 (1977).
Knight, M. & Klee, W. A. J. biol. Chem. 253, 3843–3847 (1978).
Guyon, A. et al. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 88, 919–926 (1979).
Pert, C. B., Pert, A., Chang, J. K. & Fong, B. T. W. Science 194, 331–332 (1976).
Ben-Bassat, J., Peretz, E. & Sulman, F. G. Archs int. Pharmacodyn. Ther. 122, 434–477 (1959).
Jacob, J., Tremblay, E. C. & Colombel, M. C. Psychopharmacologia 37, 217–223 (1974).
Goldstein, A., Pryor, G. T., Otis, L. S. & Larson, F. Life Sci. 18, 599–604 (1976).
Sewell, R. D. E. & Spencer, P. S. J. Neuropharmacology 15, 683–688 (1976).
Frederickson, R. C. A., Bergers, V. & Edwards, J. D. Science 198, 756–757 (1977).
Woolf, C. J. Brain Res. 190, 578–583 (1980).
Eddy, N. B., May, E. L. & Mosettig, E. J. org. Chem. 17, 321–326 (1952).
Jacob, J. & Blozovski, M. Archs int. Pharmacodyn. Ther. 133, 296–309 (1961).
Stine, S. M., Yang, H. Y. T. & Costa, E. Brain Res. 188, 295–299 (1980).
Llorens, C. et al. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. (in the press).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roques, B., Fournié-Zaluski, M., Soroca, E. et al. The enkephalinase inhibitor thiorphan shows antinociceptive activity in mice. Nature 288, 286–288 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1038/288286a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/288286a0
This article is cited by
-
Current Chemical, Biological, and Physiological Views in the Development of Successful Brain-Targeted Pharmaceutics
Neurotherapeutics (2022)
-
Dual Enkephalinase Inhibitors and Their Role in Chronic Pain Management
Current Pain and Headache Reports (2021)
-
Membrane metalloendopeptidase suppresses prostate carcinogenesis by attenuating effects of gastrin-releasing peptide on stem/progenitor cells
Oncogenesis (2020)
-
Neprilysin inhibition promotes corneal wound healing
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Neurolysin: From Initial Detection to Latest Advances
Neurochemical Research (2018)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.