Abstract
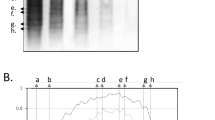
Elevated IgG distributed in oligoclonal bands is characteristically observed in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) or subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (SSPE)1–6. Similarly, IgG in bands has been detected in neutral saline (NS) and acid eluates of brain material from these two diseases7–21. We have now used isoelectric focusing (IEF) to compare IgG eluted from control brain, three plaques and a white matter pool of an MS brain, and three regions of an SSPE brain. A direct peroxidase-conjugated anti-human IgG staining technique was used to stain IgG exclusively and to visualize the minute amounts of IgG obtained from individual MS plaques. Eluates from individual MS plaques have distinct IgG patterns; in contrast, those from separate SSPE brain areas have essentially identical IgG patterns. The identical IgG patterns in three areas of SSPE brain suggest a common response to the same antigen. The different IgG patterns among MS plaques suggest: (1) variable response to the same ‘MS antigen’ in each plaque, (2) response to different MS antigens in different plaques, (3) synthesis of ‘nonsense’ antibodies irrelevant to the pathogenesis of MS in each plaque, or (4) some combination of the above.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kabat, E. A., Moore, D. H. & Landow, H. J. clin. Invest. 21, 571–577 (1942).
Bauer, H. in Encephalidites (eds van Bogaert, L. et al.) 675–680 (Eisevier, Amsterdam, 1961).
Laterre, E. C., Callewaet, A., Heremans, J. F. & Sfaello, Z. Neurology 20, 982–990 (1970).
Lowenthal, A., Van Sande, M. & Karcher, D. J. Neurochem. 6, 51–60 (1960).
Delmotte, P. & Gonsette, R. J. Neurol. 215, 27–37 (1977).
Kjellin, K. G. & Vesterberg, O. J. neurol. Sci. 23, 199–213 (1974).
Tourtellotte, W. W. & Parker, J. A. Science 154, 1044–1046 (1966); Nature 214, 683–686 (1967).
Tourtellotte, W. W., Parker, J. A., Herndon, R. M. & Cuadros, C. V. Neurology 18, 117–121 (1968).
Gerstl, B., Uyeda, C. T., Eng, L. F., Bond, P. & Smith, J. K. Neurology 19, 1019–1026 (1969).
Link, H. J. neurol. Sci. 16, 103–114 (1972).
Vandvick, B. Ann. clin. Res. 5, 308–315 (1973).
Norrby, E. & Vandvick, B. Med. Microbiol. Immun. 162, 63–72 (1975).
Vandvick, B., Norrby, E., Nordal, H. J. & Degre, M. Scand. J. Immun. 5, 979–992 (1976).
Weil, M. L., Leiva, W. A., Heiner, D. C. & Tourtellotte, W. W. J. Immun. 115, 1603–1606 (1975).
Weil, M. L. et al. Infect. Immun. 24, 202–210 (1979).
Mehta, P. D., Kane, A. & Thormar, H. J. Immun. 117, 2053–2060 (1976).
Mehta, P. D., Kane, A. & Thormar, H. J. Immun. 118, 2254–2261 (1977).
Mehta, P. D., Kane, A. & Thormar, H. Ann. Neurol. 3, 552–555 (1978).
Bollengier, F., Mahler, A., Clonet, G. & Lowenthal, A. Brain Res. 152, 133–144 (1978).
Ruth, V., Matikainen, M-T., Salmi, A. & Panelius, M. Acta neurol. scand. 57, suppl. 67, 240 (1978).
Gilden, D. & Tachovsky, T. J. Neurosci. Meth. 1, 133–142 (1979).
Gilden, D., Devlin, M. & Wroblewska, Z. Ann. Neurol. 3, 403–405 (1978).
Aarli, J. A., Aparicio, S. R., Lumsden, C. E. & Tönder, O. Immunology 28, 171–185 (1975).
Traugott, U., Snyder, S. & Raine, C. S. Ann. Neurol. 6, 13–20 (1979).
Kimball, J. W., Pappenheimer, A. M. & Jaton, J-C. J. Immun. 106, 1171–1184 (1971).
Pincus, J. H., Jaton, J-C., Bloch, J. & Haber, E. J. Immun. 104, 1143–1148 (1970).
Narayan, O., Griffin, D. E. & Chase, J. Science 197, 376–378 (1977).
Nordal, H. J., Vanvick, B. & Norrby, E. Scand. J. Immun. 7, 473–479 (1978).
Poskitt, D. C., Frost, H., Cahill, R. N. P. & Trnka, Z. Immunology 33, 81–89 (1977).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mattson, D., Roos, R. & Arnason, B. Isoelectric focusing of IgG eluted from multiple sclerosis and subacute sclerosing panencephalitis brains. Nature 287, 335–337 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1038/287335a0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/287335a0
This article is cited by
-
Neurological Complications of Measles (Rubeola)
Current Neurology and Neuroscience Reports (2020)
-
The Retrovirus/Superantigen Hypothesis of Multiple Sclerosis
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (2014)
-
Retrovirus-Superantigen-Hypothese der Multiplen Sklerose
Der Nervenarzt (2013)
-
B cells and monocytes from patients with active multiple sclerosis exhibit increased surface expression of both HERV-H Env and HERV-W Env, accompanied by increased seroreactivity
Retrovirology (2009)
-
Molecular heterogeneity, detected by two electrophoretic micro procedures, of IgG in human cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry (2003)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.