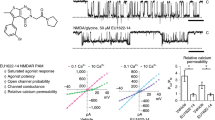
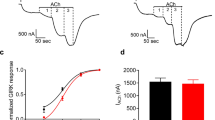
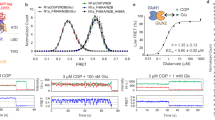
Abstract
Current evidence suggests that glutamate is a major excitatory neurotransmitter in the mammalian central nervous system (CNS)1; particularly, glutamate excites most neurones in the CNS. Until recently this effect was widely used to study glutamate receptors and to distinguish them from those of other excitatory amino acids2. The development of ligand binding studies for many neurotransmitters has facilitated the study of receptors at the molecular level and using these methods we recently reported the existence in hippocampal membranes of pharmacologically distinct sodium-dependent and sodium-independent glutamate binding sites3, the former related to high-affinity uptake and the latter exhibiting several characteristics of postsynaptic receptor sites4. We now report that, as with other neurotransmitters5–8, several ions regulate the Na-independent binding of glutamate; the monovalent cations induce a decreased binding while certain divalent cations enhance this Na-independent binding. Additionally, since some of these effects appear to be reversible, we propose that the regulation of glutamate binding by cations might account for the extremely long-lasting potentiation of synaptic responses found in the hippocampus following bursts of repetitive electrical stimulation (see ref. 9 for a review).
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Johnson, J. L. Brain Res. 37, 1–9 (1972).
Curtis, D. R. in Glutamic Acid: Advances in Biochemistry and Physiology (eds Filer, L. J.,Garattini, S., Kare, M. R., Reynolds, W. A. & Wurtman, R. J.) 163–175 (Raven, New York, 1979).
Baudry, M. & Lynch, G. Eur. J. Pharmac. 57, 283–285 (1979).
Johnston, G. A. R. in Glutamic Acid: Advances in Biochemistry and Physiology (eds Filer, L. J., Garattini, S., Kare, M. R., Reynolds, W. A. & Wurtman, R. J.) 177–185 (Raven, New York, 1979).
Young, A. B. & Snyder, S. H. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 71, 4002–4005 (1974).
Enna, S. J. & Snyder, S. H. Molec. Pharmac. 13, 442–453 (1977).
Mohler, H. & Okada, T. Molec. Pharmac. 14, 256–256 (1978).
Tsai, B. S. & Lefkowitz, R. J. Molec. Pharmac. 14, 540–548 (1978).
Lynch, G., Gall, C. & Dunwiddie, T. in Progress in Brain Research (ed. Corner, M. A.) 113–128 (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1978).
Enna, S. J. & Snyder, S. H. Brain Res. 100, 81–97 (1975).
Foster, A. C. & Roberts, P. J. J. Neurochem. 31, 1467–1477 (1978).
Pert, C. & Snyder, S. H. Molec. Pharmac. 10, 868–879 (1974).
Pasternak, G. W., Snowman, A. M. & Snyder, S. H. Molec. Pharmac. 11, 735–744 (1975).
Costa, T., Rodbard, D. & Pert, C. B. Nature 277, 315–317 (1979).
Anderson, C. R., Cull-Candy, S. G. & Miledi, R. Nature 261, 151–153 (1976).
Perrachia, C. Nature 271, 669–671 (1978).
Gilbert, D. S., Newby, B. J. & Anderton, B. H. Nature 256, 586–589 (1975).
Schlaepfer, W. W. & Hasler, M. B. Brain Res. 168, 299–309 (1979).
Snyder, S. H. & Bennett, J. P. A. Rev. Physiol. 38, 153–175 (1976).
Storm-Mathisen, J. Prog. Neurobiol. 8, 119–181 (1977).
Dunwiddie, T. V. & Lynch, G. Brain Res. 169, 103–110 (1979).
Wieraszko, A., Baudry, M., Creager, R., Finn, R. & Lynch, G. Soc. for Neuroscience Abstract, IXth Annual Meeting, Atlanta, Ga (1979).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baudry, M., Lynch, G. Regulation of glutamate receptors by cations. Nature 282, 748–750 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1038/282748a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/282748a0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.