Abstract
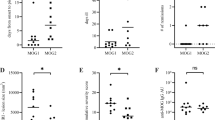
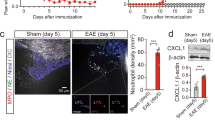
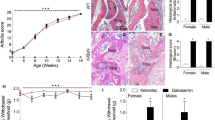
EXPERIMENTAL ALLERGIC NEURITIS (EAN) is a model of human acute inflammatory polyneuropathy, Guillain–Barré syndrome. It can be produced in several species of laboratory animal by immunisation with homologous or heterologous peripheral nerve emulsified in Freund's complete adjuvant1,2. After about two weeks the animals may develop signs varying from ataxia to paralysis and death. EAN has been produced using crude acid extracts of peripheral nerve3,4, but investigations into the neuritogenic properties of the component proteins of peripheral nerve myelin have yielded inconclusive results5–10. In experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (EAE), the central nervous system (CNS) counterpart of EAN, the encephalitogenic antigen has been shown to be a CNS myelin basic protein of molecular weight 18,000 (ref. 11). The three major proteins of peripheral nerve myelin, which together account for about 75% of the myelin protein, are usually referred to as P0, P1 and P2 (ref. 12). P0 is a glycoprotein of molecular weight 30,000 and P1 and P2 are both basic proteins with molecular weights of 18,000 and 12,000–14,000, respectively12–13. We describe here a reliable method for producing severe EAN in inbred Lewis rats with bovine intradural root material, and show that intact P2, the major basic protein of peripheral nerve myelin, is the responsible neuritogen.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Waksman, B. H. & Adams, R. D. J. exp. Med. 102, 213–235 (1955).
Waksman, B. H. & Adams, R. D. J. Neuropath. exp. Neurol. 15, 293–332 (1956).
Behan, P. O., Lamarcke, J. B., Behan, W. M., Feldman, R. G. & Kies, M. W. Trans. Am. neural. Ass. 94 219–222 (1969).
Sheremata, W. A. & Behan, P. O. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat. 36, 139–145 (1973).
Brostoff, S., Burnett, P., Lampert, P. & Eylar, E. H. Nature new Biol. 235, 210–212 (1972).
Uyemura, K., Tobari, C., Hirano, S. & Tsukada, T. J. Neurochem. 19, 2706–2614 (1972).
Brostoff, S. W., Karkhains, Y. D., Carlo, D. J., Reuter, W. & Eylar, E. H. Brain Res. 86, 449–458 (1975).
Abramsky, O., Teitelbaum, D., Webb, C. & Arnon, R. J. Neuropath. exp. Neurol. 34, 36–45 (1975).
Abramsky, O., Teitelbaum, D. & Arnon, R. Eur. J. Immun. 7, 213–217 (1977).
Brostoff, S. W., Levit, S. & Powers, J. M. Nature 268, 752–753 (1977).
Laatsch, B. A., Kies, M. W., Gordon, S. & Alvord, E. C. J. exp. Med. 115, 777–788 (1962).
Greenfield, S., Brostoff, S., Eylar, E. H. & Morell, P. J. Neurochem. 20, 1207–1216 (1973).
Deibler, G. E., Driscoll, B. P. & Kies, M. W. J. Neurochem. 30, 401–412 (1978).
Ishaque, A., Roomi, M. W., Khan, N. R. & Eylar, E. H. Biochim. biophys. Acta 495, 77–86 (1977).
Norton, W. T. & Paduslo, S. E. J. Neurochem. 21, 759–773 (1973).
Kitamura, K., Yamanaka, T. & Uyemura, K. Biochim. biophys. Acta 379, 582–591 (1975).
Smith, M. E., Forno, L. S. & Hofmann, W. W. Trans. Am. Soc. Nerurochem. 9, 55 (1978).
Brostoff, S. W. & Eylar, E. H. Archs. Biochem. Biophys. 153, 590–598 (1972).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
KADLUBOWSKI, M., HUGHES, R. Identification of the neuritogen for experimental allergic neuritis. Nature 277, 140–142 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1038/277140a0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/277140a0
This article is cited by
-
Capsaicin-enriched diet ameliorates autoimmune neuritis in rats
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2018)
-
Fingolimod attenuates experimental autoimmune neuritis and contributes to Schwann cell-mediated axonal protection
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2017)
-
Autoantibodies in chronic inflammatory neuropathies: diagnostic and therapeutic implications
Nature Reviews Neurology (2017)
-
Guillain–Barré syndrome: a century of progress
Nature Reviews Neurology (2016)
-
Administration of SB203580, a p38 MAPK Inhibitor, Reduced the Expression of MMP9, and Relieved Neurologic Severity in the Experimental Autoimmune Neuritis (EAN) in Rats
Neurochemical Research (2015)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.