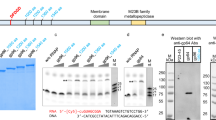
Abstract
The nucleotide sequences were analysed at the two ends of bacteriophage Mu DNA. Such analyses reveal the existence of a short stretch of common sequences that are located at the termini and are orientated as inverted repeats. They also confirm that the heterogeneous bacterial DNA covalently bound to the ends of vegetative Mu DNA is totally removed during lysogenisation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
McClintock, B. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 36, 344 (1950); Cold Spring Harb. Symp. quant. Biol. 16, 13 (1952), 21, 197 (1957).
Bukhari, A. I., Shapiro, J. A. & Adhya, S. L. (eds) DNA Insertion Elements, Plasmids and Episomes (Cold Spring Harb. Monogr. Ser., 1977).
Calos, M. P., Johnsrud, L. & Miller, J. Cell 13, 411 (1978).
Grindley, N. D. F. Cell 13, 419 (1978).
Abelson, J. et al. Virology 54, 90 (1973).
Daniell, E., Kohne, D. E. & Ableson, J. J. Virol. 15, 739 (1975).
Allet, B. & Bukhari, A. I. J. molec. Biol. 92, 529 (1975).
Bukhari, A. I. Froshauer, S. & Botchan, M. Nature 264, 580 (1976).
Hsu, M. & Davidson, N. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 69, 2823 (1972); Virology 58, 229 (1974).
Bukhari, A. I. & Allet, B. Virology 63, 30 (1975).
Magazin, M. Howe, M. & Allet, B. Virology 77, 677 (1977).
Fowler, A. V. & Zabin, I. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 74, 1507 (1977).
Maxam, A. M. & Gilbert, W. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 74, 560 (1977).
Allet, B. Biochemistry 12, 3972 (1973).
Jeppesen, P. G. N. Analyt. Biochem. 58, 195 (1974).
Mandel, M. & Higa, A. J. molec. Biol. 53, 159 (1970).
Grünstein, M. & Hogness, D. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 72, 3961 (1975).
Ohtsubo, H. & Ohtsubo, E. in DNA Insertion Elements, Plasmids, and Episomes (eds Bukhari, A. L, Shapiro, J. A. & Adhya, S. L.) 591 (Cold Spring Harb. Monogr. Ser., 1977).
Grindley, N. D. F. in DNA Insertion Elements, Plasmids, and Episomes (eds Bukhari, A. I., Shapiro, J. A. & Adhya, S. L.) 595 (Cold Spring Harb. Monogr. Ser., 1977).
Pribnow, D. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 72, 784 (1975).
Schumann, W., Bade, E. G., Delius, H. & Hübert, P. Molec. Gen. Genet. 160, 115 (1978).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Allet, B. Nucleotide sequences at the ends of bacteriophage Mu DNA. Nature 274, 553–558 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1038/274553a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/274553a0
This article is cited by
-
The tetracycline resistance transposons Tn1721 and Tn1771 have three 38-base-pair repeats and generate five-base-pair direct repeats
Molecular and General Genetics MGG (1981)
-
A signal sequence is not sufficient to lead β-galactosidase out of the cytoplasm
Nature (1980)
-
Nucleotide sequences of the attachment sites of bacteriophage Mu DNA
Nature (1979)
-
Characterisation of Tn1721, a new transposon containing tetracycline resistance genes capable of amplification
Molecular and General Genetics MGG (1979)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.