Abstract
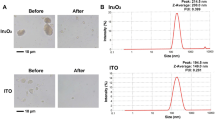
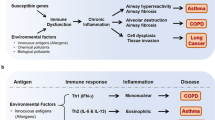
PULMONARY alveolar macrophages (PAM) phagocytose inhaled foreign particulates that reach the peripheral airways. Particulates engulfed by PAM are then transported by the mucociliary system up the respiratory tract past the bronchial epithelium to be expectorated and/or swallowed. Since these particulates may contain adsorbed chemical carcinogens, for example, those in tobacco smoke, and PAM have been shown to metabolise chemical carcinogens1–3, PAM may interact with the bronchial epithelium in the metabolic activation of respiratory carcinogens. We report here the metabo-lic activation of benzo(a)pyrene (B(a)P) by PAM into both a promutagen ( ± )r7,t8-dihydroxy-7,8-dihydrobenzo(a)pyrene; (7,8-diol; 50% ( + )) and an ultimate mutagen(s).
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cantrell, E. T., Warr, G. A. & Martin, R. R. J. clin. Invest. 52, 1881–1884 (1973)
Dehnen, W. Zentralbl. Bakteriol. (Orig. B) 161, 1–19 (1975).
Autrup, H. et al. Lab. Invest. (in press).
Huberman, E. & Sachs, L. Int. J. Cancer 13, 326–333 (1974).
Chu, E. H. Y. & Malling, H. V. Genetics 61, 1306–1312 (1968).
Huberman, E., Sachs, L., Yang, S. K. & Gelboin, H. V. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 73, 607–611 (1976).
Harris, C. C. et al. Cancer Res. 37, 3349–3356 (1977).
Selkirk, J. K., Gray, R. G., Roller, P. P. & Gelboin, H. V. Cancer Res. 34, 3474–3480 (1974).
Mankowitz, R., Buchwald, M. & Barker, R. M. Cell 3, 221–226 (1974).
Wanner, A. Am. Rev. resp. Dis. 116, 73–122 (1977).
Brain, J. D., Proctor, D. F. & Reid, L. M. (ed.) Respiratory Defense Mechanism, Part II (Marcel Dekker, New York, 1977).
Kapitulnik, J., Levin, W., Conney, A. H., Yagi, H. & Jerina, D. M. Nature 266, 378–380 (1977).
Yang, S. K., Gelboin, H. V., Trump, B. F., Autrup, H. & Harris, C. C. Cancer Res. 37, 1210–1215 (1977).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
HARRIS, C., Hsu, I., STONER, G. et al. Human pulmonary alveolar macrophages metabolise benzo(a)pyrene to proximate and ultimate mutagens. Nature 272, 633–634 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1038/272633a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/272633a0
This article is cited by
-
Dose-related cytogenetic damage in pulmonary alveolar macrophages from mice exposed to cigarette smoke early in life
Archives of Toxicology (2012)
-
TP53 mutations in vulval lichen sclerosus adjacent to squamous cell carcinoma of the vulva
British Journal of Cancer (2003)
-
A host-mediated in vivo/in vitro assay with peritoneal murine macrophages for the detection of carcinogenic chemicals
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (1990)
-
Organ specific metabolic activation of five extracts of indoor and outdoor particulate matter
Archives of Toxicology (1988)
-
In vitro cytotoxicity of chrysotile asbestos to human pulmonary alveolar macrophages is decreased by organosilane coating and surfactant
Cell Biology and Toxicology (1986)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.