Abstract
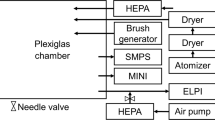
IN the current controversy over the toxicity of environmental lead, one point still at issue is the efficiency of respiratory uptake of urban lead aerosol. The rate at which lead passes into the blood is a function of the particle size and the solubility of the deposited lead. Although data on the aerodynamic particle size distribution of urban lead aerosol are plentiful, little is known of the chemical nature, and thus solubility, of the lead and so this has hampered studies of respiratory uptake. Several analytical studies of fresh auto exhaust have been reported1, but Ter Haar and Bayard2 have shown that rapid changes occur after emission into the atmosphere. Although these workers characterised the major components of aged lead aerosol, limitations of the electron microprobe techniques which they used have been pointed out by Heidel and Desborough3, and considerable doubt must attach to the structural assignments. Using two techniques to enrich the lead fraction of urban aerosol, we have now identified the major components by X-ray powder diffraction (XRD).
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ganley, J. T. & Springer, G. S. Environ. Sci. Technol. 8, 340–347 (1974).
Ter Haar, G. L. & Bayard, M. A. Nature 216, 353–355 (1971).
Heidel, R. H. & Desborough, G. A. Environ. Poll. 8, 185–191 (1975).
Olson, K. W. & Skogerboe, R. K. Environ. Sci. Technol. 9, 227–230 (1975).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
BIGGINS, P., HARRISON, R. Identification of lead compounds in urban air. Nature 272, 531–532 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1038/272531a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/272531a0
This article is cited by
-
Trace-element speciation and partitioning in environmental geochemistry and health
Minerals and the Environment (1983)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.