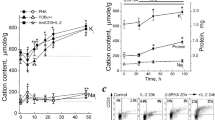
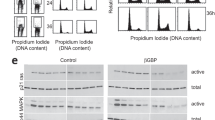
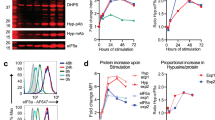
Abstract
IN the course of studies on the regulation of protein synthesis during the activation of human lymphocytes by phytohaemagglutinin (PHA), it became necessary to determine whether an effect which occurred following treatment with actinomycin D (AMD) was secondary to the action of the drug on transcription, or resulted from a direct effect on translation. Using enucleated lymphocytes, we have shown that AMD has no effect on protein synthesis in the absence of the cell nucleus and conclude that AMD interferes with protein synthesis by its effect on transcription of RNA.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reich, E., Franklin, R. M., Shatkin, A. J. & Tatum, E. L. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci U.S.A. 48, 1238–1245 (1962).
Penman, S., Scherrer, K., Becker, Y. & Darnell, J. E. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 49, 654–662 (1963).
Craig, N., Kelley, D. E. & Perry, R. P. Biochim. biophys. Acta 246, 493–498 (1971).
Singer, R. H. & Penman, S. Nature 240, 100–102 (1972).
Craig, N. J. cell. Physiol. 82, 133–150 (1973).
Greenberg, J. R. Nature 240, 102–104 (1972).
Murphy, W. & Attardi, G. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 70, 115–119 (1973).
Wigler, M. H. & Weinstein, I. B. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 63, 669–674 (1975).
Nathans, D. Fedn Proc. 23, 984–989 (1964).
McKeehan, W. & Hardesty, B. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 36, 625–630 (1969).
Berger, S. L. & Cooper, H. L. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 72, 3873–3877 (1975).
Kay, J. E., Leventhal, B. G. & Cooper, H. L. Expl Cell Res. 54, 94–100 (1969).
Perry, R. P. & Kelley, D. E. J. cell. Physiol. 72, 235–246 (1968).
Cooper, H. L. Meth. Enzymol. 32, 633–636 (1974).
Burton, K. Meth. Enzymol. 12 b, 163–166 (1968).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
COOPER, H., BRAVERMAN, R. The mechanism by which actinomycin D inhibits protein synthesis in animal cells. Nature 269, 527–529 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1038/269527a0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/269527a0
This article is cited by
-
Redefining bioactive small molecules from microbial metabolites as revolutionary anticancer agents
Cancer Gene Therapy (2024)
-
Immunoglobulin gene expression in a coupled transcription/translation system from mouse plasmacytoma cell-free extracts
Biochemical Genetics (1981)
-
Stability of polyadenylated mRNA in pig lymphocytes
Bioscience Reports (1981)
-
Changes in intracellular ribonuclease activity in the rat liver during inhibition of protein synthesis by cycloheximide
Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine (1980)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.