Abstract
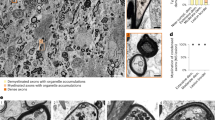
EXPERIMENTAL allergic encephalomyelitis (EAE) and experimental allergic neuritis (EAN) are autoimmune demyelinating conditions brought about by sensitisation to central and peripheral myelin extracts, respectively. The lesions are the result of a delayed hypersensitivity-type reaction which can be passively transferred by lymphoid cells but not by sera1–4. Demyelination occurs in areas of cellular infiltrate. This process is mediated in part by mononuclear cells which invade and phagocytise the target myelin tissue. A vesicular transformation of myelin sheaths is known to occur in close proximity to these invading mononuclear cells5–7. The nature of the myelin vesiculation is unclear; however, these changes have been emphasised as a characteristic accompaniment of autoimmune demyelination in experimental animals and in human peripheral nerve disease8. The present study reports the occurrence of the same type of myelin alteration in excised rat peripheral nerve fibres when incubated under conditions which promote a selective influx of calcium ions into the tissues.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Paterson, P. Y. J. exp. Med. 111, 119–136 (1960).
Stone, S. H. Science 134, 619–620 (1961).
Åstrom, K. E. & Waksman, B. H. J. path. Bact. 83, 89–106 (1962).
Levine, S. & Wenk, E. J. J. Immun. 99, 1277–1285 (1967).
Lampert, P. W. J. Neuropath. exp. Neurol. 24, 371–385 (1965); Acta Neuropath. 9, 99–126 (1967); Lab Invest. 20, 127–138 (1969).
Ballin, R. H. M. & Thomas, P. K. J. neurol. Sci. 8, 1–18 (1968).
Wisniewski, H., Prineas, J. & Raine, C. S. Lab invest. 21, 105–118 (1969).
Dal Canto, M. C., et al., J. neurol. Sci. 24, 313–319 (1975).
Schlaepfer, W. W. Brain Res. 78, 71–81 (1974).
Reed, P. W. & Lardy, H. A. J. biol. Chem. 247, 6970–6977 (1972).
Pfeiffer, D. R., Reed, P. W. & Lardy, H. A. Biochemistry 13, 4007–4014 (1974).
Deber, C. M. & Pfeiffer, D. R. Biochemistry 15, 132–141 (1976).
Blank, W. F., Bunge, M. B. & Bunge, R. P. Brain Res. 67, 503–518 (1974).
Robertson, J. D. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 4, 349–364 (1958).
Hemminki, K. Biochim. biophys. Acta 363, 202–210 (1974).
Shlatz, L. & Marinetti, G. V. Biochim. biophys. Acta 290, 70–83 (1972).
Hall, S. M. & Gregson, N. A. J. Cell Sci. 9, 769–789 (1971).
Webster, H. deF., Spiro, D., Waksman, B. & Adams, R. D. J. Neuropath. exp. Neurol. 20, 5–34 (1961).
Masurovsky, E. B., Bunge, M. B. & Bunge, R. P. J. Cell Biol. 32, 497–518 (1967).
Lampert, P. W. & Schochet, S. S. J. Neuropath. exp. Neurol. 27, 527–544 (1968).
Ballin, R. H. M. & Thomas, P. K. Acta Neuropath. 14, 237–249 (1969).
Wisniewski, H. & Raine, C. S. Lab. Invest. 25, 73–80 (1971).
Waksman, B. H. & Namoa, Y. Cell Immun. 21, 161–176 (1976).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
SCHLAEPFER, W. Vesicular disruption of myelin simulated by exposure of nerve to calcium ionophore. Nature 265, 734–736 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1038/265734a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/265734a0
This article is cited by
-
Real-time measurement of free Ca2+ changes in CNS myelin by two-photon microscopy
Nature Medicine (2007)
-
Electrolyte-induced demyelination in rats
Acta Neuropathologica (1994)
-
Purification of calcium-activated neutral proteinase (CANP) from purified myelin of bovine brain white matter
Neurochemical Research (1988)
-
Lysophosphatidyl choline-induced demyelination
Acta Neuropathologica (1988)
-
Myelopathy induced by lactic acid
Acta Neuropathologica (1987)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.