Abstract
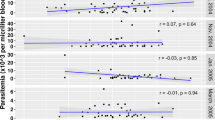
PROTECTIVE antibodies are involved in acquired immunity to malaria parasites1. Sera from monkeys immune to Plasmodium knowlesi contain antibodies which depress multiplication of the parasite in vitro2 by, it is believed, inhibiting the invasion of red cells by merozoites3,4. Antibodies inhibitory to parasites of a specific antigenic variant are of a higher titre than inhibitory antibodies which cross-react with different antigenic variants5. We have attempted to extend these findings to natural human infections with P. falciparum in The Gambia, West Africa, where P. falciparum malaria is hyperendemic. The entire population is exposed to infection and an effective immunity is only acquired over 4–5 yr (ref. 6). Immunity to P. falciparum can be passively transferred with IgG from immune Gambian adults7.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown, I. N., Adv. Immun., 11, 267 (1969).
Cohen, S., Butcher, G. A., and Crandall, R. B., Nature, 223, 368 (1969).
Miller, L. H., Aikawa, M., and Dvorak, J. A., J. Immun., 114, 1237 (1975).
Butcher, G. A., and Cohen, S., Trans. R. Soc. trop. Med. Hyg., 64, 470 (1970).
Butcher, G. A., and Cohen, S., Immunology, 23, 503 (1972).
McGregor, I. A., Gilles, H., Walters, J. H., Davies, A. H., and Pearson, F. A., Br. med. J., 2, 686 (1956).
Cohen, S., McGregor, I. A., and Carrington, S., Nature, 192, 733 (1961).
Phillips, R. S., Rahman, A. K., and Wilson, R. J. M., Trans. R. Soc. trop. Med. Hyg., 69, 432 (1975).
McGregor, I. A., and Wilson, R. J. M., Trans. R. Soc. trop. Med. Hyg., 65, 136 (1971).
Phillips, R. S., Trigg, P. I., Scott-Finnigan, T. J., and Bartholomew, R. K., Parasitology, 65, 525 (1972).
Mitchell, G. H., Butcher, G. A., Voller, A., and Cohen, S., Parasitology, 72, 149 (1976).
Wilson, R. J. M., and Bartholomew, R. K., Parasitology, 71, 183 (1975).
McChesney, E. W., Banks, W. F., Jr, and McAuliff, J. P., Antibiotics Chemother., 12, 583 (1962).
Wilson, R. J. M., McGregor, I. A., Hall, P., Williams, K., and Bartholomew, R., Lancet ii, 201 (1969).
Carter, R., and McGregor, I. A., Trans R. Soc. trop. Med. Hyg., 67, 830 (1973).
Pavanand, K., Permpanich, B., Chuanak, N., and Sookto, P., J. Parasit., 60, 537 (1974).
Coleman, R. M., Renericca, N. J., Stout, J. P., Brissette, W. H., and Smith, D. M., Immunology, 29, 49 (1975).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
WILSON, R., PHILLIPS, R. Method to test inhibitory antibodies in human sera to wild populations of Plasmodium falciparum. Nature 263, 132–134 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1038/263132a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/263132a0
This article is cited by
-
Plasmodium falciparum strain-specific antibody blocks binding of infected erythrocytes to amelanotic melanoma cells
Nature (1983)
-
Erythrocytes deficient in glycophorin resist invasion by the malarial parasite Plasmodium falciparum
Nature (1982)
-
Target antigens of purified human immunoglobulins which inhibit growth of Plasmodium falciparum in vitro
Nature (1982)
-
Inhibition of P. falciparum growth in human erythrocytes by monoclonal antibodies
Nature (1981)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.