Abstract
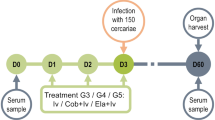
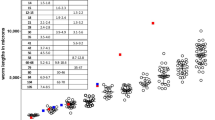
HYDATID disease is a cyclozoonotic infection of man and certain other mammals which results from the cystic intermediate stage of the cestodes Echinococcus granulosus and E. multilocularis. The growth of these two species of parasites is basically similar except that the latter undergoes tumour-like metastatic dissemination. The present knowledge about immunity to this disease is incomplete; however, recent reports from this laboratory1–3 have defined certain basic aspects of the immune response to secondary echinococcosis. These studies have demonstrated the rapid in vitro lysis of protoscoleces by the complement proteins when these are activated by surface immunoglobulins acquired in vivo by the larvae within the cysts. We also have evidence (unpublished data) that host serum proteins, including IgG and IgM immunoglobulins, are found within the cyst tissues of E. multilocularis, as previously demonstrated in E. granulosus4; Rau and Tanner3 have demonstrated that heat-inactivated serum from infected hosts is cytotoxic to the protoscolices of E. multilocularis in vitro. Based on these results, we now hypothesise that anti-Echinococcus antibodies in the serum of infected animals can “recognise” antigenic sites on the parasite but are unable to reach these sites in sufficient quantities under the natural conditions of the infection; given the opportunity of contact, these cytotoxic antibodies would subject the parasites to the deleterious effects of the immune response. We now present results which show that cysts of E. granulosus are killed when the fluid within these cysts is replaced with the fresh serum of infected animals and suggest this immunotherapy as a novel treatment of hydatid disease. Similar replacement of the fluid of E. multilocularis cysts also successfully killed the treated cysts; but the cyst mass continued to grow by surface budding.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kassis, A. I., and Tanner, C. E., Int. J. Parasit., 6, 25–35 (1976).
Kassis, A. I., Goh, S. L., and Tanner, C. E., Int. J. Parasit., 6, 199–211 (1976).
Rau, M. E., and Tanner, C. E., Int. J. Parasit., 6, 195–198 (1976).
Varela-Diaz, V. M., and Coltorti, E. A., J. Parasit., 59, 484–488 (1973).
Capron, A., Biguet, J., Vernes, A., and Afchain, D., Path. Biol., 16, 121–138 (1968).
Damian, R. T., Am. Nat., 98, 129–149 (1964).
Dineen, J. K., Nature, 197, 471–472 (1963).
Rickard, M. D., Z. Parasit., 44, 203–209 (1974).
Smithers, S. R., and Terry, R. J., Adv. Parasit., 7, 41–93 (1969).
Sprent, J. F. A., in The Evolution of Living Organisms (edit. by Leeper, G. W.), 149–165. (University Press, Melbourne, 1962).
Varela-Diaz, V. M., Gemmell, M. A., and Williams, J. F., Expl Parasit., 32, 96–101 (1973).
Varela-Diaz, V. M., Williams, J. F., Coltorti, E. A., and Williams, C. S. F., J. Parasit., 60, 608–612 (1974).
Chordi, A., and Kagan, I. G., J. Parasit., 51, 63–71 (1965).
Coltorti, E. A., and Varela-Diaz, V. M., J. Parasit., 58, 753–756 (1972).
Noble, E. R., and Noble, G. A., in Parasitology: the Biology of Animal Parasites, 3rd ed., 244–249 (Lea and Febiger, Philadelphia, 1971).
Marcial-Rojas, R. A., in Pathology of Protozoal and Helminthic Diseases, 635–657 (Robert E. Krieger, Huntington, New York, 1975).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
KASSIS, A., TANNER, C. Novel approach to the treatment of hydatid disease. Nature 262, 588–589 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1038/262588a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/262588a0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.