Abstract
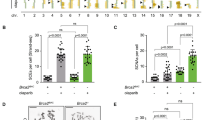
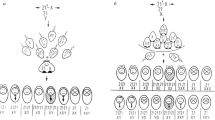
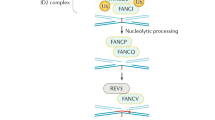
THE nature of the involvement of DNA repair in the formation of sister chromatid exchanges (SCEs) and their connection with chromosome aberrations is unknown. Some mutagens that damage DNA, including ultraviolet light and mitomycin C, considerably increase the incidence of SCEs1–6, whereas other agents, such as X rays6–8, nitrosoguanidine2 and 8-ethoxycaffeine5 cause only a slight increase, although they are potent inducers of lesions at the DNA and chromosome levels. Hamster cells infected with adenovirus 12 show no increased SCEs in spite of extensive fragmentation of the entire chromosome complement (our unpublished results). These findings suggest that the mechanism of formation of SCEs is not unitary. Whereas the mechanism of induction of SCEs could be studied by analysing their frequency after application of agents with known action on DNA, spontaneously occurring SCEs can be studied in cells with defects in the DNA repair system. This report deals chiefly with the frequency of spontaneous SCEs in several strains of xeroderma pigmenosum (XP) fibroblasts which show various levels of repair capacities, in Fanconi's anaemia (FA) cells and in control human cells at different stages of ageing.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rommelaere, J., Suskind, M., and Errera, M., Chromosoma, 41, 243–257 (1973).
Kato, H., Expl Cell Res., 82, 383–390 (1973); 85, 239–247 (1974), 89, 416–420 (1974); Nature, 249, 552–553 (1974); 251, 70–72 (1974).
Kato, H., and Shimada, H., Mutat. Res., 28, 459–464 (1975).
Latt, S. A., Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 71, 3162–3166 (1974).
Kihlman, B. A., Chromosoma, 51, 11–18 (1975).
Perry, P., and Evans, H. J., Nature, 258, 121–125 (1975).
Marin, G., and Prescott, D. M., J. Cell Biol., 21, 159–167 (1964).
Gatti, M., and Olivieri, G., Mutat. Res., 17, 101–112 (1973).
Stich, H. F., and San, R. H. C., Mutat. Res., 13, 279–282 (1971).
Stich, H. F., San, R. H. C., Miller, J. A., and Miller, E. C., Nature new Biol., 238, 9–10 (1972).
Stich, H. F., Stich, W., and Lam, P., Nature, 250, 599–601 (1974).
Wolff, S., and Perry, P., Chromosoma, 48, 341–353 (1974).
Setlow, R. B., Regan, J. D., German, J., and Carrier, W. L., Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 64, 1035–1041 (1969).
Lehmann, A. R., et al., Proc. natn. Acad. U.S.A., 72, 219–223 (1975).
Sasaki, M. S., Nature, 257, 501–503 (1975).
Fujiwara, Y., and Tatsumi, M., Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun., 66, 592–598 (1975).
Poon, P. K., O'Brien, R. O., and Parker, J. W., Nature, 250, 223–225 (1974).
Wolff, S., Bodycote, J., Thomas, G. H., and Cleaver, J. E., Genetics, 81, 349–355 (1975).
Chaganti, R. S. K., Schonberg, S., and German, J., Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 71, 4508–4512 (1974).
Saksela, E., and Moorhead, P. S., Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 50, 390–395 (1963).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
KATO, H., STICH, H. Sister chromatid exchanges in ageing and repair-deficient human fibroblasts. Nature 260, 447–448 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1038/260447a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/260447a0
This article is cited by
-
Reduced FANCD2 influences spontaneous SCE and RAD51 foci formation in uveal melanoma and Fanconi anaemia
Oncogene (2013)
-
SCE variability in lymphocytes and fibroblasts
Human Genetics (1988)
-
Sister chromatid exchange in vivo, chromosomal characterization and NORs activity of leukemia cells during 5FU-treatments
Theoretical and Applied Genetics (1987)
-
Failure of diepoxybutane to enhance sister chromatid exchange levels in Fanconi's anemia patients and heterozygotes
Human Genetics (1983)
-
Proliferative kinetics and mitomycin C-induced chromosome damage in Fanconi's anemia lymphocytes
Human Genetics (1983)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.