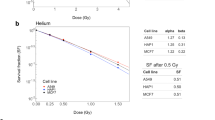
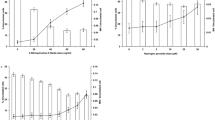
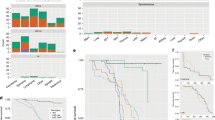
Abstract
MAMMALIAN cell cultures are used to estimate mutation induction by radiation and chemical agents in the belief that they will provide relevant data for assessing risk to man and insights into the mechanisms of mutagenesis in eukaryotic cells. It might be anticipated that these estimates would be obtained with the precision characteristic of studies with microorganisms, but very large variations in the response of mammalian cells to ionising radiation have been reported, even by workers using the same cell line and method of mutant estimation1,2. Also there has been no unequivocal demonstration of radiation-induced mutation in freshly isolated diploid (homonuclear) cell cultures3,4. We consider that these discrepancies arise primarily from methodological difficulties, and report here the similarity of mutation frequency induced by ionising radiation in an established (heteronuclear) cell line used in many previous studies (Chinese hamster V79) and in human diploid cells (early passage foetal lung cells). The mutational response of the two cell types can be considered as identical when the differences in sensitivity to the inactivating effects of radiation are taken into account.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bridges, B. A., and Huckle, J., Mutat. Res., 10, 141–151 (1970).
Chu, E. H. Y., Mutat. Res., 11, 23–34 (1971).
Albertini, R. J., and DeMars, R., Mutat. Res., 18, 199–224 (1973).
Cox, R., and Masson, W. K., Nature, 252, 308–310 (1974).
Simons, J. W. I. M., Mutat. Res., 25, 219–227 (1974).
Gillen, F. D., Roufa, D. J., Beaudet, A. L., and Casky, C. T., Genetics, 72, 239–252 (1972).
Fujimoto, W. Y., Subak-Sharpe, J. H., and Seegmiller, J. E., Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 68, 1516–1519 (1971).
Cox, R., and Masson, W. K., Int. J. radiat. Biol., 26, 193–196 (1974).
Cox, R., Masson, W. K., and Bance, D. A., Lab. Pract., 22, 733–734 (1973).
Taylor, A. M. R., et al., Nature, 258, 000–000 (1975).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
THACKER, J., Cox, R. Mutation induction and inactivation in mammalian cells exposed to ionising radiation. Nature 258, 429–431 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1038/258429a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/258429a0
This article is cited by
-
Comparison of dose-dependent enhancing effects of ?-ray irradiation on urethan-induced lung tumorigenesis in athymic nude (nu/nu) mice and euthymic (nu/+) littermates
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (1996)
-
Genetische Wirkungen kleiner Strahlendosen
Naturwissenschaften (1987)
-
X-ray sensitivity and DNA synthesis in synchronous culture ofPlasmodium falciparum
Zeitschrift f�r Parasitenkunde Parasitology Research (1985)
-
Inhibition of repair of premutational lesions in plateau phase Chinese hamster cells exposed to gamma radiation
Radiation and Environmental Biophysics (1983)
-
Do radiation-induced thioguanine-resistant mutants of cultured mammalian cells arise by HGPRT gene mutation or X-chromosome rearrangement?
Nature (1978)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.