Abstract
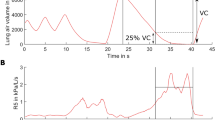
THERE have been few studies of the effects of common air pollutants on man during light exercise, and even fewer of the effects of combinations of pollutants. We have found that low concentrations of ozone and sulphur dioxide together have much greater effect on pulmonary function than when either is breathed separately. Reduction of particulate pollution in the ambient air of cities with a high traffic density creates favourable conditions for ozone formation (0.15 p.p.m. ozone has been recorded in London, England1) and subsequent interaction with ambient SO2. In environments where oxidants are already a major problem, air pollution will be compounded by energy-saving measures which encourage the use of heavy (sulphur-containing) fuels. Thus, either increased levels of photochemical pollutants in an atmosphere with already high SO2 levels or increases in SO2 concentrations in the presence of oxidants may result in a potential health hazard.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Derwent, R. G., and Stewart, H. N., Nature, 241, 342 (1973).
Bates, D. V., et al., Can. med. Ass. J., 103, 833–837 (1970).
Hazucha, M., Silverman, F., Parent, C., Field, S., and Bates, D. V., Archs environ. Hlth, 27, 183–188 (1973).
Macdowall, F. D. H., and Cole, R. F. W., Atmos. Environ., 5, 553–559 (1971).
Lebowitz, M. D., Bendheim, P., Cristea, G., Markovitz, D., Misiaszek, J., Staniec, M., and Van Wych, D., Am. Rev. resp. Dis., 109, 262–273 (1974).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
HAZUCHA, M., BATES, D. Combined effect of ozone and sulphur dioxide on human pulmonary function. Nature 257, 50–51 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1038/257050a0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/257050a0
This article is cited by
-
Association between ambient air pollutant interaction with kidney function in a large Taiwanese population study
Environmental Science and Pollution Research (2023)
-
A respiratory alert model for the Shenandoah Valley, Virginia, USA
International Journal of Biometeorology (2013)
-
Effect of exposure to 0.5 ppm hydrogen cyanide singly or combined with 200 ppm carbon monoxide and/or 5 ppm nitric oxide on coronary arteries, aorta, pulmonary artery, and lungs in the rabbit
International Archives of Occupational and Environmental Health (1979)
-
Do present levels of air pollution outdoors affect respiratory health?
Nature (1978)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.