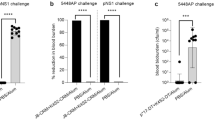
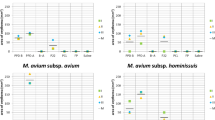
Abstract
EXPERIMENTAL allergic encephalomyelitis (EAE) is an autoimmune demyelinating disease induced by sensitisation to whole central nervous system (CNS) tissue homogenates, to myelin basic protein (BP) or to peptide regions derived from BP1–4. One such region, peptide E, was isolated from the pepsin digest of the BP and induces EAE in guinea pigs3,5. The shortest segment of peptide E which induces EAE, H-Phe-Ser-Trp-Gly-Ala-Glu-Gly-Gln-Lys-OH (peptide S3), has been synthesised by the Merrifield procedure6. Studies with analogous synthetic peptides with single amino acid residue substitutions have shown that the linearly spaced array of tryptophan, glutamine and lysine is needed to induce EAE6. We have now determined the minimum snbstitution in the amino acid sequence of peptide S3 necessary to destroy encephalitogenicity and to preserve the sequence for delayed hypersensitivity (DTH), also reported for peptide S37. The sequence requirement for induction of EAE is not restricted to tryptophan, glutamine and lysine, and certain analogous peptides retain the ability to induce and elicit DTH unaccompanied by signs of EAE.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Paterson, P. Y., Adv. Immun., 5, 131–208 (1966).
Eylar, E. H., Salk, J., Beveridge, G. C., and Brown, L. V., Archs Biochem. Biophys., 132, 34–48 (1969).
Hashim, G. A., and Eylar, E. H., Archs Biochem. Biophys., 129, 645–654 (1969).
Shapira, R., Chou, F. C. H., McKneally, S., Urban, E., and Kibler, R. F., Science, 173, 736–738 (1971).
Eylar, E. H., and Hashim, G. A., Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 61, 644–650, (1968).
Westall, F. C., Robinson, A. R., Caccam, J., Jackson, J., and Eylar, E. H., Nature, 229, 22–24 (1971).
Hashim, G. A., Hwang, F., and Schilling, F. J., Archs Biochem. Biophys., 156, 298–309 (1973).
Gutte, B., and Merrifield, R. B., J. biol. Chem., 246, 1922–1941 (1971),
Hashim, G. A., and Sharpe, R., Immunochemistry, 11, 633–640 (1974).
Eylar, E. H., Brostoff, S., Hashim, G. A., Caccam, J., and Burnett, P., J. biol. Chem., 246, 5770–5784 (1971).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
HASHIM, G., SHARPE, R. Non-encephalitogenic synthetic analogues of the determinant for allergic encephalomyelitis in guinea pigs. Nature 255, 484–485 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1038/255484a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/255484a0
This article is cited by
-
Failure of myelin basic protein to prevent or suppress experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in guinea pigs
Neurochemical Research (1980)
-
Precise determination of protein antigenic structures has unravelled the molecular immune recognition of proteins and provided a prototype for synthetic mimicking of other protein binding sites
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (1980)
-
Peptide length requirement for experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in guinea pigs
Neurochemical Research (1980)
-
Synthesis and physicochemical and encephalitogenic properties of analogs of a tryptophan-containing fragment of myelin protein
Chemistry of Natural Compounds (1977)
-
Non-encephalitogenic antigen-induced suppression and reversal of allergic encephalomyelitis
Nature (1975)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.