Abstract
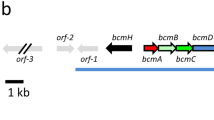
IN eubacteria, many characteristics1–3 including resistance to antibiotics and other agents are plasmid-determined. In streptomycetes there are indications that plasmid genes are involved in the production of certain antibiotics: kasugamycin and aureothricin by Streptomyces kasugaensis4 oxytetracycline by S. rimosus5 and turimycin by S. hygroscopicus6. An increased proportion of antibiotic non-producing strains is found after treatment of antibiotic producers with agents known to cause plasmid loss in eubacteria; in S. rimosus, crosses provided additional evidence that extrachromosomal genes are involved in antibiotic production. In all three species, the cause of antibiotic non-production, for example whether it involved an interruption of the biosynthetic pathway or a defect in the liberation of antibiotic into the medium, was unknown. We report here that both the production of and resistance to the same antibiotic in S. coelicolor A3(2) are determined by genes borne on the plasmid SCP1.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Meynell, G. G., Bacterial Plasmids (Macmillan, London, 1972).
Wheelis, M. L., A. Rev. Microbiol. (in the press).
Pares, R., Guinea, J., Hernandez, S., Valoix, J., and Jofre, J., J. Bact., 119, 9 (1974).
Okanishi, M., Ohta, T., and Umezawa, H., J. Antibiotics, 23, 45 (1970).
Boronin, A. M., Borisoglebskaya, A. N., and Sadovnikova, L. G., Abstracts of the Second International Symposium on the Genetics of Industrial Microorganisms, 103 (Academic, New York and London, 1974).
Noack, D., Kaeler, R., Beck, M., and Geuther, R., Abstracts of the Second International Symposium on the Genetics of Industrial Microorganisms, 104 (Academic, New York and London, 1974).
Hopwood, D. A., Chater, K. F., Dowding, J. E., and Vivian, A., Bact. Rev., 37, 371 (1973).
Vivian, A., J. gen. Microbiol., 69, 353 (1971).
Vivian, A., and Hopwood, D. A., J. gen. Microbiol., 64, 101 (1970).
Hopwood, D. A., and Wright, H. M., J. gen. Microbiol., 79, 331 (1973).
Hopwood, D. A., and Wright, H. M., Proceedings of the Second International Symposium on the Genetics of Industrial Microorganisms (Academic, New York and London, in the press).
Hopwood, D. A., and Wright, H. M., J. gen. Microbiol., 77, 187 (1973).
Delic, V., Pigac, J., and Sermonti, G., J. gen. Microbiol., 55, 103 (1969).
Benveniste, R., and Davies, J., Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 70, 2276 (1973).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
KIRBY, R., WRIGHT, L. & HOPWOOD, D. Plasmid-determined antibiotic synthesis and resistance in Streptomyces coelicolor. Nature 254, 265–267 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1038/254265a0
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/254265a0
This article is cited by
-
Exploitation of the Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) genome sequence for discovery of new natural products and biosynthetic pathways
Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology (2014)
-
Giant linear plasmids in Streptomyces: a treasure trove of antibiotic biosynthetic clusters
The Journal of Antibiotics (2011)
-
Analysis of developmental gene conservation in the Actinomycetales using DNA/DNA microarray comparisons
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek (2011)
-
The genome of Streptomyces rimosus subsp. rimosus shows a novel structure compared to other Streptomyces using DNA/DNA microarray analysis
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek (2008)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.