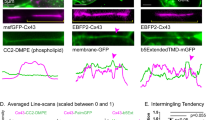
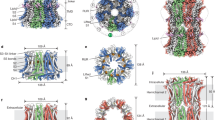
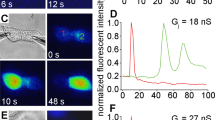
Abstract
MANY kinds of cells are coupled by junctions consisting of membrane channels through which molecules of a certain size range can flow freely from one cell interior to another1. It has been proposed that the permeability of the junctional channels depends on the concentration of free ionised calcium in cytoplasm ([Ca2+]i) (ref. 2). This hypothesis is supported by two classes of experiments. In one, the interior of a coupled cell system is allowed ito exchange freely with a known [Ca2+] in the exterior, through a hole in the (non-junctional) membrane; junctional conductance is reduced (uncoupling) when the [Ca2+]i is above 5–8 × 10−5 M (ref. 3). In the other class, uncoupling ensues when the (closed) cell system is treated with inhibitors of energy metabolism or with Ca2+ ionophores5, or on exposure for long periods to Ca,Mg-free medium or to Li medium6; in these conditions a rise in [Ca2+]i, may be expected because of known properties of cellular Ca metabolism7,8. Here, we demonstrate the changes in [Ca2+]i together with those in coupling in three of these conditions, using aequorin to display the distribution of Ca2+ in the cell. It will be shown that the uncoupling is, indeed, in each case associated with a rise in [Ca2+]. Furthermore, by local injection of Ca2+ into the cells, it will be shown that uncoupling ensues when the rise in [Ca2+]i occurs at the junction, but not when it occurs at other regions in the cell.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Loewenstein, W. R., Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci., 137, 441–472 (1966).
Loewenstein, W. R., J. Colloid Sci., 25, 34–46 (1967).
Oliveira-Castro, G. M., and Loewenstein, W. R., J. Membrane Biol., 5, 51–77 (1971).
Politoff, A. L., Socolar, S. J., and Loewenstein, W. R., J. gen. Physiol., 53, 498–515 (1969).
Rose, B., and Loewenstein, W. R., Fedn Proc., 33, 1340 (1974).
Rose, B., and Loewenstein, W. R., J. Membrane Biol., 5, 20–50 (1971).
Lehninger, A. L., Carafoli, E., and Rossi, C. J., Adv. Enzymol., 29, 259–322 (1967).
Baker, P. F., Prog. Biophys. biophys. Chem., 24, 177–322 (1972).
Shimomura, O., and Johnson, F. H., Biochemistry, 8, 3991–3997 (1967).
Azzi, A., and Chance, B., Biochim. biophys. Acta, 189, 141–151 (1969).
Ashley, C. C., and Ridgway, E. B., J. Physiol., Lond., 209, 105–130 (1970).
Baker, P. F., Hodgkin, A. L., and Ridgway, E. B., J. Physiol., Lond., 218, 709–755 (1971).
Harris, E. J., Biochim. biophys. Acta, 23, 80–87 (1957).
Hodgkin, A. L., and Keynes, R. D., J. Physiol., Lond., 138, 253–281 (1957).
Vasington, F. D., Gazzotti, P., Tiozzo, R., and Carafoli, E., Biochim. biophys. Acta, 256, 43–58 (1972).
Baker, P. F., Blaustein, M. P., Hodgkin, A. L., and Steinhardt, R. A., J. Physiol., Lond., 200, 431–458 (1969).
Carafoli, E., Tiozzo, R., Lugli, G., Crovetti, F., and Kratzing, C., J. Mol. Cell Cardiol., 6, 361–378 (1974).
Rose, B., and Loewenstein, W. R., J. Membrane Biol. (in the press).
Romero, P. J., and Whittam, R., J. Physiol., Lond., 214, 481–507 (1971).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
ROSE, B., LOEWENSTEIN, W. Permeability of cell junction depends on local cytoplasmic calcium activity. Nature 254, 250–252 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1038/254250a0
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/254250a0
This article is cited by
-
Generation of myocyte agonal Ca2+ waves and contraction bands in perfused rat hearts following irreversible membrane permeabilisation
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Connexin43 and connexin50 channels exhibit different permeability to the second messenger inositol triphosphate
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Regulation of Cx45 hemichannels mediated by extracellular and intracellular calcium
Pflügers Archiv - European Journal of Physiology (2012)
-
Unusual Slow Gating of Gap Junction Channels in Oocytes Expressing Connexin32 or Its COOH-Terminus Truncated Mutant
Journal of Membrane Biology (2007)
-
Opposite Cx32 and Cx26 Voltage-Gating Response to CO2 Reflects Opposite Voltage-Gating Polarity
The Journal of Membrane Biology (2004)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.