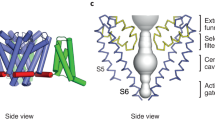
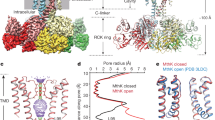
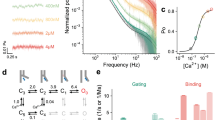
Abstract
IN most cases where the action potential of nerve cells has been studied the initial inward current has been found to be carried by sodium ions. More recently calcium has been shown to be an important charge carrier in the inward current of vertebrate cardiac muscle, vertebrate smooth muscle and many nerve cell bodies1. It is therefore of interest to know whether the properties of the calcium conductance mechanism are similar to those which have been described for sodium conductance. An important property of the sodium conductance mechanism is its reduction or ‘inactivation’ by a conditioning depolarisation prior to an action potential and its increase by conditioning hyperpolarisation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reuter, H., Prog. Biophys. molec. Biol., 26, 1–43 (1973).
Hodgkin, A. L., and Huxley, A. F., J. Physiol., Lond., 116, 497–506 (1952).
Geduldig, D., and Gruener, R., J. Physiol., Lond., 211, 217–244 (1970).
Neher, E., J. gen. Physiol., 58, 36–53 (1971).
Kerkut, G. A., and Meech, R. W., Comp. Biochem. Physiol., 19, 819–832 (1966).
Klee, M. R., Faber, D. S., and Heiss, W. D., Science, 179, 1133–1135 (1973).
Frankenhauser, B., and Hodgkin, A. L., J. Physiol., Lond., 137, 218–244 (1957).
Meech, R. W., and Standen, N. B., J. Physiol., Lond., (in the press).
Vassort, G., J. Physiol., Lond., (in the press).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
STANDEN, N. Properties of a calcium channel in snail neurones. Nature 250, 340–342 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1038/250340a0
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/250340a0
This article is cited by
-
Effects of divalent cation ionophores on the neuron membrane of the crayfish
The Journal of Membrane Biology (1979)
-
Action of intracellular calcium on the inward calcium current
Neurophysiology (1978)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.