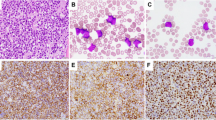
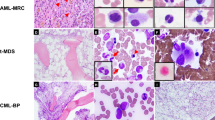
Abstract
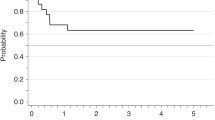
Most cases of acute leukemia can be assigned to the myeloid, B or T lineage. In a few cases, definitive assignment cannot be achieved because blasts express antigens of more than one lineage. A subset of these, referred to as acute bilineal leukemias (aBLLs), is characterized by the presence of more than one population of blasts, each comprising a single lineage. We identified 19 cases of aBLL, including 10 mixed T and myeloid (T-My) and nine mixed B and myeloid (B-My); no mixed B and T cases were identified. Cytogenetic data were available for 16 patients. Three of seven patients with B-My had a t(9;22)(q34q11.2), two had 11q23 translocations and one had del(9). Two of nine patients with T-My had 2p13 translocations; five had other unrelated abnormalities. Of 16 patients with outcome data, only six achieved complete remission and only two remain free of disease 2.5 and 4.5 years after chemotherapy or stem cell transplantation. aBLL is a rare disease that combines B or T and myeloid blasts. Cytogenetic abnormalities of t(9;22) and 11q23 are common in, and may be restricted to, B-My cases, while T-My cases have frequent but generally non-recurring abnormalities. Both types of aBLL are associated with poor outcome.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett JM, Catovsky D, Daniel MT, Flandrin G, Galton DAG, Gralnick HR et al. Proposed revised criteria for the classification of acute myeloid leukemia: a report of the French–American–British cooperative group. Ann Intern Med 1985; 103: 620–625.
Weir EG, Borowitz MJ . Flow cytometry in the diagnosis of acute leukemia. Semin Hematol 2001; 38: 124–138.
Bene MC, Castoldi G, Knapp W, Ludwig WD, Matutes E, Orfao A et al. Proposals for the immunologic classification of acute leukemias. European Group for the Immunologic Characterization of Leukemias (EGIL). Leukemia 1995; 9: 1783–1786.
Brunning RD, Head D, Matutes E, Vardiman J, Borowitz M, Bennett J et al. Acute leukemias of ambiguous lineage. In: Jaffe ES, Harris NL, Stein H, Vardiman JW (eds). World Health Organization Classification of Tumours. Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2001, pp 106–107.
Gale RP, Ben Bassat I . Hybrid acute leukaemia. Br J Haematol 1987; 65: 261–264.
Schmitt-Graff A, Jurgens H, Reifenhauser A, Schwamborn D, Gobel U . Childhood biphenotypic leukemia: detection of mixed lymphoid and myeloid populations in bone marrow specimens. Hum Pathol 1988; 19: 651–656.
Mirro J, Kitchingman GR, Williams DL, Murphy SB, Zipf TF, Stass SA . Mixed lineage leukemia: the implications for hematopoietic differentiation. Blood 1986; 68: 597–599.
Jinnai I, Kusumoto S, Shiomi Z, Bessho M, Saitoh M, Hirashima K et al. Transformation of bilineal hybrid acute leukemia to acute lymphoid leukemia: a case report with serial analyses of cytogenetics and gene rearrangement. Am J Hematol 1990; 35: 118–124.
Matutes E, Morilla R, Farahat N, Carbonell F, Swansbury J, Dyer M et al. Definition of acute biphenotypic leukemia. Haematologica 1997; 82: 64–66.
Carbonell F, Swansbury J, Min T, Matutes E, Farahat N, Buccheri V et al. Cytogenetic findings in acute biphenotypic leukaemia. Leukemia 1996; 10: 1283–1287.
Thalhammer-Scherrer R, Mitterbauer G, Simonitsch I, Jaeger U, Lechner K, Schneider B et al. The immunophenotype of 325 adult acute leukemias. Am J Clin Path 2002; 117: 380–389.
Killick S, Matutes E, Powles RL, Hamblin M, Swansbury J, Treleaven JG et al. Outcome of biphenotypic acute leukemia. Haematologica 1999; 84: 699–706.
Hayashi Y, Sugita K, Nakazawa S, Abe T, Kojima S, Inaba T et al. Karyotypic patterns in acute mixed lineage leukemia. Leukemia 1990; 4: 121–126.
Sulak LE, Clare CN, Morale BA, Hansen KL, Montiel MM . Biphenotypic leukemia in adults. Am J Clin Pathol 1990; 94: 54–58.
Buccheri V, Matutes E, Dyer MJS, Catovsky D . Lineage commitment in biphenotypic acute leukemia. Leukemia 1993; 7: 919–927.
Legrand O, Perrot JY, Simonin G, Baudard M, Cadiou M, Blanc C et al. Adult biphenotypic acute leukaemia: an entity with poor prognosis which is related to unfavourable cytogenetics and P-glycoprotein over-expression. Br J Haematol 1998; 100: 147–155.
Rubio MT, Dhedin N, Boucheix C, Bourhis JH, Reman O, Boiron JM et al. Adult T-biphenotypic acute leukaemia: clinical and biological features and outcome. Br J Haematol 2003; 123: 842–849.
Owaidah TM, Al Beihany A, Iqbal MA, Elkum N, Roberts GT . Cytogenetics, molecular and ultrastructural characteristics of biphenotypic acute leukemia identified by the EGIL scoring system. Leukemia 2006; 20: 620–626.
Cuneo A, Boogaerts M, Ferrant A, Michaux JL, Bosly A, Louwagie A et al. Cytogenetics of hybrid acute leukemias. Leuk Lymphoma 1995; 18 (Suppl 1): 19–23.
Ortin X, Escoda L, Nomdedeu J, Llorente A, Cabezudo E, Boixadera J et al. Childhood T-acute lymphoblastic leukemia relapsed as minimally differentiated acute myeloid leukemia (AML-M0). Leuk Lymphoma 2003; 44: 2159–2161.
Stass S, Mirro J, Melvin S, Pui CH, Murphy SB, Williams D . Lineage switch in acute leukemia. Blood 1984; 64: 701–706.
Kawamoto H . A close developmental relationship between the lymphoid and myeloid lineages. Trends Immunol 2006; 27: 169–175.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weir, E., Ali Ansari-Lari, M., Batista, D. et al. Acute bilineal leukemia: a rare disease with poor outcome. Leukemia 21, 2264–2270 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404848
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404848
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Multicenter retrospective analysis of clinical outcome of adult patients with mixed-phenotype acute leukemia treated with acute myeloid leukemia–like or acute lymphoblastic leukemia–like chemotherapy and impact of allogeneic stem cell transplantation: a Campus ALL study
Annals of Hematology (2023)
-
Mixed Phenotype Acute Leukemia: Current Approaches to Diagnosis and Treatment
Current Oncology Reports (2021)
-
Mixed Phenotype Acute Leukemia, B/Myeloid with t(9;22): Diagnostic and Therapeutic Challenges
Indian Journal of Hematology and Blood Transfusion (2019)
-
Aberrant Wnt Signaling Pathway in the Hematopoietic Stem/Progenitor Compartment in Experimental Leukemic Animal
Journal of Cell Communication and Signaling (2019)
-
Multiparametric Flow Cytometry in Mixed Phenotype Acute Leukemia
Indian Journal of Hematology and Blood Transfusion (2019)