Abstract
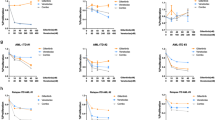
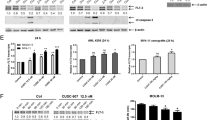
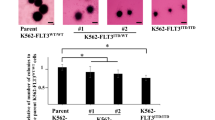
FLT3 defines a promising target for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (AML). In contrast to their efficacy in cell lines, FLT3-specific inhibitors as single agents have only modest clinical activity in patients with AML. As demonstrated here, overexpression of anti-apoptotic proteins of the BCL2 family leads to resistance against FLT3 inhibitors in a hematopoietic cell line model with activating FLT3 mutations. The susceptibility to FLT3 inhibition could be restored by treatment with the novel BH3 mimetic ABT-737. Primary AML samples tested in our study showed a high expression of BCL2 protein, but not of BCL-xL or MCL1. BCL2 protein levels were not reduced after dephosphorylation of FLT3 and its downstream target STAT5 in patient samples with FLT3 internal tandem duplications. Interestingly, treatment with ABT-737 caused apoptotic cell death in all primary AML samples at submicromolar level and synergized efficiently with FLT3 inhibition in AML samples with activating FLT3 mutations. In contrast to AML cell lines, BCR-ABL transformed human cells showed resistance to ABT-737, which might be due to the induction of MCL1 by BCR-ABL. Inhibition of BCL2 family members might define a novel highly efficient and specific strategy in the combined or monotreatment of AML.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tallman MS, Gilliland DG, Rowe JM . Drug therapy for acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2005; 106: 1154–1163.
Frohling S, Scholl C, Gilliland DG, Levine RL . Genetics of myeloid malignancies: pathogenetic and clinical implications. J Clin Oncol 2005; 23: 6285–6295.
Schnittger S, Schoch C, Dugas M, Kern W, Staib P, Wuchter C et al. Analysis of FLT3 length mutations in 1003 patients with acute myeloid leukemia: correlation to cytogenetics, FAB subtype, and prognosis in the AMLCG study and usefulness as a marker for the detection of minimal residual disease. Blood 2002; 100: 59–66.
Thiede C, Steudel C, Mohr B, Schaich M, Schakel U, Platzbecker U et al. Analysis of FLT3-activating mutations in 979 patients with acute myelogenous leukemia: association with FAB subtypes and identification of subgroups with poor prognosis. Blood 2002; 99: 4326–4335.
Stirewalt DL, Radich JP . The role of FLT3 in haematopoietic malignancies. Nat Rev Cancer 2003; 3: 650–665.
Stirewalt DL, Kopecky KJ, Meshinchi S, Appelbaum FR, Slovak ML, Willman CL et al. FLT3, RAS, and TP53 mutations in elderly patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2001; 97: 3589–3595.
Spiekermann K, Bagrintseva K, Schwab R, Schmieja K, Hiddemann W . Overexpression and constitutive activation of FLT3 induces STAT5 activation in primary acute myeloid leukemia blast cells. Clin Cancer Res 2003; 9: 2140–2150.
Hayakawa F, Towatari M, Kiyoi H, Tanimoto M, Kitamura T, Saito H et al. Tandem-duplicated Flt3 constitutively activates STAT5 and MAP kinase and introduces autonomous cell growth in IL-3-dependent cell lines. Oncogene 2000; 19: 624–631.
Pollard JA, Alonzo TA, Gerbing RB, Woods WG, Lange BJ, Sweetser DA et al. FLT3 internal tandem duplication in CD34+/CD33− precursors predicts poor outcome in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2006; 108: 2764–2769.
Sawyers CL . Finding the next Gleevec: FLT3 targeted kinase inhibitor therapy for acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Cell 2002; 1: 413–415.
Weisberg E, Boulton C, Kelly LM, Manley P, Fabbro D, Meyer T et al. Inhibition of mutant FLT3 receptors in leukemia cells by the small molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitor PKC412. Cancer Cell 2002; 1: 433–443.
Spiekermann K, Dirschinger RJ, Schwab R, Bagrintseva K, Faber F, Buske C et al. The protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor SU5614 inhibits FLT3 and induces growth arrest and apoptosis in AML-derived cell lines expressing a constitutively activated FLT3. Blood 2003; 101: 1494–1504.
Knapper S, Mills KI, Gilkes AF, Austin SJ, Walsh V, Burnett AK . The effects of lestaurtinib (CEP701) and PKC412 on primary AML blasts: the induction of cytotoxicity varies with dependence on FLT3 signaling in both FLT3-mutated and wild-type cases. Blood 2006; 108: 3494–3503.
Knapper S, Burnett AK, Littlewood T, Kell WJ, Agrawal S, Chopra R et al. A phase 2 trial of the FLT3 inhibitor lestaurtinib (CEP701) as first-line treatment for older patients with acute myeloid leukemia not considered fit for intensive chemotherapy. Blood 2006; 108: 3262–3270.
Chou TC, Talalay P . Generalized equations for the analysis of inhibitions of Michaelis-Menten and higher-order kinetic systems with two or more mutually exclusive and nonexclusive inhibitors. Eur J Biochem 1981; 115: 207–216.
Bagrintseva K, Schwab R, Kohl TM, Schnittger S, Eichenlaub S, Ellwart JW et al. Mutations in the tyrosine kinase domain of FLT3 define a new molecular mechanism of acquired drug resistance to PTK inhibitors in FLT3-ITD-transformed hematopoietic cells. Blood 2004; 103: 2266–2275.
Feuring-Buske M, Frankel A, Gerhard B, Hogge D . Variable cytotoxicity of diphtheria toxin 388-granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor fusion protein for acute myelogenous leukemia stem cells. Exp Hematol 2000; 28: 1390–1400.
Oltersdorf T, Elmore SW, Shoemaker AR, Armstrong RC, Augeri DJ, Belli BA et al. An inhibitor of Bcl-2 family proteins induces regression of solid tumours. Nature 2005; 435: 677–681.
Xu ZW, Friess H, Buchler MW, Solioz M . Overexpression of Bax sensitizes human pancreatic cancer cells to apoptosis induced by chemotherapeutic agents. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 2002; 49: 504–510.
Kohl TM, Schnittger S, Ellwart JW, Hiddemann W, Spiekermann K . KIT exon 8 mutations associated with core-binding factor (CBF)-acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cause hyperactivation of the receptor in response to stem cell factor. Blood 2005; 105: 3319–3321.
Schnittger S, Kohl TM, Haferlach T, Kern W, Hiddemann W, Spiekermann K et al. KIT-D816 mutations in AML1-ETO-positive AML are associated with impaired event-free and overall survival. Blood 2006; 107: 1791–1799.
Bagrintseva K, Geisenhof S, Kern R, Eichenlaub S, Reindl C, Ellwart JW et al. FLT3-ITD-TKD dual mutants associated with AML confer resistance to FLT3 PTK inhibitors and cytotoxic agents by overexpression of Bcl-x(L). Blood 2005; 105: 3679–3685.
Aichberger KJ, Mayerhofer M, Krauth MT, Skvara H, Florian S, Sonneck K et al. Identification of mcl-1 as a BCR/ABL-dependent target in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML): evidence for cooperative antileukemic effects of imatinib and mcl-1 antisense oligonucleotides. Blood 2005; 105: 3303–3311.
Wang K, Gross A, Waksman G, Korsmeyer SJ . Mutagenesis of the BH3 domain of BAX identifies residues critical for dimerization and killing. Mol Cell Biol 1998; 18: 6083–6089.
Willis SN, Chen L, Dewson G, Wei A, Naik E, Fletcher JI et al. Proapoptotic Bak is sequestered by Mcl-1 and Bcl-xL, but not Bcl-2, until displaced by BH3-only proteins. Genes Dev 2005; 19: 1294–1305.
Lin X, Morgan-Lappe S, Huang X, Li L, Zakula DM, Vernetti LA et al. Seed' analysis of off-target siRNAs reveals an essential role of Mcl-1 in resistance to the small-molecule Bcl-2/Bcl-X(L) inhibitor ABT-737. Oncogene 2006, advance online publication 18 December 2006, [E-pub ahead of print].
Chen S, Dai Y, Harada H, Dent P, Grant S . Mcl-1 down-regulation potentiates ABT-737 lethality by cooperatively inducing Bak activation and Bax translocation. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 782–791.
Konopleva M, Contractor R, Tsao T, Samudio I, Ruvolo PP, Kitada S et al. Mechanisms of apoptosis sensitivity and resistance to the BH3 mimetic ABT-737 in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Cell 2006; 10: 375–388.
van Delft MF, Wei AH, Mason KD, Vandenberg CJ, Chen L, Czabotar PE et al. The BH3 mimetic ABT-737 targets selective Bcl-2 proteins and efficiently induces apoptosis via Bak/Bax if Mcl-1 is neutralized. Cancer Cell 2006; 10: 389–399.
Zhong Q, Gao W, Du F, Wang X . Mule/ARF-BP1, a BH3-only E3 ubiquitin ligase, catalyzes the polyubiquitination of Mcl-1 and regulates apoptosis. Cell 2005; 121: 1085–1095.
Kuroda J, Puthalakath H, Cragg MS, Kelly PN, Bouillet P, Huang DC et al. Bim and Bad mediate imatinib-induced killing of Bcr/Abl+ leukemic cells, and resistance due to their loss is overcome by a BH3 mimetic. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 14907–14912.
Piechocki MP, Yoo GH, Dibbley SK, Amjad EH, Lonardo F . Iressa induces cytostasis and augments Fas-mediated apoptosis in acinic cell adenocarcinoma overexpressing HER2/neu. Int J Cancer 2006; 119: 441–454.
Del Gaizo Moore V, Brown JR, Certo M, Love TM, Novina CD, Letai A . Chronic lymphocytic leukemia requires BCL2 to sequester prodeath BIM, explaining sensitivity to BCL2 antagonist ABT-737. J Clin Invest 2007; 117: 112–121.
Yee KW, Schittenhelm M, O'Farrell AM, Town AR, McGreevey L, Bainbridge T et al. Synergistic effect of SU11248 with cytarabine or daunorubicin on FLT3 ITD-positive leukemic cells. Blood 2004; 104: 4202–4209.
Fiedler W, Serve H, Dohner H, Schwittay M, Ottmann OG, O'Farrell AM et al. A phase 1 study of SU11248 in the treatment of patients with refractory or resistant acute myeloid leukemia (AML) or not amenable to conventional therapy for the disease. Blood 2005; 105: 986–993.
O'Farrell AM, Foran JM, Fiedler W, Serve H, Paquette RL, Cooper MA et al. An innovative phase I clinical study demonstrates inhibition of FLT3 phosphorylation by SU11248 in acute myeloid leukemia patients. Clin Cancer Res 2003; 9: 5465–5476.
Chou TC, Talalay P . Quantitative analysis of dose-effect relationships: the combined effects of multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv Enzyme Regul 1984; 22: 27–55.
Minami Y, Yamamoto K, Kiyoi H, Ueda R, Saito H, Naoe T . Different antiapoptotic pathways between wild-type and mutated FLT3: insights into therapeutic targets in leukemia. Blood 2003; 102: 2969–2975.
Jaiswal S, Traver D, Miyamoto T, Akashi K, Lagasse E, Weissman IL . Expression of BCR/ABL and BCL-2 in myeloid progenitors leads to myeloid leukemias. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100: 10002–10007.
Chauhan D, Velankar M, Brahmandam M, Hideshima T, Podar K, Richardson P et al. A novel Bcl-2/Bcl-X(L)/Bcl-w inhibitor ABT-737 as therapy in multiple myeloma. Oncogene 2007; 26: 2374–2380.
Slack FJ, Weidhaas JB . MicroRNAs as a potential magic bullet in cancer. Future Oncol 2006; 2: 73–82.
Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ . Oncomirs - microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2006; 6: 259–269.
Cimmino A, Calin GA, Fabbri M, Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Shimizu M et al. miR-15 and miR-16 induce apoptosis by targeting BCL2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 13944–13949.
Illmer T, Kosel D, Schaich MA, Thiede C, Neubauer A, Mueller-Tidow C et al. MiRNA Expression Signatures in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Are Predictors for Patient Outcome. ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts 2006; 108: 152.
Klampfer L, Zhang J, Zelenetz AO, Uchida H, Nimer SD . The AML1/ETO fusion protein activates transcription of BCL-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1996; 93: 14059–14064.
Amarante-Mendes GP, McGahon AJ, Nishioka WK, Afar DE, Witte ON, Green DR . Bcl-2-independent Bcr-Abl-mediated resistance to apoptosis: protection is correlated with up regulation of Bcl-xL. Oncogene 1998; 16: 1383–1390.
Dai Y, Rahmani M, Corey SJ, Dent P, Grant S . A Bcr/Abl-independent, Lyn-dependent form of imatinib mesylate (STI-571) resistance is associated with altered expression of Bcl-2. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 34227–34239.
Danial NN, Korsmeyer SJ . Cell death: critical control points. Cell 2004; 116: 205–219.
Acknowledgements
We thank Evelyn Zellmeier, Gudrun Mellert, Elke Habben and Belay Tizazu for excellent technical assistance in Ficoll separation of primary samples and Dres. Christina Schessl, Grit Hutter, Harald Ehrhard, Philipp Greif, Vijay Rawat, and Marc Weinkauf for helpful discussions. We also thank Abbott Laboratories for providing ABT-737 and ABT control substance. This study was supported in part by a grant from the ‘NOVARTIS-STIFTUNG FÜR THERAPEUTISCHE FORSCHUNG’.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Leukemia Web site (http://www.nature.com/leu)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kohl, T., Hellinger, C., Ahmed, F. et al. BH3 mimetic ABT-737 neutralizes resistance to FLT3 inhibitor treatment mediated by FLT3-independent expression of BCL2 in primary AML blasts. Leukemia 21, 1763–1772 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404776
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404776
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
TP-0184 inhibits FLT3/ACVR1 to overcome FLT3 inhibitor resistance and hinder AML growth synergistically with venetoclax
Leukemia (2024)
-
FLT3 targeting in the modern era: from clonal selection to combination therapies
International Journal of Hematology (2023)
-
Dasatinib and navitoclax act synergistically to target NUP98-NSD1+/FLT3-ITD+ acute myeloid leukemia
Leukemia (2019)
-
Repression of Mcl-1 expression by the CDC7/CDK9 inhibitor PHA-767491 overcomes bone marrow stroma-mediated drug resistance in AML
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
FLT3 inhibitors for acute myeloid leukemia: a review of their efficacy and mechanisms of resistance
International Journal of Hematology (2013)