Abstract
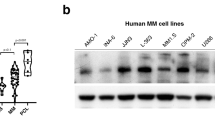
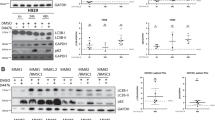
Survivin is a fascinating member of the inhibitor of apoptosis protein (IAP) family with its dual roles in mitosis and apoptosis, and emerges as an attractive target for cancer therapy. Multiple myeloma (MM) is a plasma cell malignancy, characterized by deregulated proliferation, cell-death processes and fatal outcome. We thus investigated survivin expression in myeloma cells and its role in MM biology to evaluate its potential interest as a target in MM treatment. Our results describe the cancer-specific overexpression of survivin in myeloma cells and show a significant correlation between survivin expression at protein level and clinical course of MM. Moreover, survivin knockdown by RNA interference led to growth rate inhibition of myeloma cells related to apoptosis induction and deep cell-cycle disruption. Finally, survivin knockdown sensitized myeloma cells to conventional anti-myeloma agents. Altogether, these data argue for the interest to evaluate survivin antagonists in MM treatment.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA . The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 2000; 100: 57–70.
Altieri DC . Survivin, versatile modulation of cell division and apoptosis in cancer. Oncogene 2003; 22: 8581–8589.
Li F . Survivin study: what is the next wave? J Cell Physiol 2003; 197: 8–29.
Altieri DC . The case for survivin as a regulator of microtubule dynamics and cell-death decisions. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2006; 18: 609–615.
Liston P, Fong WG, Korneluk RG . The inhibitors of apoptosis: there is more to life than Bcl2. Oncogene 2003; 22: 8568–8580.
Altieri DC . Validating survivin as a cancer therapeutic target. Nat Rev Cancer 2003; 3: 46–54.
Chen-Kiang S . Cell-cycle control of plasma cell differentiation and tumorigenesis. Immunol Rev 2003; 194: 39–47.
Zhan F, Hardin J, Kordsmeier B, Bumm K, Zheng M, Tian E et al. Global gene expression profiling of multiple myeloma, monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance, and normal bone marrow plasma cells. Blood 2002; 99: 1745–1757.
Specht K, Haralambieva E, Bink K, Kremer M, Mandl-Weber S, Koch I et al. Different mechanisms of cyclin D1 overexpression in multiple myeloma revealed by fluorescence in situ hybridization and quantitative analysis of mRNA levels. Blood 2004; 104: 1120–1126.
Magrangeas F, Lode L, Wuilleme S, Minvielle S, Avet-Loiseau H . Genetic heterogeneity in multiple myeloma. Leukemia 2005; 19: 191–194.
Chng WJ, Ahmann GJ, Henderson K, Santana-Davila R, Greipp PR, Gertz MA et al. Clinical implication of centrosome amplification in plasma cell neoplasm. Blood 2006; 107: 3669–3675.
Derenne S, Monia B, Dean NM, Taylor JK, Rapp MJ, Harousseau JL et al. Antisense strategy shows that Mcl-1 rather than Bcl-2 or Bcl-x(L) is an essential survival protein of human myeloma cells. Blood 2002; 100: 194–199.
Kardosh A, Soriano N, Liu YT, Uddin J, Petasis NA, Hofman FM et al. Multitarget inhibition of drug-resistant multiple myeloma cell lines by dimethyl-celecoxib (DMC), a non-COX-2 inhibitory analog of celecoxib. Blood 2005; 106: 4330–4338.
Stromberg T, Ekman S, Girnita L, Dimberg LY, Larsson O, Axelson M et al. IGF-1 receptor tyrosine kinase inhibition by the cyclolignan PPP induces G2/M-phase accumulation and apoptosis in multiple myeloma cells. Blood 2006; 107: 669–678.
Mitsiades N, Mitsiades CS, Poulaki V, Chauhan D, Richardson PG, Hideshima T et al. Biologic sequelae of nuclear factor-kappaB blockade in multiple myeloma: therapeutic applications. Blood 2002; 99: 4079–4086.
Bataille R, Jégo G, Robillard N, Barillé-Nion S, Harousseau JL, Moreau P et al. The phenotype of normal, reactive and malignant plasma cells. Identification of ‘many and multiple myelomas’ and of new targets for myeloma therapy. Hematologica 2006; 91: 1234–1240.
Barille S, Bataille R, Rapp MJ, Harousseau JL, Amiot M . Production of metalloproteinase-7 (matrilysin) by human myeloma cells and its potential involvement in metalloproteinase-2 activation. J Immunol 1999; 163: 5723–5728.
Jego G, Bataille R, Pellat-Deceunynck C . Interleukin-6 is a growth factor for nonmalignant human plasmablasts. Blood 2001; 97: 1817–1822.
Brummelkamp TR, Bernards R, Agami R . A system for stable expression of short interfering RNAs in mammalian cells. Science 2002; 296: 550–553.
Carvalho A, Carmena M, Sambade C, Earnshaw WC, Wheatley SP . Survivin is required for stable checkpoint activation in taxol-treated HeLa cells. J Cell Sci 2003; 116: 2987–2998.
Qin XF, An DS, Chen IS, Baltimore D . Inhibiting HIV-1 infection in human T cells by lentiviral-mediated delivery of small interfering RNA against CCR5. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100: 183–188.
Li F, Altieri DC . Transcriptional analysis of human survivin gene expression. Biochem J 1999; 344 (Part 2): 305–311.
Bao R, Connolly DC, Murphy M, Green J, Weinstein JK, Pisarcik DA et al. Activation of cancer-specific gene expression by the survivin promoter. J Natl Cancer Inst 2002; 94: 522–528.
Gritsko T, Williams A, Turkson J, Kaneko S, Bowman T, Huang M et al. Persistent activation of stat3 signaling induces survivin gene expression and confers resistance to apoptosis in human breast cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 2006; 12: 11–19.
Hoffman WH, Biade S, Zilfou JT, Chen J, Murphy M . Transcriptional repression of the anti-apoptotic survivin gene by wild type p53. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 3247–3257.
Li F, Yang J, Ramnath N, Javle MM, Tan D . Nuclear or cytoplasmic expression of survivin: what is the significance? Int J Cancer 2005; 114: 509–512.
Adida C, Haioun C, Gaulard P, Lepage E, Morel P, Briere J et al. Prognostic significance of survivin expression in diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Blood 2000; 96: 1921–1925.
Martinez A, Bellosillo B, Bosch F, Ferrer A, Marce S, Villamor N et al. Nuclear survivin expression in mantle cell lymphoma is associated with cell proliferation and survival. Am J Pathol 2004; 164: 501–510.
Adida C, Recher C, Raffoux E, Daniel MT, Taksin AL, Rousselot P et al. Expression and prognostic significance of survivin in de novo acute myeloid leukaemia. Br J Haematol 2000; 111: 196–203.
Nakagawa Y, Abe S, Kurata M, Hasegawa M, Yamamoto K, Inoue M et al. IAP family protein expression correlates with poor outcome of multiple myeloma patients in association with chemotherapy-induced overexpression of multidrug resistance genes. Am J Haematol 2006; 81: 824–831.
Conway EM, Pollefeyt S, Steiner-Mosonyi M, Luo W, Devriese A, Lupu F et al. Deficiency of survivin in transgenic mice exacerbates Fas-induced apoptosis via mitochondrial pathways. Gastroenterology 2002; 123: 619–631.
Salvesen GS, Duckett CS . IAP proteins: blocking the road to death's door. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2002; 3: 401–410.
Song Z, Yao X, Wu M . Direct interaction between survivin and Smac/DIABLO is essential for the anti-apoptotic activity of survivin during taxol-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 23130–23140.
Liu T, Brouha B, Grossman D . Rapid induction of mitochondrial events and caspase-independent apoptosis in Survivin-targeted melanoma cells. Oncogene 2004; 23: 39–48.
Dohi T, Beltrami E, Wall NR, Plescia J, Altieri DC . Mitochondrial survivin inhibits apoptosis and promotes tumorigenesis. J Clin Invest 2004; 114: 1117–1127.
Grossman D, Kim PJ, Schechner JS, Altieri DC . Inhibition of melanoma tumor growth in vivo by survivin targeting. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001; 98: 635–640.
Fukuda S, Pelus LM . Elevation of Survivin levels by hematopoietic growth factors occurs in quiescent CD34+ hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells before cell cycle entry. Cell Cycle 2002; 1: 322–326.
Suzuki A, Hayashida M, Ito T, Kawano H, Nakano T, Miura M et al. Survivin initiates cell cycle entry by the competitive interaction with Cdk4/p16(INK4a) and Cdk2/cyclin E complex activation. Oncogene 2000; 19: 3225–3234.
Mazars GR, Portier M, Zhang XG, Jourdan M, Bataille R, Theillet C et al. Mutations of the p53 gene in human myeloma cell lines. Oncogene 1992; 7: 1015–1018.
Beltrami E, Plescia J, Wilkinson JC, Duckett CS, Altieri DC . Acute ablation of survivin uncovers p53-dependent mitotic checkpoint functions and control of mitochondrial apoptosis. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 2077–2084.
Yang D, Welm A, Bishop JM . Cell division and cell survival in the absence of survivin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 15100–15105.
Acknowledgements
We thank Alexandrine Geoffroy-Luseau for providing us plasma cell precursors. This work has been supported by La Ligue Nationale contre le Cancer (équipe labellisée 2005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Romagnoli, M., Trichet, V., David, C. et al. Significant impact of survivin on myeloma cell growth. Leukemia 21, 1070–1078 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404602
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404602
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Overexpression of HIF-1α contributes to melphalan resistance in multiple myeloma cells by activation of ERK1/2, Akt, and NF-κB
Laboratory Investigation (2019)
-
FOXM1 is a therapeutic target for high-risk multiple myeloma
Leukemia (2016)
-
PTTG1 expression is associated with hyperproliferative disease and poor prognosis in multiple myeloma
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2015)
-
Survivin-specific CD4+ T cells are decreased in patients with survivin-positive myeloma
Journal for Immunotherapy of Cancer (2015)
-
Bcl-xL controls a switch between cell death modes during mitotic arrest
Cell Death & Disease (2014)