Abstract
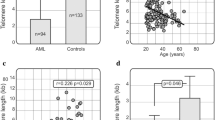
Some evidences suggest that telomere restriction fragment length (TRF-L) is an effective indicator of histopathogenesis in B-cell tumors. As histopathogenesis is relevant for B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL) prognosis, TRF-L was assessed by Southern blot in 201 patients and compared to variable immunoglobulin heave chain gene mutational status (VH-MS) and to other known prognostic features. Overall survival (OS), time to first treatment (TTFT) and progression-free survival (PFS) were evaluated. Our results indicate the following: (1) TRF-L is heterogeneous among B-CLL patients (median 6014 bp, range 1465–16 762); (2) TRF-L correlates to VH-MS (r2=0.1994, P<0.0001) with VH-mutated patients showing long and VH-unmutated short telomeres; however, 41% of VH-unmutated and 5% of VH-mutated patients did not show this correlation and were thus defined as ‘discordant’; (3) TRF-L effectively predicts outcome in terms of TTFT, PFS and OS; (4) VH-unmutated discordant patients have a better clinical outcome than VH-unmutated concordant patients (OS P<0.01, PFS P<0.05) and similar to that of VH-mutated patients (OS, PFS P=NS). Compared to VH-unmutated concordant patients, VH-unmutated discordant patients showed no peculiarity in their immunoglobulin rearrangement nor in their flow cytometry or fluorescence in situ hybridization profile. In conclusion, TRF-L can be helpful to refine prognostication of B-CLL patients, particularly those with a VH-unmutated immunoglobulin sequence.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dighiero G, Maloum K, Desablens B, Cazin B, Navarro M, Leblay R et al. Chlorambucil in indolent chronic lymphocytic leukemia. French cooperative group on chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med 1998; 338: 1506–1514.
Shanafelt TD, Geyer SM, Kay NE . Prognosis at diagnosis: integrating molecular biologic insights into clinical practice for patients with CLL. Blood 2004; 103: 1202–1210.
Rai KR, Sawitsky A, Cronkite EP, Chanana AD, Levy RN, Pasternack BS . Clinical staging of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 1975; 46: 219–234.
Keating MJ, Chiorazzi N, Messmer B, Damle RN, Allen SL, Rai KR et al. Biology and treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Hematology (Am Soc Hematol Educ Program) 2003, 153–175.
Binet JL, Caligaris-Cappio F, Catovsky D, Cheson B, Davis T, Dighiero G et al. Perspectives on the use of new diagnostic tools in the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2006; 107: 859–861.
Stilgenbauer S, Döhner H . Molecular genetics and its clinical relevance. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am 2004; 18: 827–848.
Binet JL, Auquier A, Dighiero G, Chastang C, Piguet H, Goasguen J et al. A new prognostic classification of chronic lymphocytic leukemia derived from a multivariate survival analysis. Cancer 1981; 48: 198–206.
Döhner H, Stilgenbauer S, Benner A, Leupolt E, Kröber A, Bullinger L et al. Genomic aberrations and survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med 2000; 343: 1910–1916.
Damle RN, Wasil T, Fais F, Ghiotto F, Valetto A, Allen SL et al. Ig V gene mutation status and CD38 expression as novel prognostic indicators in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 1999; 94: 1840–1847.
Crespo M, Bosch F, Villamor N, Bellosillo B, Colomer D, Rozman M et al. ZAP-70 expression as a surrogate for immunoglobulin-variable-region mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med 2003; 348: 1764–1775.
Rassenti LZ, Huynh L, Toy TL, Chen L, Keating MJ, Gribben JG et al. ZAP-70 compared with immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene mutation status as a predictor of disease progression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med 2004; 351: 893–901.
Hamblin TJ, Davis Z, Gardiner A, Oscier DG, Stevenson FK . Unmutated Ig V(H) genes are associated with a more aggressive form of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 1999; 94: 1848–1854.
Hamblin TJ, Orchard JA, Ibbotson RE, Davis Z, Thomas PW, Stevenson FK et al. CD38 expression and immunoglobulin variable region mutations are independent prognostic variables in chronic lymphocytic leukemia, but CD38 expression may vary during the course of the disease. Blood 2002; 99: 1023–1029.
Duke VM, Gandini D, Sherrington PD, Lin K, Heelan B, Amlot P et al. V(H) gene usage differs in germline and mutated B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Haematologica 2003; 88: 1259–1271.
Migliazza A, Cayanis E, Bosch-Albareda F, Komatsu H, Martinotti S, Toniato E et al. Molecular pathogenesis of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia: analysis of 13q14 chromosomal deletions. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 2000; 252: 275–284.
Kuppers R, Dalla-Favera R . Mechanisms of chromosomal translocations in B cell lymphomas. Oncogene 2001; 20: 5580–5594.
Capello D, Guarini A, Berra E, Mauro FR, Rossi D, Ghia E et al. Evidence of biased immunoglobulin variable gene usage in highly stable B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 2004; 18: 1941–1947.
Ladetto M, Compagno M, Ricca I, Pagano M, Rocci A, Astolfi M et al. Telomere length correlates with histopathogenesis according to the germinal center in mature B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders. Blood 2004; 103: 4644–4649.
Bechter OE, Eisterer W, Pall G, Hilbe W, Kuhr T, Thaler J . Telomere length and telomerase activity predict survival in patients with B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer Res 1998; 58: 4918–4922.
Hultdin M, Rosenquist R, Thunberg U, Tobin G, Norrback KF, Johnson A et al. Association between telomere length and V(H) gene mutation status in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: clinical and biological implications. Br J Cancer 2003; 88: 593–598.
Damle RN, Batliwalla FM, Ghiotto F, Valetto A, Albesiano E, Sison C et al. Telomere length and telomerase activity delineate distinctive replicative features of the B-CLL subgroups defined by immunoglobulin V gene mutations. Blood 2004; 103: 375–382.
Grabowski P, Hultdin M, Karlsson K, Tobin G, leskog A, Thunberg U et al. Telomere length as a prognostic parameter in chronic lymphocytic leukemia with special reference to VH gene mutation status. Blood 2005; 105: 4807–4812.
Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Diebold J, Flandrin G, Muller-Hermelink HK, Vardiman J et al. World Health Organization classification of neoplastic diseases of the hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues: report of the Clinical Advisory Committee meeting-Airlie House, Virginia, November 1997. J Clin Oncol 1999; 17: 3835–3849.
Matutes E, Owusu-Ankomah K, Morilla R, Garcia Marco J, Houlihan A, Que TH et al. The immunological profile of B cell disorders and proposal of a scoring system for the diagnosis of CLL. Leukemia 1994; 8: 1640–1645.
Ricca I, Compagno M, Ladetto M, Rocci A, Dell’Aquila M, Omedè P et al. Marked telomere shortening in mobilized peripheral blood progenitor cells (PBPC) following two tightly spaced high-dose chemotherapy courses with G-CSF. Leukemia 2005; 19: 644–651.
Ladetto M, Donovan JW, Harig S, Trojan A, Poor C, Schlossnan R et al. Real-Time polymerase chain reaction of immunoglobulin rearrangements for quantitative evaluation of minimal residual disease in multiple myeloma. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2000; 6: 241–253.
Donovan JW, Ladetto M, Zou G, Neuberg D, Poor C, Bowers D et al. Immunoglobulin heavy-chain consensus probes for real-time PCR quantification of residual disease in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2000; 95: 2651–2658.
Ladetto M, Omede P, Sametti S, Donovan JW, Astolfi M, Drandi D et al. Real-time polymerase chain reaction in multiple myeloma: quantitative analysis of tumor contamination of stem cell harvests. Exp Hematol 2002; 30: 529–536.
Voena C, Ladetto M, Astolfi M, Provan D, Gribben JG, Boccadoro M et al. A novel nested-PCR strategy for the detection of rearranged immunoglobulin heavy-chain genes in B cell tumors. Leukemia 1997; 11: 1793–1798.
Durig J, Naschar M, Schmucker U, Renzing-Kohler K, Holter T, Huttmann A et al. CD38 expression is an important prognostic marker in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Leukemia 2002; 16: 30–35.
Döhner H, Stilgenbauer S, James MR, Benner A, Weilguni T, Bentz M et al. 11q deletions identify a new subset of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia characterized by extensive nodal involvement and inferior prognosis. Blood 1997; 89: 2516–2522.
Zweig MH, Campbell G . Receiver-Operating Characteristic (ROC) plots: a fundamental evaluation tool in clinical medicine. Clin Chem 1993; 39: 561–577.
Schroers R, Griesinger F, Trümper L, Haase D, Kulle B, Klein-Hitpass L et al. Combined analysis of Zap-70 and CD38 expression as a predictor of disease progression in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 2005; 19: 750–758.
Tobin G, Thunberg U, Karlsson K, Murray F, Laurell A, Willander K et al. Subsets with restricted immunoglobulin gene rearrangement features indicate a role for antigen selection in the development of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2004; 104: 2879–2885.
Falt S, Merup M, Tobin G, Thunberg U, Gahrton G, Rosenquist R et al. Distinctive gene expression pattern in VH3-21 utilizing B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2005; 06: 681–689.
Kröber A, Bloehdorn J, Hafner S, Buhler A, Seiler T, Kienle D et al. Additional genetic high-risk features such as 11q deletion, 17p deletion, and V3-21 usage characterize discordance of ZAP-70 and VH mutation status in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol 2006; 24: 969–975.
Dreger P, Stilgenbauer S, Benner A, Ritgen M, Krober A, Kneba M et al. The prognostic impact of autologous stem cell transplantation in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a risk-matched analysis based on the VH gene mutational status. Blood 2004; 103: 2850–2858.
Moreno C, Villamor N, Colomer D, Esteve J, Martino R, Nomdedeu J et al. Allogeneic stem-cell transplantation may overcome the adverse prognosis of unmutated VH gene in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol 2005; 23: 3433–3438.
Johnson TA, Rassenti LZ, Kipps TJ . Ig VH1 genes expressed in B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia exhibit distinctive molecular features. J Immunol 1997; 158: 235–246.
Bojarska-Junak A, Giannopoulos K, Kowal M, Dmoszynska A, Rolinski J . Comparison of methods for determining zeta-chain associated protein – 70 (ZAP-70) expression in patients with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL). Cytometry B Clin Cytom 2006; 70: 293–301.
Remes K, Norrback KF, Rosenquist R, Mehle C, Lindh J, Roos G . Telomere length and telomerase activity in malignant lymphomas at diagnosis and relapse. Br J Cancer 2000; 82: 601–607.
Cottliar A, Pedrazzini E, Corrado C, Engelberger MI, Narbaitz M, Slavutsky I . Telomere shortening in patients with plasma cell disorders. Eur J Haematol 2003; 71: 334–340.
Wu KD, Orme LM, Shaughnessy Jr J, Jacobson J, Barlogie B, Moore MA . Telomerase and telomere length in multiple myeloma: correlations with disease heterogeneity, cytogenetic status, and overall survival. Blood 2003; 101: 4982–4989.
Smith LL, Coller HA, Roberts JM . Telomerase modulates expression of growth-controlling genes and enhances cell proliferation. Nat Cell Biol 2003; 5: 474–479.
van der Velden VH, Hochhaus A, Cazzaniga G, Szczepanski T, Gabert J, van Dongen JJ . Detection of minimal residual disease in hematologic malignancies by real-time quantitative PCR: principles, approches and laboratory aspects. Leukemia 2003; 17: 1013–1034.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by Compagnia di San Paolo, Turin, Italy, by Ministero dell’ Università e della Ricerca (MIUR) and by Regione Piemonte. IR was recipient of a fellowship from Fondazione Italiana Ricerca sul Cancro (FIRC), Milan, Italy. AR is recipient of a Research Fellowship from the Fondazione Internazionale di Ricerca in Medicina Sperimentale, Turin, Italy. MC was recipient of a fellowship from Fondazione Angela Bossolasco, Turin, Italy.
Contributions: I Ricca designed and performed the research, analyzed data and wrote the paper. A Rocci and C Lobetti Bodoni performed research and analyzed data. D Drandi, R Francese, M Compagno, M Astolfi, L Monitillo and P Omedè performed research. F De Marco, S Vallet, R Calvi, F Ficara, A Gallamini, C Marinone, L Bergui, M Boccadoro and C Tarella contributed patients. M Ladetto designed the research, contributed vital new reagents, analyzed data and wrote the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ricca, I., Rocci, A., Drandi, D. et al. Telomere length identifies two different prognostic subgroups among VH-unmutated B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients. Leukemia 21, 697–705 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404544
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404544
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Short telomeres are associated with inferior outcome, genomic complexity, and clonal evolution in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Leukemia (2019)
-
Association between telomere length and survival in cancer patients: a meta-analysis and review of literature
Frontiers of Medicine (2016)
-
Telomere shortening associated with increased genomic complexity in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Tumor Biology (2015)
-
IGHV unmutated CLL B cells are more prone to spontaneous apoptosis and subject to environmental prosurvival signals than mutated CLL B cells
Leukemia (2011)
-
Telomeres and prognosis in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia
International Journal of Hematology (2011)