Abstract
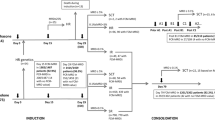
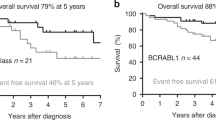
Minimal residual disease (MRD) diagnostics is used for treatment stratification in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. We aimed to identify and solve potential problems in multicenter MRD studies to achieve and maintain consistent results between the AIEOP/BFM ALL-2000 MRD laboratories. As the dot-blot hybridization method was replaced by the real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RQ-PCR) method during the treatment protocol, special attention was given to the comparison of MRD data obtained by both methods and to the reproducibility of RQ-PCR data. Evaluation of all key steps in molecular MRD diagnostics identified several pitfalls that resulted in discordant MRD results. In particular, guidelines for RQ-PCR data interpretation appeared to be crucial for obtaining concordant MRD results. The experimental variation of the RQ-PCR was generally less than three-fold, but logically became larger at low MRD levels below the reproducible sensitivity of the assay (<10−4). Finally, MRD data obtained by dot-blot hybridization were comparable to those obtained by RQ-PCR analysis (r2=0.74). In conclusion, MRD diagnostics using RQ-PCR analysis of immunoglobulin/T-cell receptor gene rearrangements is feasible in multicenter studies but requires standardization; particularly strict guidelines for interpretation of RQ-PCR data are required. We further recommend regular quality control for laboratories performing MRD diagnostics in international treatment protocols.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cave H, van der Werff ten Bosch J, Suciu S, Guidal C, Waterkeyn C, Otten J et al. Clinical significance of minimal residual disease in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer–Childhood Leukemia Cooperative Group. N Engl J Med 1998; 339: 591–598.
Coustan-Smith E, Sancho J, Hancock ML, Boyett JM, Behm FG, Raimondi SC et al. Clinical importance of minimal residual disease in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2000; 96: 2691–2696.
van Dongen JJM, Seriu T, Panzer-Grumayer ER, Biondi A, Pongers-Willemse MJ, Corral L et al. Prognostic value of minimal residual disease in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in childhood. Lancet 1998; 352: 1731–1738.
Panzer-Grumayer ER, Schneider M, Panzer S, Fasching K, Gadner H . Rapid molecular response during early induction chemotherapy predicts a good outcome in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2000; 95: 790–794.
Knechtli CJ, Goulden NJ, Hancock JP, Grandage VL, Harris EL, Garland RJ et al. Minimal residual disease status before allogeneic bone marrow transplantation is an important determinant of successful outcome for children and adolescents with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 1998; 92: 4072–4079.
van der Velden VHJ, Joosten SA, Willemse MJ, van Wering ER, Lankester AW, van Dongen JJM et al. Real-time quantitative PCR for detection of minimal residual disease before allogeneic stem cell transplantation predicts outcome in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2001; 15: 1485–1487.
Szczepanski T, Orfao A, van der Velden VHJ, San Miguel JF, van Dongen JJM . Minimal residual disease in leukaemia patients. Lancet Oncol 2001; 2: 409–417.
Marshall GM, Haber M, Kwan E, Zhu L, Ferrara D, Xue C et al. Importance of minimal residual disease testing during the second year of therapy for children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Oncol 2003; 21: 704–709.
Willemse MJ, Seriu T, Hettinger K, d’Aniello E, Hop WC, Panzer-Grumayer ER et al. Detection of minimal residual disease identifies differences in treatment response between T-ALL and precursor B-ALL. Blood 2002; 99: 4386–4393.
Szczepanski T, Flohr T, van der Velden VHJ, Bartram CR, van Dongen JJM . Molecular monitoring of residual disease using antigen receptor genes in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2002; 15: 37–57.
van der Velden VHJ, Hochhaus A, Cazzaniga G, Szczepanski T, Gabert J, van Dongen JJM . Detection of minimal residual disease in hematologic malignancies by real-time quantitative PCR: principles, approaches, and laboratory aspects. Leukemia 2003; 17: 1013–1034.
Verhagen OJ, Wijkhuijs AJ, van der Sluijs-Gelling AJ, Szczepanski T, van der Linden-Schrever BE, Pongers-Willemse MJ et al. Suitable DNA isolation method for the detection of minimal residual disease by PCR techniques. Leukemia 1999; 13: 1298–1299.
Pongers-Willemse MJ, Seriu T, Stolz F, d’Aniello E, Gameiro P, Pisa P et al. Primers and protocols for standardized detection of minimal residual disease in acute lymphoblastic leukemia using immunoglobulin and T cell receptor gene rearrangements and TAL1 deletions as PCR targets: report of the BIOMED-1 CONCERTED ACTION: investigation of minimal residual disease in acute leukemia. Leukemia 1999; 13: 110–118.
Peham M, Panzer S, Fasching K, Haas OA, Fischer S, Marschalek R et al. Low frequency of clonotypic Ig and T-cell receptor gene rearrangements in t(4;11) infant acute lymphoblastic leukaemia and its implication for the detection of minimal residual disease. Br J Haematol 2002; 117: 315–321.
Verhagen OJ, Willemse MJ, Breunis WB, Wijkhuijs AJ, Jacobs DC, Joosten SA et al. Application of germline IGH probes in real-time quantitative PCR for the detection of minimal residual disease in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2000; 14: 1426–1435.
van der Velden VHJ, Wijkhuijs JM, Jacobs DC, van Wering ER, van Dongen JJM . T cell receptor gamma gene rearrangements as targets for detection of minimal residual disease in acute lymphoblastic leukemia by real-time quantitative PCR analysis. Leukemia 2002; 16: 1372–1380.
van der Velden VHJ, Willemse MJ, van der Schoot CE, Hahlen K, van Wering ER, van Dongen JJM . Immunoglobulin kappa deleting element rearrangements in precursor-B acute lymphoblastic leukemia are stable targets for detection of minimal residual disease by real-time quantitative PCR. Leukemia 2002; 16: 928–936.
Nakao M, Janssen JW, Flohr T, Bartram CR . Rapid and reliable quantification of minimal residual disease in acute lymphoblastic leukemia using rearranged immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor loci by LightCycler technology. Cancer Res 2000; 60: 3281–3289.
Beishuizen A, Verhoeven MA, Mol EJ, Breit TM, Wolvers-Tettero IL, van Dongen JJ . Detection of immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene rearrangements by Southern blot analysis: recommendations for optimal results. Leukemia 1993; 7: 2045–2053.
Breit TM, Wolvers-Tettero IL, Beishuizen A, Verhoeven MA, van Wering ER, van Dongen JJ . Southern blot patterns, frequencies, and junctional diversity of T-cell receptor-delta gene rearrangements in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 1993; 82: 3063–3074.
van der Velden VH, Hoogeveen PG, Pieters R, van Dongen JJ . Impact of two independent bone marrow samples on minimal residual disease monitoring in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Br J Haematol 2006; 133: 382–388.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr Martin Zimmermann (Hannover, Germany) for advice on statistical issues and to Marieke Comans-Bitter for preparing the figures. We acknowledge the Kind-Phillip Stiftung, BMBF, Deutsche Krebshilfe, St Anna Kinderkrebsforschung, Fondazione Tettamanti, Fondazione Cariplo, Fondazione Città Della Speranza, Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (AIRC), MIUR PRIN 2005 no. 2005069388_001, NH & MRC and Cancer Council (Australia) for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van der Velden, V., Panzer-Grümayer, E., Cazzaniga, G. et al. Optimization of PCR-based minimal residual disease diagnostics for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia in a multi-center setting. Leukemia 21, 706–713 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404535
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404535
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Utility of Measurable Residual Disease (MRD) Assessment in Mantle Cell Lymphoma
Current Treatment Options in Oncology (2023)
-
Prognostic value of Oncogenetic mutations in pediatric T Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: a comparison of UKALL2003 and FRALLE2000T protocols
Leukemia (2022)
-
A phase I study of inotuzumab ozogamicin as a single agent in pediatric patients in Japan with relapsed/refractory CD22-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia (INO-Ped-ALL-1)
International Journal of Hematology (2022)
-
Inotuzumab ozogamicin as single agent in pediatric patients with relapsed and refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia: results from a phase II trial
Leukemia (2022)
-
Whole-genome sequencing facilitates patient-specific quantitative PCR-based minimal residual disease monitoring in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia, neuroblastoma and Ewing sarcoma
British Journal of Cancer (2022)