Abstract
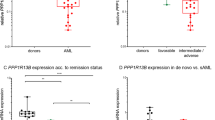
The T-lineage phenotype of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL) is associated with an increased relapse-risk and in vitro resistance to drugs as compared to a precursor B phenotype. Antiapoptotic isoforms of p73 that lack part of the transactivation (TA) domain (ΔTA-p73, i.e. p73Δex2, p73Δex3, p73Δex2/3 and ΔN-p73) may cause resistance to anticancer agents through inhibition of p53 and/or proapoptotic p73 family members (TA-p73). We demonstrate in our study that the expression of total p73 mRNA was higher in childhood T-ALL compared to controls (P=0.004). In T-ALL, the relative contribution of antiapoptotic ΔTA-p73 (88%) was larger than of proapoptotic TA-p73 (12%). Leukaemic cells of T-ALL patients expressing higher levels of antiapoptotic p73 were more resistant to the DNA-damaging drug daunorubicin compared to cells of patients with low or negative expression or these isoforms (Ptrend=0.045). Interestingly, p73Δex2 was the most abundantly expressed antiapoptotic isoform in daunorubicin-resistant patient cells (44% of total p73). No association was found between high expression of proapoptotic TA-p73 or antiapoptotic ΔTA-p73 and relapse-risk. Our results suggest that childhood T-ALL is associated with a high expression of ΔTA-p73. These isoforms may play a role in cellular resistance to DNA-damaging drugs in children at initial diagnosis of T-ALL.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kaghad M, Bonnet H, Yang A, Creancier L, Biscan JC, Valent A et al. Monoallelically expressed gene related to p53 at 1p36, a region frequently deleted in neuroblastoma and other human cancers. Cell 1997; 90: 809–819.
De Laurenzi V, Costanzo A, Barcaroli D, Terrinoni A, Falco M, Annicchiarico-Petruzzelli M et al. Two new p73 splice variants, gamma and delta, with different transcriptional activity. J Exp Med 1998; 188: 1763–1768.
De Laurenzi VD, Catani MV, Terrinoni A, Corazzari M, Melino G, Costanzo A et al. Additional complexity in p73: induction by mitogens in lymphoid cells and identification of two new splicing variants epsilon and zeta. Cell Death Differ 1999; 6: 389–390.
Ueda Y, Hijikata M, Takagi S, Chiba T, Shimotohno K . New p73 variants with altered C-terminal structures have varied transcriptional activities. Oncogene 1999; 18: 4993–4998.
Ishimoto O, Kawahara C, Enjo K, Obinata M, Nukiwa T, Ikawa S . Possible oncogenic potential of DeltaNp73: a newly identified isoform of human p73. Cancer Res 2002; 62: 636–641.
Zhu J, Jiang J, Zhou W, Chen X . The potential tumor suppressor p73 differentially regulates cellular p53 target genes. Cancer Res 1998; 58: 5061–5065.
Alarcon-Vargas D, Fuchs SY, Deb S, Ronai Z . p73 transcriptional activity increases upon cooperation between its spliced forms. Oncogene 2000; 19: 831–835.
Ueda Y, Hijikata M, Takagi S, Chiba T, Shimotohno K . Transcriptional activities of p73 splicing variants are regulated by inter-variant association. Biochem J 2001; 356: 859–866.
Dietz S, Rother K, Bamberger C, Schmale H, Mossner J, Engeland K . Differential regulation of transcription and induction of programmed cell death by human p53-family members p63 and p73. FEBS Lett 2002; 525: 93–99.
Benard J, Douc-Rasy S, Ahomadegbe JC . TP53 family members and human cancers. Hum Mutat 2003; 21: 182–191.
Stiewe T, Theseling CC, Putzer BM . Transactivation-deficient Delta TA-p73 inhibits p53 by direct competition for DNA binding: implications for tumorigenesis. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 14177–14185.
Grob TJ, Novak U, Maisse C, Barcaroli D, Luthi AU, Pirnia F et al. Human delta Np73 regulates a dominant negative feedback loop for TAp73 and p53. Cell Death Differ 2001; 8: 1213–1223.
Kartasheva NN, Contente A, Lenz-Stoppler C, Roth J, Dobbelstein M . p53 induces the expression of its antagonist p73 Delta N, establishing an autoregulatory feedback loop. Oncogene 2002; 21: 4715–4727.
Vossio S, Palescandolo E, Pediconi N, Moretti F, Balsano C, Levrero M et al. DN-p73 is activated after DNA damage in a p53-dependent manner to regulate p53-induced cell cycle arrest. Oncogene 2002; 21: 3796–3803.
Stiewe T, Zimmermann S, Frilling A, Esche H, Putzer BM . Transactivation-deficient DeltaTA-p73 acts as an oncogene. Cancer Res 2002; 62: 3598–3602.
Fillippovich I, Sorokina N, Gatei M, Haupt Y, Hobson K, Moallem E et al. Transactivation-deficient p73alpha (p73Deltaexon2) inhibits apoptosis and competes with p53. Oncogene 2001; 20: 514–522.
Melino G, De Laurenzi V, Vousden KH . p73: friend or foe in tumorigenesis. Nat Rev Cancer 2002; 2: 605–615.
Gasco M, Crook T . p53 family members and chemoresistance in cancer: what we know and what we need to know. Drug Resist Updat 2003; 6: 323–328.
Strano S, Blandino G . p73-mediated chemosensitivity: a preferential target of oncogenic mutant p53. Cell Cycle 2003; 2: 348–349.
Irwin MS . Family feud in chemosensitvity: p73 and mutant p53. Cell Cycle 2004; 3: 319–323.
Bergamaschi D, Gasco M, Hiller L, Sullivan A, Syed N, Trigiante G et al. p53 polymorphism influences response in cancer chemotherapy via modulation of p73-dependent apoptosis. Cancer Cell 2003; 3: 387–402.
Pieters R, den Boer ML, Durian M, Janka G, Schmiegelow K, Kaspers GJ et al. Relation between age, immunophenotype and in vitro drug resistance in 395 children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia – implications for treatment of infants. Leukemia 1998; 12: 1344–1348.
Gump J, McGavran L, Wei Q, Hunger SP . Analysis of TP53 mutations in relapsed childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 2001; 23: 416–419.
Kawamura M, Ohnishi H, Guo SX, Sheng XM, Minegishi M, Hanada R et al. Alterations of the p53, p21, p16, p15 and RAS genes in childhood T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leuk Res 1999; 23: 115–126.
Peller S, Rotter V . TP53 in hematological cancer: low incidence of mutations with significant clinical relevance. Hum Mutat 2003; 21: 277–284.
Peters UR, Tschan MP, Kreuzer KA, Baskaynak G, Lass U, Tobler A et al. Distinct expression patterns of the p53-homologue p73 in malignant and normal hematopoiesis assessed by a novel real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction assay and protein analysis. Cancer Res 1999; 59: 4233–4236.
Leupin N, Luthi A, Novak U, Grob TJ, Hugli B, Graber H et al. P73 status in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Leuk Lymphoma 2004; 45: 1205–1207.
Rizzo MG, Giombini E, Diverio D, Vignetti M, Sacchi A, Testa U et al. Analysis of p73 expression pattern in acute myeloid leukemias: lack of DeltaN-p73 expression is a frequent feature of acute promyelocytic leukemia. Leukemia 2004; 18: 1804–1809.
Tschan MP, Grob TJ, Peters UR, Laurenzi VD, Huegli B, Kreuzer KA et al. Enhanced p73 expression during differentiation and complex p73 isoforms in myeloid leukemia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2000; 277: 62–65.
Novak U, Grob TJ, Baskaynak G, Peters UR, Aebi S, Zwahlen D et al. Overexpression of the p73 gene is a novel finding in high-risk B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Ann Oncol 2001; 12: 981–986.
Sahu GR, Das BR . Alteration of p73 in pediatric de novo acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2005; 327: 750–755.
Yuan ZM, Shioya H, Ishiko T, Sun X, Gu J, Huang YY et al. p73 is regulated by tyrosine kinase c-Abl in the apoptotic response to DNA damage. Nature 1999; 399: 814–817.
Kaspers GJ, Veerman AJ, Pieters R, Broekema GJ, Huismans DR, Kazemier KM et al. Mononuclear cells contaminating acute lymphoblastic leukaemic samples tested for cellular drug resistance using the methyl-thiazol-tetrazolium assay. Br J Cancer 1994; 70: 1047–1052.
Den Boer ML, Harms DO, Pieters R, Kazemier KM, Gobel U, Korholz D et al. Patient stratification based on prednisolone-vincristine-asparaginase resistance profiles in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Oncol 2003; 21: 3262–3268.
Stam RW, den Boer ML, Meijerink JP, Ebus ME, Peters GJ, Noordhuis P et al. Differential mRNA expression of Ara-C-metabolizing enzymes explains Ara-C sensitivity in MLL gene-rearranged infant acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2003; 101: 1270–1276.
Meijerink J, Mandigers C, van de Locht L, Tonnissen E, Goodsaid F, Raemaekers J . A novel method to compensate for different amplification efficiencies between patient DNA samples in quantitative real-time PCR. J Mol Diagn 2001; 3: 55–61.
O'Nions J, Brooks LA, Sullivan A, Bell A, Dunne B, Rozycka M et al. p73 is over-expressed in vulval cancer principally as the Delta 2 isoform. Br J Cancer 2001; 85: 1551–1556.
Douc-Rasy S, Barrois M, Echeynne M, Kaghad M, Blanc E, Raguenez G et al. DeltaN-p73alpha accumulates in human neuroblastic tumors. Am J Pathol 2002; 160: 631–639.
Zaika AI, Slade N, Erster SH, Sansome C, Joseph TW, Pearl M et al. DeltaNp73, a dominant-negative inhibitor of wild-type p53 and TAp73, is up-regulated in human tumors. J Exp Med 2002; 196: 765–780.
Irwin MS, Kondo K, Marin MC, Cheng LS, Hahn WC, Kaelin WG . Chemosensitivity linked to p73 function. Cancer Cell 2003; 3: 403–410.
Flores ER, Tsai KY, Crowley D, Sengupta S, Yang A, McKeon F et al. p63 and p73 are required for p53-dependent apoptosis in response to DNA damage. Nature 2002; 416: 560–564.
Casciano I, Mazzocco K, Boni L, Pagnan G, Banelli B, Allemanni G et al. Expression of DeltaNp73 is a molecular marker for adverse outcome in neuroblastoma patients. Cell Death Differ 2002; 9: 246–251.
Uramoto H, Sugio K, Oyama T, Nakata S, Ono K, Morita M et al. Expression of deltaNp73 predicts poor prognosis in lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2004; 10: 6905–6911.
Scaruffi P, Casciano I, Masiero L, Basso G, Romani M, Tonini GP . Lack of p73 expression in mature B-ALL and identification of three new splicing variants restricted to pre B and C-ALL indicate a role of p73 in B cell ALL differentiation. Leukemia 2000; 14: 518–519.
Kawano S, Miller CW, Gombart AF, Bartram CR, Matsuo Y, Asou H et al. Loss of p73 gene expression in leukemias/lymphomas due to hypermethylation. Blood 1999; 94: 1113–1120.
Liu M, Taketani T, Li R, Takita J, Taki T, Yang HW et al. Loss of p73 gene expression in lymphoid leukemia cell lines is associated with hypermethylation. Leuk Res 2001; 25: 441–447.
Corn PG, Kuerbitz SJ, van Noesel MM, Esteller M, Compitello N, Baylin SB et al. Transcriptional silencing of the p73 gene in acute lymphoblastic leukemia and Burkitt's lymphoma is associated with 5′ CpG island methylation. Cancer Res 1999; 59: 3352–3356.
Martinez-Delgado B, Melendez B, Cuadros M, Jose Garcia M, Nomdedeu J, Rivas C et al. Frequent inactivation of the p73 gene by abnormal methylation or LOH in non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. Int J Cancer 2002; 102: 15–19.
Acknowledgements
This study is supported by The Sophia Foundation for Medical Research (project number SSWO-322). We thank Ms Aranzazu Fariña Sarasqueta for participating in this study. In addition, we thank members of the Dutch Childhood Oncology Group (DCOG) and the German Cooperative Study Group for Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia (COALL) for their support of this study by collecting patient samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meier, M., den Boer, M., Meijerink, J. et al. Differential expression of p73 isoforms in relation to drug resistance in childhood T-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Leukemia 20, 1377–1384 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404288
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404288
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The p53 family member p73 in the regulation of cell stress response
Biology Direct (2021)
-
Clinical implications of the deregulated TP73 isoforms expression in cancer
Clinical and Translational Oncology (2018)
-
Regulating the genome surveillance system: miRNAs and the p53 super family
Apoptosis (2010)
-
Targeting survival cascades induced by activation of Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK, PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR and Jak/STAT pathways for effective leukemia therapy
Leukemia (2008)