Abstract
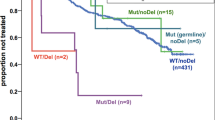
The G(-248)A polymorphism in the promoter region of the Bax gene was recently associated with low Bax expression, more advanced stage, treatment resistance and short overall survival in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), the latter particularly in treated patients. To investigate this further, we analyzed 463 CLL patients regarding the presence or absence of the G(-248)A polymorphism and correlated with overall survival, treatment status and known prognostic factors, for example, Binet stage, VH mutation status and genomic aberrations. In this material, similar allele and genotype frequencies of the Bax polymorphism were demonstrated in CLL patients and controls (n=207), where 19 and 21% carried this polymorphism, respectively, and no skewed distribution of the polymorphism was evident between different Binet stages and VH mutated and unmutated CLLs. Furthermore, no difference in overall survival was shown between patients displaying the G(-248)A polymorphism or not (median survival 85 and 102 months, respectively, P=0.21), and the polymorphism did not influence outcome specifically in treated CLL. Neither did the polymorphism affect outcome in prognostic subsets defined by VH mutation status or genomic aberrations. In conclusion, the pathogenic role and clinical impact of the Bax polymorphism is limited in CLL.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilar-Santelises M, Rottenberg ME, Lewin N, Mellstedt H, Jondal M . Bcl-2, Bax and p53 expression in B-CLL in relation to in vitro survival and clinical progression. Int J Cancer 1996; 69: 114–119.
McConkey DJ, Chandra J, Wright S, Plunkett W, McDonnell TJ, Reed JC et al. Apoptosis sensitivity in chronic lymphocytic leukemia is determined by endogenous endonuclease content and relative expression of BCL-2 and BAX. J Immunol 1996; 156: 2624–2630.
Pepper C, Hoy T, Bentley DP . Bcl-2/Bax ratios in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia and their correlation with in vitro apoptosis and clinical resistance. Br J Cancer 1997; 76: 935–938.
Schena M, Larsson LG, Gottardi D, Gaidano G, Carlsson M, Nilsson K et al. Growth- and differentiation-associated expression of bcl-2 in B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Blood 1992; 79: 2981–2989.
Faderl S, Keating MJ, Do KA, Liang SY, Kantarjian HM, O’Brien S et al. Expression profile of 11 proteins and their prognostic significance in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Leukemia 2002; 16: 1045–1052.
Zha H, Aime-Sempe C, Sato T, Reed JC . Proapoptotic protein Bax heterodimerizes with Bcl-2 and homodimerizes with Bax via a novel domain (BH3) distinct from BH1 and BH2. J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 7440–7444.
Saxena A, Viswanathan S, Moshynska O, Tandon P, Sankaran K, Sheridan DP . Mcl-1 and Bcl-2/Bax ratio are associated with treatment response but not with Rai stage in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Am J Hematol 2004; 75: 22–33.
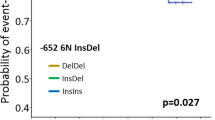
Saxena A, Moshynska O, Sankaran K, Viswanathan S, Sheridan DP . Association of a novel single nucleotide polymorphism, G(-248)A, in the 5′-UTR of BAX gene in chronic lymphocytic leukemia with disease progression and treatment resistance. Cancer Lett 2002; 187: 199–205.
Moshynska O, Moshynskyy I, Misra V, Saxena A . G125A single-nucleotide polymorphism in the human BAX promoter affects gene expression. Oncogene 2005; 24: 2042–2049.
Starczynski J, Pepper C, Pratt G, Hooper L, Thomas A, Milligan D et al. Common polymorphism G(-248)A in the promoter region of the bax gene results in significantly shorter survival in patients with chronic lymphocytic Leukemia once treatment is initiated. J Clin Oncol 2005; 23: 1514–1521.
Binet JL, Lepoprier M, Dighiero G, Charron D, D’Athis P, Vaugier G et al. A clinical staging system for chronic lymphocytic leukemia: prognostic significance. Cancer 1977; 40: 855–864.
Damle RN, Wasil T, Fais F, Ghiotto F, Valetto A, Allen SL et al. Ig V gene mutation status and CD38 expression as novel prognostic indicators in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 1999; 94: 1840–1847.
Hamblin TJ, Davis Z, Gardiner A, Oscier DG, Stevenson FK . Unmutated Ig V(H) genes are associated with a more aggressive form of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 1999; 94: 1848–1854.
Döhner H, Stilgenbauer S, Benner A, Leupolt E, Kröber A, Bullinger L et al. Genomic aberrations and survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med 2000; 343: 1910–1916.
Jaffe ES, Harris NL, Stein H, Vardiman JW . World Health Organization Classification of Tumours. Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. IARC Press: Lyon, 2001.
Li AH, Rosenquist R, Forestier E, Holmberg D, Lindh J, Löfvenberg E et al. Clonal rearrangements in childhood and adult precursor B acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a comparative polymerase chain reaction study using multiple sets of primers. Eur J Haematol 1999; 63: 211–218.
Li AH, Rosenquist R, Forestier E, Lindh J, Roos G . Detailed clonality analysis of relapsing precursor B acute lymphoblastic leukemia: implications for minimal residual disease detection. Leuk Res 2001; 25: 1033–1045.
Kröber A, Seiler T, Benner A, Bullinger L, Bruckle E, Lichter P et al. V(H) mutation status, CD38 expression level, genomic aberrations, and survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2002; 100: 1410–1416.
Tobin G, Thunberg U, Johnson A, Eriksson I, Söderberg O, Karlsson K et al. Chronic lymphocytic leukemias utilizing the VH3–21 gene display highly restricted Vlambda2–14 gene use and homologous CDR3s: implicating recognition of a common antigen epitope. Blood 2003; 101: 4952–4957.
Tobin G, Thunberg U, Laurell A, Karlsson K, Åleskog A, Willander K et al. Patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia with mutated VH genes presenting with Binet stage B or C form a subgroup with a poor outcome. Haematologica 2005; 90: 465–469.
Korz C, Pscherer A, Benner A, Mertens D, Schaffner C, Leupolt E et al. Evidence for distinct pathomechanisms in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia and mantle cell lymphoma by quantitative expression analysis of cell cycle and apoptosis-associated genes. Blood 2002; 99: 4554–4561.
Kienle DL, Korz C, Hosch B, Benner A, Mertens D, Habermann A et al. Evidence for distinct pathomechanisms in genetic subgroups of chronic lymphocytic leukemia revealed by quantitative expression analysis of cell cycle, activation, and apoptosis-associated genes. J Clin Oncol 2005; 23: 3780–3792.
el Rouby S, Thomas A, Costin D, Rosenberg CR, Potmesil M, Silber R et al. p53 gene mutation in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia is associated with drug resistance and is independent of MDR1/MDR3 gene expression. Blood 1993; 82: 3452–3459.
Döhner H, Fischer K, Bentz M, Hansen K, Benner A, Cabot G et al. p53 gene deletion predicts for poor survival and non-response to therapy with purine analogs in chronic B-cell leukemias. Blood 1995; 85: 1580–1589.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Drs Lars Klareskog and Leonid Padyukov and to the EIRA group for help with the collection of the normal control material. This study was supported by grants from the Swedish Cancer Society, Lion's Cancer Research Foundation, Uppsala, the research foundation of the Department of Oncology at Uppsala University, and Deutsche Krebshilfe (70-3183-Li1; Nr. 106116) and DFG STI 296/1-1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Skogsberg, Å., Tobin, G., Kröber, A. et al. The G(-248)A polymorphism in the promoter region of the Bax gene does not correlate with prognostic markers or overall survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 20, 77–81 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404030
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404030
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The role of FAS, FAS-L, BAX, and BCL-2 gene polymorphisms in determining susceptibility to unexplained recurrent pregnancy loss
Journal of Assisted Reproduction and Genetics (2019)
-
Polymorphism in apoptotic BAX (-248G>A) gene but not in anti-apoptotic BCL2 (-938C>A) gene and its protein and mRNA expression are associated with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia
Apoptosis (2015)
-
Influence of BCL2-938C>A and BAX-248G>A promoter polymorphisms in the development of AML: case–control study from South India
Tumor Biology (2015)
-
MicroRNA-223 is a novel negative regulator of HSP90B1 in CLL
BMC Cancer (2015)
-
BAX and CDKN1A polymorphisms correlated with clinical outcomes of gastric cancer patients treated with postoperative chemotherapy
Medical Oncology (2014)