Abstract
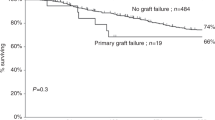
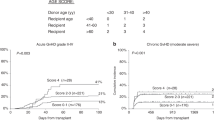
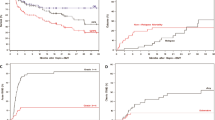
We report long-term outcome in 102 patients with cCML transplanted from an HLA-identical sibling donor from 1982 to 1998. The conditioning regimen was based on cyclophosphamide associated with either total body irradiation (TBI) (37 patients) or with busulfan (63 patients). Graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) prophylaxis consisted of cyclosporin and methotrexate in the majority of the patients. Fifteen year overall survival was estimated at 53% (95% confidence interval (CI), 44–65) with a plateau after 2.5 years. Long-term survival was adversely affected by: longer time from chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) diagnosis to transplantation, older age at time of transplantation and GvHD (acute grade III–IV or chronic extensive). The main cause of death was infection, related to GvHD in 69% of patients. Splenectomy also significantly increased the risk of bacterial infection. 15-year relapse was estimated at 8% (95% CI, 0.1–14). Late malignancies occurred in seven patients, four of whom had an invasive cancer. Other frequent late complications included cataracts, psychological depression, osteonecrosis and hypothyroidism. These complications were more frequent following splenectomy, TBI and in patients with chronic extensive GvHD. We conclude that allogeneic transplantation with a related donor can cure more than half of CML patients in chronic phase, although physicians should be alert to long-term complications.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Radich JP, Gooley T, Bensinger W, Chauncey T, Clift R, Flowers M et al. HLA-matched related hematopoietic cell transplantation for chronic-phase CML using a targeted busulfan and cyclophosphamide preparative regimen. Blood 2003; 102: 31–35.
Silver RT, Woolf SH, Hehlmann R, Appelbaum FR, Anderson J, Bennett C et al. An evidence-based analysis of the effect of busulfan, hydroxyurea, interferon, and allogeneic bone marrow transplantation in treating the chronic phase of chronic myeloid leukemia: developed for the American Society of Hematology. Blood 1999; 94: 1517–1536.
Socie G, Clift RA, Blaise D, Devergie A, Ringden O, Martin PJ et al. Busulfan plus cyclophosphamide compared with total-body irradiation plus cyclophosphamide before marrow transplantation for myeloid leukemia: long-term follow-up of 4 randomized studies. Blood 2001; 98: 3569–3574.
van Rhee F, Szydlo RM, Hermans J, Devergie A, Frassoni F, Arcese W et al. Long-term results after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for chronic myelogenous leukemia in chronic phase: a report from the Chronic Leukemia Working Party of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 1997; 20: 553–560.
Bonifazi F, de Vivo A, Rosti G, Guilhot F, Guilhot J, Trabacchi E et al. Chronic myeloid leukemia and interferon-alpha: a study of complete cytogenetic responders. Blood 2001; 98: 3074–3081.
Hehlmann R, Heimpel H, Hasford J, Kolb HJ, Pralle H, Hossfeld DK et al. Randomized comparison of interferon-alpha with busulfan and hydroxyurea in chronic myelogenous leukemia. The German CML Study Group. Blood 1994; 84: 4064–4077.
Hughes TP, Kaeda J, Branford S, Rudzki Z, Hochhaus A, Hensley ML et al. Frequency of major molecular responses to imatinib or interferon alfa plus cytarabine in newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 2003; 349: 1423–1432.
Talpaz M, Kantarjian HM, McCredie K, Trujillo JM, Keating MJ, Gutterman JU . Hematologic remission and cytogenetic improvement induced by recombinant human interferon alpha A in chronic myelogenous leukemia. N Engl J Med 1986; 314: 1065–1069.
Guilbert-Douet N, Morel F, Le Bris MJ, Berthou C, Morice P, Bourquard P et al. Clonal chromosomal abnormalities in the Philadelphia chromosome negative cells of chronic myeloid leukemia patients treated with imatinib. Leukemia 2004; 18: 1140–1142.
Gratwohl A, Hermans J, Goldman JM, Arcese W, Carreras E, Devergie A et al. Risk assessment for patients with chronic myeloid leukaemia before allogeneic blood or marrow transplantation. Chronic Leukemia Working Party of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Lancet 1998; 352: 1087–1092.
Glucksberg H, Storb R, Fefer A, Buckner CD, Neiman PE, Clift RA et al. Clinical manifestations of graft-versus-host disease in human recipients of marrow from HL-A-matched sibling donors. Transplantation 1974; 18: 295–304.
Shulman HM, Sullivan KM, Weiden PL, McDonald GB, Striker GE, Sale GE et al. Chronic graft-versus-host syndrome in man. A long-term clinicopathologic study of 20 Seattle patients. Am J Med 1980; 69: 204–217.
Kaplan ES, Meier P . Non parametric estimation from incomplete observations. J Am Stat Assoc 1958; 53: 457–481.
Gray RJ . Spline-based tests in survival analysis. Biometrics 1994; 50: 640–652.
Cox D . Regression models and life tables. J R Stat Soc 1972; 34: 187–220.
Devergie A, Reiffers J, Vernant JP, Herve P, Guyotat D, Maraninchi D et al. Long-term follow-up after bone marrow transplantation for chronic myelogenous leukemia: factors associated with relapse. Bone Marrow Transplant 1990; 5: 379–386.
Galimberti M, Polchi P, Lucarelli G, Angelucci E, Baronciani D, Giardini C et al. Allogeneic marrow transplantation in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase following preparation with busulfan and cyclophosphamide. Bone Marrow Transplant 1994; 13: 197–201.
Beelen DW, Graeven U, Elmaagacli AH, Niederle N, Kloke O, Opalka B et al. Prolonged administration of interferon-alpha in patients with chronic-phase Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myelogenous leukemia before allogeneic bone marrow transplantation may adversely affect transplant outcome. Blood 1995; 85: 2981–2990.
Hehlmann R, Hochhaus A, Kolb HJ, Hasford J, Gratwohl A, Heimpel H et al. Interferon-alpha before allogeneic bone marrow transplantation in chronic myelogenous leukemia does not affect outcome adversely, provided it is discontinued at least 90 days before the procedure. Blood 1999; 94: 3668–3677.
Morton AJ, Gooley T, Hansen JA, Appelbaum FR, Bruemmer B, Bjerke JW et al. Association between pretransplant interferon-alpha and outcome after unrelated donor marrow transplantation for chronic myelogenous leukemia in chronic phase. Blood 1998; 92: 394–401.
Aschan J, Ringden O, Sundberg B, Klaesson S, Ljungman P, Lonnqvist B . Increased risk of relapse in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia given T-cell depleted marrow compared to methotrexate combined with cyclosporin or monotherapy for the prevention of graft-versus-host disease. Eur J Haematol 1993; 50: 269–274.
Clift RA, Radich J, Appelbaum FR, Martin P, Flowers ME, Deeg HJ et al. Long-term follow-up of a randomized study comparing cyclophosphamide and total body irradiation with busulfan and cyclophosphamide for patients receiving allogenic marrow transplants during chronic phase of chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 1999; 94: 3960–3962.
Devergie A, Blaise D, Attal M, Tigaud JD, Jouet JP, Vernant JP et al. Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for chronic myeloid leukemia in first chronic phase: a randomized trial of busulfan-cytoxan versus cytoxan-total body irradiation as preparative regimen: a report from the French Society of Bone Marrow Graft (SFGM). Blood 1995; 85: 2263–2268.
DeAngelo DJ, Hochberg EP, Alyea EP, Longtine J, Lee S, Galinsky I et al. Extended follow-up of patients treated with imatinib mesylate (gleevec) for chronic myelogenous leukemia relapse after allogeneic transplantation: durable cytogenetic remission and conversion to complete donor chimerism without graft-versus-host disease. Clin Cancer Res 2004; 10: 5065–5071.
Guglielmi C, Arcese W, Dazzi F, Brand R, Bunjes D, Verdonck LF et al. Donor lymphocyte infusion for relapsed chronic myelogenous leukemia: prognostic relevance of the initial cell dose. Blood 2002; 100: 397–405.
Kantarjian HM, O'Brien S, Cortes JE, Giralt SA, Rios MB, Shan J et al. Imatinib mesylate therapy for relapse after allogeneic stem cell transplantation for chronic myelogenous leukemia. Blood 2002; 100: 1590–1595.
Olavarria E, Ottmann OG, Deininger M, Clark RE, Bandini G, Byrne J et al. Response to imatinib in patients who relapse after allogeneic stem cell transplantation for chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2003; 17: 1707–1712.
Koh LP, Hwang WY, Tan CH, Linn YC, Goh YT, Chuah CT et al. Long term follow-up of Asian patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) receiving allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) from HLA-identical sibling-evaluation of risks and benefits. Ann Hematol 2004; 83: 286–294.
Engelhard D, Cordonnier C, Shaw PJ, Parkalli T, Guenther C, Martino R et al. Early and late invasive pneumococcal infection following stem cell transplantation: a European Bone Marrow Transplantation survey. Br J Haematol 2002; 117: 444–450.
Kulkarni S, Powles R, Treleaven J, Riley U, Singhal S, Horton C et al. Chronic graft versus host disease is associated with long-term risk for pneumococcal infections in recipients of bone marrow transplants. Blood 2000; 95: 3683–3686.
Ribaud P, Chastang C, Latge JP, Baffroy-Lafitte L, Parquet N, Devergie A et al. Survival and prognostic factors of invasive aspergillosis after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Clin Infect Dis 1999; 28: 322–330.
Bittencourt H, Rocha V, Chevret S, Socie G, Esperou H, Devergie A et al. Association of CD34 cell dose with hematopoietic recovery, infections, and other outcomes after HLA-identical sibling bone marrow transplantation. Blood 2002; 99: 2726–2733.
Kalhs P, Schwarzinger I, Anderson G, Mori M, Clift RA, Storb R et al. A retrospective analysis of the long-term effect of splenectomy on late infections, graft-versus-host disease, relapse, and survival after allogeneic marrow transplantation for chronic myelogenous leukemia. Blood 1995; 86: 2028–2032.
Curtis RE, Rowlings PA, Deeg HJ, Shriner DA, Socie G, Travis LB et al. Solid cancers after bone marrow transplantation. N Engl J Med 1997; 336: 897–904.
Cohen A, Rovelli A, Bakker B, Uderzo C, van Lint MT, Esperou H et al. Final height of patients who underwent bone marrow transplantation for hematological disorders during childhood: a study by the Working Party for Late Effects-EBMT. Blood 1999; 93: 4109–4115.
Zierhut D, Lohr F, Schraube P, Huber P, Wenz F, Haas R et al. Cataract incidence after total-body irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2000; 46: 131–135.
Clift RA, Buckner CD, Thomas ED, Bensinger WI, Bowden R, Bryant E et al. Marrow transplantation for chronic myeloid leukemia: a randomized study comparing cyclophosphamide and total body irradiation with busulfan and cyclophosphamide. Blood 1994; 84: 2036–2043.
Ringden O, Ruutu T, Remberger M, Nikoskelainen J, Volin L, Vindelov L et al. A randomized trial comparing busulfan vs total body irradiation in allogeneic marrow transplant recipients with hematological malignancies. Transplant Proc 1994; 26: 1831–1832.
Chronowski GM, Wilder RB, Levy LB, Atkinson EN, Ha CS, Hagemeister FB et al. Second malignancies after chemotherapy and radiotherapy for Hodgkin disease. Am J Clin Oncol 2004; 27: 73–80.
Friedberg JW, Neuberg D, Stone RM, Alyea E, Jallow H, LaCasce A et al. Outcome in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome after autologous bone marrow transplantation for non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 1999; 17: 3128–3135.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Robin, M., Guardiola, P., Devergie, A. et al. A 10-year median follow-up study after allogeneic stem cell transplantation for chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase from HLA-identical sibling donors. Leukemia 19, 1613–1620 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2403821
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2403821
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Late Complications of Allogenic Stem Cells Transplantation in Leukaemia
Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine (2019)
-
Bacterial meningitis in hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients: a population-based prospective study
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2016)
-
Imatinib results in better outcomes than HLA-identical sibling transplants in young persons with newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myelogenous leukemia
Leukemia (2013)
-
Osteoporosis after Stem Cell Transplantation
Current Osteoporosis Reports (2013)
-
Passé et futur de la LMC: allogreffe de CSH, omacetaxine et ponatinib
Oncologie (2012)