Abstract
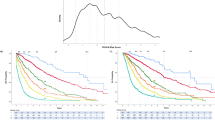
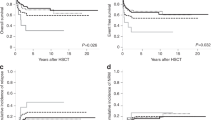
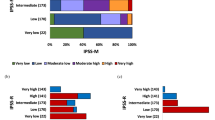
The impact of clinical parameters, International Prognostic Scoring System (IPSS) scores/cytogenetic categories, and some single cytogenetic defects on overall survival (OS) and time to myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS)/AML progression (progression-free interval (PFI)) was evaluated in 331 MDS patients. Statistical analysis demonstrated that OS and PFI were significantly affected by all these parameters. Since single 7q- showed a better survival than the poor IPSS cytogenetic category (P=0.009), it was considered as a new prognostic entity (‘modified IPSS categories’). In multivariate analysis OS was significantly influenced by age, marrow blast cell percentage, number of cytopenias and either modified or standard IPSS cytogenetic categories; hazard ratios for MDS/AML progression were influenced by all the former, except for age and cytopenias. Multivariate analysis of del(7)(q31q35) confirmed the results of univariate analysis, but the Akaike Information Criterion showed no difference in evaluating OS and PFI between the modified and standard IPSS cytogenetic grouping. In conclusion, (i) chromosome defects as grouped by IPSS and blast cell percentage are the most relevant parameters for predicting OS and PFI; (ii) the prognostic power of the IPSS cytogenetic grouping is not ameliorated by the introduction of del(7)(q31q35) as a new entity; (iii) complex karyotypes have a prognostic value independent of blast cell percentage.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aul C, Bowen DT, Yoshida Y . Pathogenesis, etiology and epidemiology of myelodysplastic syndromes. Haematologica 1998; 83: 71–86.
Bennett JM, Catovsky D, Daniel MT, Flandrin G, Galton DAG, Gralnick HR et al. Proposal for the classification of the myelodysplastic syndromes. Br J Haematol 1982; 51: 189–199.
Fenaux P, Morel P, Lai JL . Cytogenetics of myelodysplastic syndromes. Semin Hematol 1996; 33: 127–138.
Jotterand M, Parlier V . Diagnostic and prognostic significance of cytogenetics in adult primary myelodysplastic syndromes. Leukemia and Lymphoma 1996; 23: 253–266.
Olney HJ, Le Beau MM . The cytogenetics of myelodysplastic syndromes. Best Pract Res Clin Hematol 2001; 14: 479–495.
Tricot G, Boogaerts MA, De Wolf-Peeters C, van den Berghe H, Verwilghen RL . The myelodysplastic syndromes: different evolution patterns based on sequential morphological and cytogenetic investigations. Br J Haematol 1985; 59: 659–670.
Yunis JJ, Lobell M, Arnesen MA, Oken MM, Mayer MG, Rydell RE et al. Refined chromosome study helps define prognostic subgroups in most patients with primary myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myelogenous leukaemia. Br J Haematol 1988; 68: 189–194.
Jacobs RH, Cornbleet MA, Vardiman JW, Larson RA, Le Beau MM, Rowley JD . Prognostic implications of morphology and karyotype in primary myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 1986; 67: 1765–1772.
Pierre RV, Catovsky D, Mufti GJ, Swansbury GJ, Mecucci C, Dewald GW et al. Clinical–cytogenetic correlations in myelodysplasia (preleukemia). Cancer Genet Cytogenet 1989; 40: 149–161.
Mufti GJ, Stevens JR, Oscier DG, Hamblin TJ, Machin D . Myelodysplastic syndromes: a scoring system with prognostic significance. Br J Haematol 1985; 59: 425–433.
Sanz GF, Sanz MA, Vallespi T, Canizo MC, Torrabadella M, Garcia S et al. Two regression models and a scoring system for predicting survival and planning treatment in myelodysplastic syndromes: a multivariate analysis of prognostic factors in 370 patients. Blood 1989; 74: 395–408.
Aul C, Gattermann N, Heyll A, Germing U, Derigs G, Schneider W . Primary myelodysplastic syndromes: analysis of prognostic factors in 235 patients and proposal for an improved scoring system. Leukemia 1992; 6: 52–59.
Morel P, Hebbar M, Lai JL, Duhamel A, Preudhomme C, Wattel E et al. Cytogenetic analysis has strong independent prognostic value in de novo myelodysplastic syndromes and can be incorporated in a new scoring system: a report on 408 cases. Leukemia 1993; 9: 1315–1323.
Toyama K, Ohyashiki K, Yoshida Y, Abe T, Asano S, Hirai H et al. Clinical implications of chromosome abnormalities in 401 patients with myelodysplastic syndromes: a multicentric study in Japan. Leukemia 1993; 7: 499–508.
Greenberg P, Cox C, Le Beau MM, Fenaux P, Morel P, Sanz G et al. International system for evaluating prognosis in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 1997; 89: 2079–2088.
Mitelman F (ed) ISCN: An International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature. Basel: S. Karger, 1995.
Kaplan E, Meier P . Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations. J Am Statisti Assoc 1958; 53: 457–481.
Suciu S, Kuse R, Weh HJ, Hossfeld DK . Results of chromosome studies and their relation to morphology, course, and prognosis in 120 patients with de novo myelodysplastic syndrome. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 1990; 44: 15–26.
Solè F, Prieto F, Badia L, Woessner S, Florensa L, Caballin MR et al. Cytogenetic studies in 112 cases of untreated myelodysplastic syndromes. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 1992; 64: 12–20.
Parlier V, van Melle G, Beris P, Schmidt PM, Tobler A, Haller E et al. Hematologic, clinical, and cytogenetic analysis in 109 patients with primary myelodysplastic syndrome. Prognostic significance of morphology and chromosome findings. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 1994; 78: 219–231.
Bernasconi P, Alessandrino EP, Boni M, Bonfichi M, Morra E, Lazzarino M et al. Karyotype in myelodysplastic syndromes: relations to morphology, clinical evolution and survival. Am J Hematol 1994; 46: 270–277.
Haase D, Fonatsch C, Freund M, Wörmann B, Bodenstein H, Bartels H et al. Cytogenetic findings in 179 patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Ann Hematol 1995; 70: 171–187.
Pfeilstöcker M, Reisner R, Nösslinger T, Grüner H, Nowotny H, Tüchler H et al. Cross-validation of prognostic scores in myelodysplastic sybdromes on 386 patients from a single intitution confirms the importance of cytogenetics. Br J Haematol 1999; 106: 455–463.
Solè F, Espinet B, Sanz G, Cervera J, Calasanz MJ, Luno E et al. Incidence, characterization and prognostic significance of chromosomal abnormalities in 640 patients with primary myelodysplastic syndromes. Br J Haematol 2000; 108: 346–356.
Nösslinger T, Reisner R, Koller E, Grüner H, Tüchler H, Nowotny H et al. Myelodysplastic syndromes, from French–American–British to World Health Organization: comparison of classifications on 431 unselected patients from a single institution. Blood 2001; 98: 2935–2941.
Mauritzson N, Johansson B, Rylander L, Albin M, Strömberg U, Billström R et al. The prognostic impact of karyotypic subgroups in myelodysplastic syndromes is strongly modified by sex. Br J Haematol 2001; 113: 347–356.
Nevill T, Fung HC, Shepherd JD, Horsman DE, Nantel SH, Klingemann HG et al. Cytogenetic abnormalities in primary myelodysplastic syndrome are highly predictive of outcome after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Blood 1998; 92: 1910–1917.
Oosterveld M, Wittebol SH, Lemmens WA, Kiemeney BA, Catik A, Muus P et al. The impact of intensive antileukemic treatment strategies on prognosis of myelodysplastic syndrome patients aged less than 61 years according to International Prognostic Scoring System risk groups. Br J Haematol 2003; 123: 81–89.
Germing U, Gattermann N, Strupp C, Aivado M, Aul C . Validation of the WHO proposal for a new classification of primary myelodysplastic syndromes: a retrospective analysis of 1600 patients. Leuk Res 2000; 24: 983–992.
Zhao WL, Xu L, Wu W, Tang W, Hu J, Chen Y et al. The myelodysplastic syndromes. Analysis of prognostic factors and comparison of prognostic systems in 128 Chinese patients from a single institution. Hematol J 2002; 3: 137–144.
Washington LT, Doherty D, Glassman A, Martins J, Ibrahim S, Lai R . Myeloid disorders with deletion 5q as the sole karyotypic abnormality: the clinical and pathologic spectrum. Leukemia Lymphoma 2002; 43: 761–765.
Giagounidis AAN, Germing U, Haase S, Hildebrandt B, Schlegelberger B, Schoch C et al. Clinical, morphological, cytogenetic, and prognostic features of patients with myelodysplastic syndromes and del(5q) including band q31. Leukemia 2004; 18: 113–119.
Èermàk J, Michalova K, Bøezinovà J, Zemanova Z . A prognostic impact of separation of refractory cytopenia with multilineage dysplasia and 5q- syndrome from refractory anemia in primary myelodysplastic syndrome. Leuk Res 2003; 27: 221–229.
Pedersen B . 5q-: does longer survival of female patients explain the preponderance. Anticancer Res 1997; 17: 3281–3285.
Dewald GW, Davis MP, Pierre RV, O'Fallon JR, Hoagland HC . Clinical characteristics and prognosis of 50 patients with a myeloproliferative syndrome and deletion of part of the long arm of chromosome 5. Blood 1985; 66: 189–197.
Pedersen B, Jensen M . Clinical and prognostic implications of chromosome 5q deletions: 96 high resolution studied patients. Leukemia 1991; 5: 52–59.
Pasquali F, Bernasconi P, Casalone R, Fraccaro M, Bernasconi C, Lazzarino M et al. Pathogenetic significance of ‘pure’ monosomy 7 in myeloproliferative disorders. Analysis of 14 cases. Hum Genet 1982; 62: 40–51.
Velloso ER, Michaux L, Ferrant A, Hernandez JM, Meeus P, Dierlam J et al. Deletions of the long arm of chromosome 7 in myeloid disorders:loss of band 7q32 implies worst prognosis. Br J Haematol 1996; 92: 574–581.
Johnson E, Cotter FE . Monosomy 7 and 7q- associated with myeloid malignancy. Blood Rev 1997; 11: 46–55.
Le Beau MM, Espinosa III R, Davis EM, Eisenbart JD, Larson RA, Green ED . Cytogenetic and molecular delineation of a region of chromosome 7 commonly deleted in malignant myeloid diseases. Blood 1996; 88: 1930–1935.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bernasconi, P., Klersy, C., Boni, M. et al. Incidence and prognostic significance of karyotype abnormalities in de novo primary myelodysplastic syndromes: a study on 331 patients from a single institution. Leukemia 19, 1424–1431 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2403806
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2403806
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Impact of somatic mutations in myelodysplastic patients with isolated partial or total loss of chromosome 7
Leukemia (2020)
-
Genetic abnormalities and pathophysiology of MDS
International Journal of Clinical Oncology (2019)
-
Atypical ringed sideroblasts in association with trisomy 19 and myelodysplasia
Comparative Clinical Pathology (2012)
-
Does cytogenetic evolution have any prognostic relevance in myelodysplastic syndromes? A study on 153 patients from a single institution
Annals of Hematology (2010)
-
Analysis of WHO-based Prognostic Scoring System (WPSS) of myelody-splastic syndrome and its comparison with international prognostic scoring system (IPSS) in 100 Chinese patients
Chinese Journal of Cancer Research (2009)