Abstract
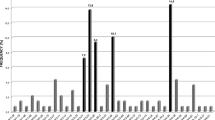
Recognition of biased immunoglobulin variable (IgV) gene usage in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL) may yield insight into leukemogenesis and may help to refine prognostic categories. We explored Ig variable heavy (VH) and light (VL) chain gene usage in highly stable and indolent B-CLL (n=25) who never required treatment over 10 or more years. We observed an unexpectedly high usage of mutated VH3-72 (6/25; 24.0%), a gene that was otherwise rare in B-CLL (7/805; 0.87%; P<0.01), including mutated cases (6/432; 1.39%; P<0.01) and was exceptional among indolent (1/230, 0.435%; P<0.01), and aggressive B-cell lymphomas (0/105; P<0.01). Three of six VH3-72 B-CLL cases utilized the same VL Vκ4-1 gene. Two VH3-72 B-CLL cases had highly homologous VH complementarity determining regions 3 (CDR3s), encoding Cys-XXXX-Cys domains, and utilized Vκ4-1 genes with homologous IgVL CDR3s. An identical threonine to isoleucine change at codon 84 of VH3-72 framework region 3 (FR3) recurred in four cases of highly stable VH3-72 B-CLL. This mutation is expected to cause a conformational change of FR3 proximal to CDR3 that might critically affect high-affinity antigen binding. B-cell receptors encoded by VH3-72 may identify a specific B-CLL group and be implicated in leukemogenesis through an antigen-driven expansion of B cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Damle RN, Wasil T, Fais F, Ghiotto F, Valetto A, Allen SL et al. Ig V gene mutation status and CD38 expression as novel prognostic indicators in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 1999; 94: 1840–1847.
Hamblin TJ, Davis Z, Gardiner A, Oscier DG, Stevenson FK . Unmutated Ig V(H) genes are associated with a more aggressive form of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 1999; 94: 1848–1854.
Crespo M, Bosch F, Villamor N, Bellosillo B, Colomer D, Rozman M et al. ZAP-70 expression as a surrogate for immunoglobulin-variable-region mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med 2003; 348: 1764–1775.
Dighiero G . Unsolved issues in CLL biology and management. Leukemia 2003; 17: 2385–2391.
Keating MJ, Chiorazzi N, Messmer B, Damle RN, Allen SL, Rai KR et al. Biology and treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Hematology 2003, 153–175.
Stevenson FK, Caligaris-Cappio F . Chronic lymphocytic leukemia: revelations from the B-cell receptor. Blood 2004; 103: 4389–4395.
Johnson TA, Rassenti LZ, Kipps TJ . Ig VH1 genes expressed in B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia exhibit distinctive molecular features. J Immunol 1997; 158: 235–246.
Fais F, Ghiotto F, Hashimoto S, Sellars B, Valetto A, Allen SL et al. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells express restricted sets of mutated and unmutated antigen receptors. J Clin Invest 1998; 102: 1515–1525.
Widhopf II GF, Kipps T . Normal B-cells express 51p1-encoded Ig heavy chains that are distinct from those expressed by chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells. J Immunol 2001; 166: 95–102.
Tobin G, Thunberg U, Johnson A, Thorn I, Soderberg O, Hultdin M et al. Somatically mutated Ig VH3-21 genes characterize a new subset of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2002; 99: 2262–2264.
Potter K, Orchard J, Critchley E, Mockridge CJ, Jose A, Stevenson FK . Features of overexpressed V1-69 genes in the unmutated subset of chronic lymphocytic leukemia are distinct from those in the healthy elderly repertoire. Blood 2003; 101: 3082–3084.
Tobin G, Thunberg U, Johnson A, Eriksson I, Soderberg O, Karlsson K et al. Chronic lymphocytic leukemias utilizing the VH3-21 gene display highly restricted Vλ2-14 gene use and homologous CDR3s: implicating recognition of a common antigen epitope. Blood 2003; 101: 4952–4957.
Ghiotto F, Fais F, Valetto A, Albesiano E, Hashimoto S, Dono M et al. Remarkably similar antigen receptors among a subset of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Invest 2004; 113: 1008–1016.
Tobin G, Thunberg U, Karlsson K, Murray F, Laurell A, Willander K et al. Subsets with restricted immunoglobulin gene rearrangement features indicate a role for antigen selection in the development of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Blood 2004, June 24 [Epub ahead of print].
Widhopf II GF, Rassenti L, Toy TL, Gribben JG, Wierda WG, Kipps T . Chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells of over one percent of patients express virtually identical immunoglobulins. Blood 2004, June 24 [Epub ahead of print].
Kolar GR, Capra JD . Ig V restrictions in human chronic lymphocytic leukemia suggest some cases have a common origin. J Clin Invest 2004; 113: 952–954.
Guarini A, Gaidano G, Mauro FR, Capello D, Mancini F, De Propris MS et al. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients with highly stable and indolent disease show distinctive phenotypic and genotypic features. Blood 2003; 102: 1035–1041.
Küppers R, Zhao M, Hansmann M-L, Rajewsky K . Tracing B cell development in human germinal centres by molecular analysis of single cells picked from histological sections. EMBO J 1993; 12: 4955–4967.
Fais F, Gaidano G, Capello D, Gloghini A, Ghiotto F, Roncella S et al. Immunoglobulin V region gene use and structure suggest antigen selection in AIDS-related primary effusion lymphomas. Leukemia 1999; 13: 1093–1099.
Farner NL, Dörner T, Lipsky PE . Molecular mechanisms and selection influence the generation of the human VλJλ repertoire. J Immunol 1999; 162: 2137–2145.
Capello D, Cerri M, Muti G, Berra E, Oreste P, Deambrogi C et al. Molecular histogenesis of posttransplantation lymphoproliferative disorders. Blood 2003; 102: 3775–3785.
Klein U, Küppers R, Rajewsky K . Variable gene analysis of B cell subsets derived from a 4-year-old child. Somatically mutated memory B cells accumulate in the peripheral blood already at young age. J Exp Med 1994; 180: 1383–1393.
Corbett SJ, Tomlinson IM, Sonnhammer ELL, Buck D, Winter G . Sequence of the human immunoglobulin diversity (D) segment locus: a systematic analysis provides no evidence for the use of DIR segments, inverted D segments, ‘minor’ D segments or D-D recombinations. J Mol Biol 1997; 270: 587–597.
Kabat EA, Wu TT, Perry HM, Gottesman KS, Foeller C . Sequences of Proteins of Immunological Interest, 5th edn. National Institute of Health (US) publication; no. 91–3242. Bethesda, MD: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Public Health Service National Institute of Health, 1991.
Chang B, Casali P . The CDR1 sequences of a major proportion of human germline Ig VH genes are inherently susceptible to amino acid replacement. Immunol Today 1994; 15: 367–373.
Lossos IS, Tibshirani N, Narasimhan B, Levy R . The inference of antigen selection on Ig genes. J Immunol 2000; 165: 5122–5126.
Demaison C, David D, Letourner F, Théze J, Saragosti S, Zouali M . Analysis of human VH gene repertoire expression in peripheral CD19+ B cells. Immunogenetics 1995; 42: 342–352.
Suzuki I, Pfister L, Glas A, Nottenburg C, Milner ECB . Representation of rearranged VH gene segments in the human adult antibody repertoire. J Immunol 1995; 154: 3902–3911.
Brezinschek H-P, Foster SJ, Brezinschek RI, Dörner T, Domiati-Saad R, Lipsky PE . Analysis of the human VH gene repertoire. J Clin Invest 1997; 99: 2488–2501.
Kraj P, Rao SP, Glas AM, Hardy RR, Milner ECB, Silberstain LE . The human heavy chain IgV region gene repertoire is biased at all stages of B cell ontogeny, including early pre-B cells. J Immunol 1997; 158: 5824–5832.
Rao SP, Riggs JM, Friedman DF, Scully MS, LeBien TK, Silberstein LE . Biased VH gene usage in early lineage human B cells: evidence for preferential Ig gene rearrangement in the absence of selection. J Immunol 1999; 163: 2732–2740.
Wang X, Stollar D . Immunoglobulin VH gene expression in human aging. Clin Immunol 1999; 93: 132–142.
Cox JPL, Tomlinson IM, Winter G . A directory of human germ-line Vk segments reveals a strong bias in their usage. Eur J Immunol 1994; 24: 827–836.
Foster SJ, Brezinschek H-P, Brezinschek RI, Lipsky PE . Molecular mechanisms and selective influences that shape the kappa gene repertoire of IgM+ B cells. J Clin Invest 1997; 99: 1614–1627.
Tomlinson IM, Walter G, Marks JD, Llevelyn MB, Winter G . The repertoire of human germline VH sequences reveals about fifty groups of VH segments with different hypervariable loops. J Mol Biol 1992; 227: 776–798.
Matsuda F, Ishii K, Bourvagnet P, Kuma K, Hayashida H, Miyata T et al. The complete nucleotide sequence of the human immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region locus. J Exp Med 1998; 188: 2151–2162.
Raaphorst FM, Raman CS, Tami J, Fischbach M, Sanz I . Human Ig heavy chain CDR3 regions in adult bone marrow pre-B cells display an adult phenotype of diversity: evidence for structural selection of DH amino acid sequences. Int Immunol 1997; 9: 1503–1515.
Zemlin M, Bauer K, Hummel M, Pfeiffer S, Devers S, Zemlin C et al. The diversity of rearranged immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region genes in peripheral blood B cells of preterm infants is restricted by short third complementarity-determining regions but not by limited gene segment usage. Blood 2001; 97: 1511–1513.
Acknowledgements
This study has been supported by Progetto Strategico Oncologia, CNR-MIUR, Rome, Italy; Cofin 2002 – MIUR, Rome, Italy; Ricerca Finalizzata 2002, Ministero della Salute, Rome, Italy; Regione Piemonte, Torino, Italy; Novara-AIL Onlus, Novara, Italy; and Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (AIRC), Milano, Italy. EB has been supported by Fondazione ‘Piera Pietro Giovanni Ferrero’, Alba, Italy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Capello, D., Guarini, A., Berra, E. et al. Evidence of biased immunoglobulin variable gene usage in highly stable B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 18, 1941–1947 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2403537
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2403537
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Mimicking the tumour microenvironment of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia in vitro critically depends on the type of B-cell receptor stimulation
British Journal of Cancer (2016)
-
Prognostic signature and clonality pattern of recurrently mutated genes in inactive chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Blood Cancer Journal (2015)
-
Telomere length is an independent predictor of survival, treatment requirement and Richter's syndrome transformation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Leukemia (2009)
-
Telomere length identifies two different prognostic subgroups among VH-unmutated B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients
Leukemia (2007)
-
Chromosome abnormalities with prognostic impact in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Pathology & Oncology Research (2005)