Abstract
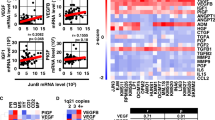
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) controls angiogenesis and glycolysis, two leading characteristics of solid tumor invasion, metastasis, and lethality. Increased angiogenesis is also found in the bone marrow (BM) of leukemias. Less is known in leukemia about the role of HIF-1 and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), the most important proangiogenic target gene of HIF-1. We show by immunohistochemistry that the oxygen-regulated component of HIF-1 (HIF-1α) is overexpressed in clusters of leukemic cells in BM specimens of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and absent in biopsies of normal BM. Half the HIF-1α-positive ALL biopsies exhibited VEGF coexpression. Among 96 children with relapsed ALL, diagnostic BM aspirates with high VEGF mRNA levels were associated with a significantly lower probability of event-free survival at 3 years (0.31±0.08 vs 0.65±0.07, P=0.003). Those with poor molecular response to therapy (evaluated by MRD assessment) had 2.2-fold higher VEGF levels than those responding well to chemotherapy (P=0.005). In conclusion, the data demonstrate activation of the HIF pathway in the BM of ALL patients and indicate that the expression of HIF target genes, such as VEGF, play an important role in leukemia progression, therapy response, and outcome.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carmeliet P, Jain RK . Angiogenesis in cancer and other diseases. Nature 2000; 407: 249–257.
Neufeld G, Cohen T, Gengrinovitch S, Poltorak Z . Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its receptors. FASEB J 1999; 13: 9–22.
Folkman J, D'Amore PA . Blood vessel formation: what is its molecular basis? Cell 1996; 87: 1153–1155.
Gerber HP, Ferrara N . The role of VEGF in normal and neoplastic hematopoiesis. J Mol Med 2003; 81: 20–31.
Perez Atayde AR, Sallan SE, Tedrow U, Connors S, Allred E, Folkman J . Spectrum of tumor angiogenesis in the bone marrow of children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Am J Pathol 1997; 150: 815–821.
Aguayo A, Kantarjian H, Manshouri T, Gidel C, Estey E, Thomas D et al. Angiogenesis in acute and chronic leukemias and myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 2000; 96: 2240–2245.
Pule MA, Gullmann C, Dennis D, McMahon C, Jeffers M, Smith OP . Increased angiogenesis in bone marrow of children with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia has no prognostic significance. Br J Haematol 2002; 118: 991–998.
Aguayo A, Estey E, Kantarjian H, Mansouri T, Gidel C, Keating M et al. Cellular vascular endothelial growth factor is a predictor of outcome in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 1999; 94: 3717–3721.
Verstovsek S, Kantarjian H, Manshouri T, Cortes J, Giles FJ, Rogers A et al. Prognostic significance of cellular vascular endothelial growth factor expression in chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 2002; 99: 2265–2267.
Jeha S, Smith FO, Estey E, Shen Y, Liu D, Manshouri T et al. Comparison between pediatric acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and adult AML in VEGF and KDR (VEGF-R2) protein levels. Leuk Res 2002; 26: 399–402.
De Bont ES, Fidler V, Meeuwsen T, Scherpen F, Hahlen K, Kamps WA . Vascular endothelial growth factor secretion is an independent prognostic factor for relapse-free survival in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia patients. Clin Cancer Res 2002; 8: 2856–2861.
Koomagi R, Zintl F, Sauerbrey A, Volm M . Vascular endothelial growth factor in newly diagnosed and recurrent childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia as measured by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Clin Cancer Res 2001; 7: 3381–3384.
Maxwell PH, Dachs GU, Gleadle JM, Nicholls LG, Harris AL, Stratford IJ et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 modulates gene expression in solid tumors and influences both angiogenesis and tumor growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997; 94: 8104–8109.
Wenger RH . Cellular adaptation to hypoxia: O2-sensing protein hydroxylases, hypoxia-inducible transcription factors, and O2-regulated gene expression. FASEB J 2002; 16: 1151–1162.
Harris AL . Hypoxia – a key regulatory factor in tumour growth. Nat Rev Cancer 2002; 2: 38–47.
Scortegagna M, Morris MA, Oktay Y, Bennett M, Garcia JA . The HIF family member EPAS1/HIF-2alpha is required for normal hematopoiesis in mice. Blood 2003; 102: 1634–1640.
Ishikawa Y, Ito T . Kinetics of hemopoietic stem cells in a hypoxic culture. Eur J Haematol 1988; 40: 126–129.
Chow DC, Wenning LA, Miller WM, Papoutsakis ET . Modeling pO(2) distributions in the bone marrow hematopoietic compartment. I. Krogh's model. Biophys J 2001; 81: 675–684.
Chow DC, Wenning LA, Miller WM, Papoutsakis ET . Modeling pO(2) distributions in the bone marrow hematopoietic compartment. II. Modified Kroghian models. Biophys J 2001; 81: 685–696.
Weiss L, Geduldig U . Barrier cells: stromal regulation of hematopoiesis and blood cell release in normal and stressed murine bone marrow. Blood 1991; 78: 975–990.
Kojima H, Gu H, Nomura S, Caldwell CC, Kobata T, Carmeliet P et al. Abnormal B lymphocyte development and autoimmunity in hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha-deficient chimeric mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 2170–2174.
Adelman DM, Maltepe E, Simon MC . HIF-1 is essential for multilineage hematopoiesis in the embryo. Adv Exp Med Biol 2000; 475: 275–284.
Henze G, Fengler R, Hartmann R, Kornhuber B, Janka-Schaub G, Niethammer D et al. Six-year experience with a comprehensive approach to the treatment of recurrent childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL-REZ BFM 85). A relapse study of the BFM group. Blood 1991; 78: 1166–1172.
Henze G, Fengler R, Hartmann R . Chemotherapy for relapsed childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: results of the BFM Study Group. Haematol Blood Transfus 1994; 36: 374–379.
Eckert C, Biondi A, Seeger K, Cazzaniga G, Hartmann R, Beyermann B et al. Prognostic value of minimal residual disease in relapsed childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Lancet 2001; 358: 1239–1241.
Wiesener MS, Munchenhagen PM, Berger I, Morgan NV, Roigas J, Schwiertz A et al. Constitutive activation of hypoxia-inducible genes related to overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha in clear cell renal carcinomas. Cancer Res 2001; 61: 5215–5222.
Rosenberger C, Mandriota S, Jurgensen JS, Wiesener MS, Horstrup JH, Frei U et al. Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and -2alpha in hypoxic and ischemic rat kidneys. J Am Soc Nephrol 2002; 13: 1721–1732.
Wellmann S, Taube T, Paal K, Graf VEH, Geilen W, Seifert G et al. Specific reverse transcription-PCR quantification of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) splice variants by LightCycler technology. Clin Chem 2001; 47: 654–660.
Karge III WH, Schaefer EJ, Ordovas JM . Quantification of mRNA by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using an internal standard and a nonradioactive detection method. Methods Mol Biol 1998; 110: 43–61.
Lee PD, Sladek R, Greenwood CM, Hudson TJ . Control genes and variability: absence of ubiquitous reference transcripts in diverse mammalian expression studies. Genome Res 2002; 12: 292–297.
Yeoh EJ, Ross ME, Shurtleff SA, Williams WK, Patel D, Mahfouz R et al. Classification, subtype discovery, and prediction of outcome in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia by gene expression profiling. Cancer Cell 2002; 1: 133–143.
Schrappe M, Camitta B, Pui CH, Eden T, Gaynon P, Gustafsson G et al. Long-term results of large prospective trials in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2000; 14: 2193–2194.
Harms DO, Janka-Schaub GE . Co-operative study group for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (COALL): long-term follow-up of trials 82, 85, 89 and 92. Leukemia 2000; 14: 2234–2239.
Talks KL, Turley H, Gatter KC, Maxwell PH, Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ et al. The expression and distribution of the hypoxia-inducible factors HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha in normal human tissues, cancers, and tumor-associated macrophages. Am J Pathol 2000; 157: 411–421.
Zhong H, De Marzo AM, Laughner E, Lim M, Hilton DA, Zagzag D et al. Overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha in common human cancers and their metastases. Cancer Res 1999; 59: 5830–5835.
Stewart M, Talks K, Leek R, Turley H, Pezzella F, Harris A et al. Expression of angiogenic factors and hypoxia inducible factors HIF 1, HIF 2 and CA IX in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Histopathology 2002; 40: 253–260.
Zhong H, Mabjeesh N, Willard M, Simons J . Nuclear expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha protein is heterogeneous in human malignant cells under normoxic conditions. Cancer Lett 2002; 181: 233–238.
Mayerhofer M, Valent P, Sperr WR, Griffin JD, Sillaber C . BCR/ABL induces expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its transcriptional activator, hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha, through a pathway involving phosphoinositide 3-kinase and the mammalian target of rapamycin. Blood 2002; 100: 3767–3775.
Brown JM . Exploiting the hypoxic cancer cell: mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Mol Med Today 2000; 6: 157–162.
Mortensen BT, Jensen PO, Helledie N, Iversen PO, Ralfkiaer E, Larsen JK et al. Changing bone marrow micro-environment during development of acute myeloid leukaemia in rats. Br J Haematol 1998; 102: 458–464.
Jensen PO, Mortensen BT, Hodgkiss RJ, Iversen PO, Christensen IJ, Helledie N et al. Increased cellular hypoxia and reduced proliferation of both normal and leukaemic cells during progression of acute myeloid leukaemia in rats. Cell Prolif 2000; 33: 381–395.
Wiesener MS, Turley H, Allen WE, Willam C, Eckardt KU, Talks KL et al. Induction of endothelial PAS domain protein-1 by hypoxia: characterization and comparison with hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha. Blood 1998; 92: 2260–2268.
Olive PL, Banath JP, Aquino-Parsons C . Measuring hypoxia in solid tumours – is there a gold standard? Acta Oncol 2001; 40: 917–923.
Loncaster JA, Harris AL, Davidson SE, Logue JP, Hunter RD, Wycoff CC et al. Carbonic anhydrase (CA IX) expression, a potential new intrinsic marker of hypoxia: correlations with tumor oxygen measurements and prognosis in locally advanced carcinoma of the cervix. Cancer Res 2001; 61: 6394–6399.
Bellamy WT, Richter L, Frutiger Y, Grogan TM . Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors in hematopoietic malignancies. Cancer Res 1999; 59: 728–733.
Padro T, Bieker R, Ruiz S, Steins M, Retzlaff S, Burger H et al. Overexpression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its cellular receptor KDR (VEGFR-2) in the bone marrow of patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2002; 16: 1302–1310.
Gerber HP, Malik AK, Solar GP, Sherman D, Liang XH, Meng G et al. VEGF regulates haematopoietic stem cell survival by an internal autocrine loop mechanism. Nature 2002; 417: 954–958.
Katoh O, Takahashi T, Oguri T, Kuramoto K, Mihara K, Kobayashi M et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor inhibits apoptotic death in hematopoietic cells after exposure to chemotherapeutic drugs by inducing MCL1 acting as an antiapoptotic factor. Cancer Res 1998; 58: 5565–5569.
Dias S, Shmelkov SV, Lam G, Rafii S . VEGF(165) promotes survival of leukemic cells by Hsp90-mediated induction of Bcl-2 expression and apoptosis inhibition. Blood 2002; 99: 2532–2540.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the Madelaine Schickedanz Kinderkrebs-Stiftung, the Deutsche Kinderkrebsstiftung and the Deutsche José Carreras Leukämie-Stiftung (Project DJCLS-R03/16).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wellmann, S., Guschmann, M., Griethe, W. et al. Activation of the HIF pathway in childhood ALL, prognostic implications of VEGF. Leukemia 18, 926–933 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2403332
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2403332
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) is a new therapeutic target in JAK2V617F-positive myeloproliferative neoplasms
Leukemia (2020)
-
Therapeutic targeting of membrane-associated GRP78 in leukemia and lymphoma: preclinical efficacy in vitro and formal toxicity study of BMTP-78 in rodents and primates
The Pharmacogenomics Journal (2018)
-
HIF-1α promoted vasculogenic mimicry formation in hepatocellular carcinoma through LOXL2 up-regulation in hypoxic tumor microenvironment
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2017)
-
Integration of hypoxic HIF-α signaling in blood cancers
Oncogene (2017)
-
Role of Microenvironment in Resistance to Therapy in AML
Current Hematologic Malignancy Reports (2015)