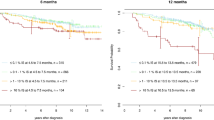
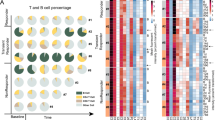
Abstract
Rarely has progress in treatment of leukemia been as dramatic and convincing as with the BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase inhibitor imatinib.1 Imatinib induces remissions of CML as fast as hydroxyurea, achieves rates of cytogenetic remissions that by far exceed those induced by interferon α and has a toxicity profile as favourable as that of hydroxyurea and much superior to that of interferon α.2 In addition, the causal approach of this new drug, which may well serve as a model for new treatment modalities in other neoplasias is reassuring.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Druker BJ, Talpaz M, Resta DJ, Peng B, Buchdunger E, Ford JM et al. Efficacy and safety of a specific inhibitor of the BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase in chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 2001; 344: 1031–1037.
O'Brien S, Guilhot F, Larson R, Gathmann I, Baccarani M, Cervantes F et al. The IRIS study: International randomized study of interferon and low-dose ara-C versus STI571 (imatinib) in patients with newly-diagnosed chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 2003; 348: 994–1004.
Hasford J, Pfirrmann M, Hehlmann R, Allan NC, Baccarani M, Kluin-Nelemans J et al. A new prognostic score for the survival of patients with chronic myeloid leukemia treated with interferon alfa. J Natl Cancer Inst 1998; 90: 850–858.
Silver RT, Woolf SH, Hehlmann R, Appelbaum FA, Anderson J, Bennett C et al. Review: an evidence-based analysis of the effect of busulfan, hydroxyurea, interferon, and allogeneic bone marrow transplantation in treating the chronic phase of chronic myeloid leukemia: developed for the American Society of Hematology. Blood 1999; 94: 1517–1536.
Hansen JA, Gooley TA, Martin PJ, Appelbaum F, Chauncey TR, Clift RA et al. Bone marrow transplants from unrelated donors for patients with chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 1998; 338: 962–968.
Gratwohl A, Hermans J, Goldman JM, Frassoni F, Devergie A, Carreras E et al. for the Chronic Leukemia Working Party of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT). Risk assessment for patients with chronic myeloid leukemia before allogeneic blood or marrow transplantation. Lancet 1998; 352: 1087–1092.
van Rhee F, Szydlo RM, Hermans J, Devergie A, Frassoni F, Arcese W et al. Long-term results after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for chronic myelogenous leukemia in chronic phase: a report from the Chronic Leukemia Working Party of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation European results of matched unrelated donor bone marrow transplantation for chronic myeloid leukemia. Impact of HLA class II matching. Chronic Leukemia Working Party of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 1997; 20: 11–19.
Cross NCP, Feng L, Chase A, Bungey J, Hughes TP, Goldman JM . Competitive polymerase chain reaction to estimate the number of BCR-ABL transcripts in chronic myeloid leukemia patients after bone marrow transplantation. Blood 1993; 82: 1929–1936.
Hochhaus A, Kreil S, Corbin AS, La Rosee P, Müller MC,, Lahaye T et al. Molecular and chromosomal mechanisms of resistance to imatinib (STI571) therapy. Leukemia 2002; 16: 2190–2196.
Hehlmann R . Trial of IFN or STI571 before proceeding to allografting for CML? Leukemia 2000; 14: 1560–1562.
Hochhaus A, Reiter A, Saussele S, Reichert A, Emig M, Kaeda J et al. Molecular heterogeneity in complete cytogenetic responders after interferon alpha therapy for chronic myelogenous leukemia: low levels of minimal residual disease are associated with continuing remission. Blood 2000; 95: 62–66.
Bonifazi F, De Vivo A, Rosti G, Guilhot F, Guilhot J, Trabacchi E et al. Chronic myeloid leukemia and interferon-alpha: a study of complete cytogenetic responders. Blood 2001; 98: 3074–3081.
Kantarjian H, Sawyers C, Hochhaus A, Guilhot F, Schiffer C, Gambacorti-Passerini C et al. Hematologic and cytogenetic responses to imatinib mesylate in chronic myelogenous leukemia. N Engl J Med 2002; 346: 645–652.
Burchert A, Wolfl S, Schmidt M, Brendel C, Denecke B, Cai D et al. Interferon-alpha, but not the ABL-kinase inhibitor imatinib (STI571), induces expression of myeloblastin and a specific T-cell response in chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 2003; 101: 259–264.
Hehlmann R, Berger U, Pfirrmann M, Hochhaus A, Metzgerdth G, Maywald O et al. Randomized comparison of interferon α and hydroxyurea with hydroxyurea monotherapy in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML-Study II): prolongation of survival by the combination of interferon α and hydoxyurea. Leukemia 2003 (in press).
Talpaz M, Silver RT, Druker BJ, Goldman JM, Gambacorti-Passerini C, Guilhot F et al. Imatinib induces durable hematologic and cytogenetic responses in patients with accelerated phase chronic myeloid leukemia: results of a phase 2 study. Blood 2002; 99: 1928–1937.
Lipton JH, Khoroshko ND, Golenkov AK, Abdulkadyrov KM, Nair MK, Raghunadharao D et al. A randomized multicenter comparative study of peginterferon alfa-2a (40KD) vs interferon-alfa-2a in patients with treatment-naive chronic-phase chronic myelogenous leukemia. Blood. 2002; 100: 782a.
Hoover RR, Mahon FX, Melo JV, Daley GQ . Overcoming STI571 resistance with the farnesyl transferase inhibitor SCH66336. Blood 2002; 100: 1068–1071.
La Rosee P, O'Dwyer ME, Druker BJ . Insights from pre-clinical studies for new combination treatment regimens with the Bcr-Abl kinase inhibitor imatinib mesylate (Gleevec/Glivec) in chronic myelogenous leukemia: a translational perspective. Leukemia 2002; 16: 1213–1219.
Hehlmann R, Berger U, Engelich G . Imatinib-Kombinationstherapien – die neue CML – Studie IV. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 2002; 127: 2224–2226.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hehlmann, R. Current CML therapy: progress and dilemma. Leukemia 17, 1010–1012 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2402951
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2402951
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
DHS (trans−4,4′-dihydroxystilbene) suppresses DNA replication and tumor growth by inhibiting RRM2 (ribonucleotide reductase regulatory subunit M2)
Oncogene (2019)
-
Pathogenesis, treatment effects, and resistance dynamics in chronic myeloid leukemia - insights from mathematical model analyses
Journal of Molecular Medicine (2008)
-
Therapeutic use of Aldara™ in chronic myeloid leukemia
Journal of Translational Medicine (2007)
-
Arsenic trioxide and proteasome inhibitor bortezomib synergistically induce apoptosis in leukemic cells: the role of protein kinase Cδ
Leukemia (2007)
-
Interstitial pneumonia induced by imatinib mesylate: pathologic study demonstrates alveolar destruction and fibrosis with eosinophilic infiltration
Leukemia (2004)