Abstract
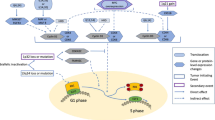
The retinoblastoma protein (pRb), p16INK4A, D-type cyclins, and their partners cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 4 and 6 constitute a G1 regulatory pathway commonly targeted in tumorigenesis. Several malignancies show a reciprocal correlation between genetic alterations of single members of the pRb pathway. Therefore, we determined the frequency of Rb deletions and cyclin D1 alterations by fluorescence in situ hybridization as well as 5′ CpG island hypermethylation of the p16INK4Agene using methylation-specific polymerase chain reaction in bone marrow mononuclear cells from 82 individuals with plasma cell disorders. Alterations in at least one of the components of the pathway were found in 75%. Cyclin D1 translocations or amplifications were detected in 14/82 (17.1%), Rb deletions at 13q14 in 23/82 (28%) of the cases, including three (3.6%) homozygous deletions. p16INK4A was hypermethylated in 33/57 (57.9%) of the samples. Further analysis revealed a highly significant correlation between cyclin D1 alterations and extramedullar or leukemic myeloma manifestations (P = 0.014; Fisher's test). Whereas Rb deletions seemed to occur alternatively to cyclin D1 alterations, no reciprocal correlation was found between p16INK4A hypermethylations and cyclin D1 or Rb locus aberrations. Cyclin D1 locus alterations and Rb deletions were associated with a significantly worse prognosis whereas p16INK4A hypermethylation had no impact on survival. We conclude that cyclin D1 and Rb aberrations seem to occur as alternative events in plasma cell malignancies and contribute to clinical course and prognosis. In contrast, although p16INK4A hypermethylation is frequent, inactivation of p16INK4A seems not to be involved in the pathogenesis of plasma cell disorders.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kamb A . Cell-cycle regulators and cancer Trends Genet 1995 11: 136–140
Sherr CJ, Roberts JM . Inhibitors of mammalian G1 cyclin-dependent kinases Genes Dev 1995 9: 1149–1163
Strauss M, Lukas J, Bartek J . Unrestricted cell cycling and cancer Nat Med 1995 1: 1245–1246
Weinberg RA . The retinoblastoma protein and cell cycle control Cell 1995 81: 323–330
Hall M, Peters G . Genetic alterations of cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases, and Cdk inhibitors in human cancer Adv Cancer Res 1996 68: 67–108
Nevins JR . E2F, a link between the Rb tumor suppressor protein and viral oncoproteins Science 1992 258: 424–429
Krämer A, Carstens CP, Fahl WE . A novel CCAAT-binding protein necessary for adhesion-dependent cyclin A transcription at the G1/S boundary is sequestered by a retinoblastoma-like protein in G0 J Biol Chem 1996 271: 6579–6582
Krämer A, Carstens CP, Wasserman WW, Fahl WE . CBP/cycA, a CCAAT-binding protein necessary for adhesion-dependent cyclin A transcription at the G1/S boundary consists of NF-Y and a novel 115 kDa subunit Cancer Res 1997 57: 5117–5121
Hunter T, Pines J . Cyclins and cancer II: cyclin D and CDK inhibitors come of age Cell 1994 79: 573–582
Bosch F, Jares P, Campo E, Lopez-Guillermo A, Piris MA, Villamor N, Tassies D, Jaffe ES, Monserrat E, Rozman C . Prad-1/cyclin D1 gene overexpression in chronic lymphoproliferative disorders: a highly specific marker for mantle cell lymphoma Blood 1994 84: 2726–2732
de Boer CJ, van Krieken JHM, Kluin-Nelemans HC, Kluin PM, Schuuring E . Cyclin D1 messenger RNA overexpression as a marker for mantle cell lymphoma Oncogene 1995 10: 1833–1840
Yatabe Y, Suzuki R, Tobinai K, Matsuno Y, Ichinohasama R, Okamoto M, Yamaguchi M, Tamaru J, Uike N, Hashimoto Y, Morishima Y, Suchi T, Seto M, Nakamura S . Significance of cyclin D1 overexpression for the diagnosis of mantle cell lymphoma: a clinicopathologic comparison of cyclin D1-positive MCL and cyclin D1-negative MCL-like B-cell lymphoma Blood 2000 95: 2253–2261
Levy V, Ugo V, Delmer A, Tang R, Ramond S, Perrot JY, Vrhovac R, Marie JP, Zittoun R, Ajchenbaum-Cymbalista F . Cyclin D1 overexpression allows identification of an aggressive subset of leukemic lymphoproliferative disorders Leukemia 1999 13: 1343–1351
Gillett C, Fantl V, Smith R, Fisher C, Bartek J, Dickson C, Barnes D, Peters G . Amplification and overexpression of cyclin D1 in breast cancer detected by immunohistochemical staining Cancer Res 1994 54: 1812–1817
Michalides R, van Veelen N, Hart A, Balm A . Overexpression of cyclin D1 correlates with recurrence in a group of forty-seven operable squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck Cancer 1995 55: 975–978
Bartkova J, Lukas J, Guldberg P, Alsner J, Kirkin AF, Zeuthen J, Bartek J . The p16-cyclin D/cdk4-pRb pathway as a functional unit frequently altered in melanoma pathogenesis Cancer Res 1996 56: 5475–5483
Wölfel T, Hauer M, Schneider J, Serrano M, Wolfel C, Klehmann-Hieb E, De Plaen E, Hankeln T, Meyer zum Buschenfelde KH, Beach D . A p16INK4a-insensitive CDK4 mutant targeted by cytolytic T lymphocytes in a human melanoma Science 1995 269: 1281–1284
He J, Olson JJ, James CD . Lack of p16INK4 or retinoblastoma protein (pRb), or amplification-associated overexpression of cdk4 is observed in distinct subsets of malignant glial tumors and cell lines Cancer Res 1995 55: 4833–4836
Kamb A, Gruis NA, Weaver-Feldhaus J, Liu Q, Harshman K, Tavtigian SV, Stockert E, Day RS 3rd, Johnson BE, Skolnick MH . A cell cycle regulator potentially involved in genesis of many tumor types Science 1994 264: 436–440
Nobori T, Miura K, Wu DJ, Lois A, Takabayashi K, Carson DA . Deletions of the cyclin-dependent kinase-4 inhibitor gene in multiple human cancers Nature 1994 368: 753–756
Hebert J, Cayuela JM, Berkeley J, Sigaux F . Candidate tumor-suppressor gene MTS1 (p16/INK4A) and MTS2 (p15/INK4B) display frequent homozygous deletions in primary cells from T- but not from B-cell lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemias Blood 1994 84: 4038–4044
Hangaishi A, Ogawa S, Imamura N, Miyawaki S, Miura Y, Uike N, Shimazaki C, Emi N, Takeyama K, Hirosawa S, Kamada N, Kobayashi Y, Takemoto Y, Kitani T, Toyama K, Ohtake S, Yazaki Y, Ueda R, Hirai H . Inactivation of multiple tumor-suppressor genes involved in negative regulation of the cell cycle, MTS1/p16INK4A/CDKN2, MTS2/p15INK4B, p53, and Rb genes in primary lymphoid malignancies Blood 1996 87: 4949–4958
Merlo A, Herman JG, Mao L, Lee DJ, Gabrielson E, Burger PC, Baylin SB, Sidransky D . 5′CpG island methylation is associated with transcriptional silencing of the tumour suppressor p16/CDKN2/MTS1 in human cancers Nat Med 1995 1: 686–692
He J, Allen JR, Collins VP, Allalunis-Turner MJ, Godbout R, Day RS 3rd, James CD . CDK4 amplification is an alternative mechanism to p16 homozygous deletion in glioma cell lines Cancer Res 1994 54: 5804–5807
Shapiro GI, Edwards CD, Kobzik L, Godleski J, Richards W, Sugarbaker DJ, Rollins BJ . Reciprocal Rb inactivation and the p16INK4A expression in primary lung cancers and cell lines Cancer Res 1995 55: 505–509
Schauer IE, Siriwardana S, Langan TA, Sclafani RI . Cyclin D1 overexpression vs. retinoblastoma inactivation: implications for growth control evasion in non-small and small cell lung cancer Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1994 91: 7827–7831
Dreyling MH, Bullinger L, Ott G, Stilgenbauer S, Muller-Hermelink HK, Bentz M, Hiddemann W, Döhner H . Alterations of the cyclin D1/p16-pRB pathway in mantle cell lymphoma Cancer Res 1997 57: 4608–4614
Jadayel DM, Lukas J, Nacheva E, Bartkova J, Stranks G, De Schouwer PJ, Lens D, Bartek J, Dyer MJ, Kruger AR, Catovsky D . Potential role for concurrent abnormalities of the cyclin D1, p16CDKN2 and p15CDKN2B genes in certain B cell non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. Functional studies in a cell line (Granta 519) Leukemia 1997 11: 64–72
Hallek M, Bergsagel PL, Anderson KC . Multiple myeloma: evidence for a multistep transformation process Blood 1998 91: 3–21
Gould J, Alexanian R, Goodacre A, Pathak S, Hecht B, Barlogie B . Plasma cell karyotype in multiple myeloma Blood 1988 71: 453–456
Barlogie B, Hoover R, Epstein J . Multiple myeloma – recent developments in molecular and cellular biology Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 1995 194: 37–41
Bunn PA, Krasnow S, Makuch RW, Schlam M, Schechter G . Flow cytometric analysis of DNA content of bone marrow cells in patients with plasma cell myeloma: clinical implications Blood 1982 59: 528–535
Drach J, Schuster J, Nowotny H, Angerler J, Rosenthal F, Fiegl M, Rothermundt C, Gsur A, Jager U, Heinz R . Multiple myeloma: high incidence of chromosomal aneuploidy as detected by interphase fluorescence in situ hybridization Cancer Res 1995 55: 3854–3859
Weh HJ, Gutensohn K, Selbach J, Kruse R, Wacker-Backhaus G, Seeger D, Fiedler W, Fett W, Hossfeld DK . Karyotype in multiple myeloma and plasma cell leukaemia Eur J Cancer 1993 29A: 1269–1273
Tricot G, Barlogie B, Jagannath S, Bracy D, Mattox S, Vesole DH, Naucke S, Sawyer JR . Poor prognosis in multiple myeloma is associated only with partial or complete deletions of chromosome 13 or abnormalities involving 11q and not with other karyotype abnormalities Blood 1995 86: 4250–4256
Pérez-Simón JA, García-Sanz R, Tabernero MD, Almeida J, Gonzalez M, Fernandez-Calvo J, Moro MJ, Hernandez JM, San Miguel JF, Orfao A . Prognostic value of numerical chromosome aberrations in multiple myeloma: a FISH analysis of 15 different chromosomes Blood 1998 91: 3366–3371
Zojer N, Königsberg R, Ackermann J, Fritz E, Dallinger S, Kromer E, Kaufmann H, Riedl L, Gisslinger H, Schreiber S, Heinz R, Ludwig H, Huber H, Drach J . Deletion of 13q14 remains an independent adverse prognostic variable in multiple myeloma despite its frequent detection by interphase fluorescence in situ hybridization Blood 2000 95: 1925–1930
Schultheis B, Krämer A, Willer A, Hegenbart U, Goldschmidt H, Hehlmann R . Analysis of p73 and p53 gene deletions in multiple myeloma Leukemia 1999 13: 2099–2103
Siebert R, Matthiesen P, Harder S, Zhang Y, Borowski A, Zuhlke-Jenisch R, Metzke S, Joos S, Weber-Matthiesen K, Grote W, Schlegelberger B . Application of interphase fluorescence in situ hybridization for the detection of the Burkitt translocation t(8;14)(q24;q32) in B-cell lymphomas Blood 1998 91: 984–990
Dreyling MH, Bohlander SK, LeBeau MM, Olopade OI . Refined mapping of genomic rearrangements involving the short arm of chromosome 9 in acute lymphoblastic leukemia and other hematological malignancies Blood 1995 86: 1931–1938
Lichter P, Cremer T . Chromosome analysis by non-isotopic in situ hybridization. In: Rooney DE, Czepulkowski BH (eds) Human Cytogenetics Oxford University Press: New York 1992 157–192
Herman JG, Graff JR, Myohanen S, Nelkin BD, Baylin SB . Methylation-specific PCR: a novel PCR assay for methylation status of CpG islands Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1996 93: 9821–9826
Dao DD, Sawyer JR, Epstein J, Hoover RG, Barlogie B, Tricot G . Deletion of the retinoblastoma gene in multiple myeloma Leukemia 1994 8: 1280–1284
Juge-Morineau N, Mellerin MP, Francois S, Rapp MJ, Harousseau JL, Amiot M, Bataille R . High incidence of deletions but infrequent inactivation of the retinoblastoma gene in human myeloma cells Br J Haematol 1995 91: 664–667
Avet-Loiseau H, Li J-Y, Facon T, Brigaudeau C, Morineau N, Maloisel F, Rapp MJ, Talmant P, Trimoreau F, Jaccard A, Harousseau JL, Bataille R . High incidence of translocations t(11;14)(q13;q32) and t(4;14)(p16;q32) in patients with plasma cell malignancies Cancer Res 1998 58: 5640–5645
Fonseca R, Witzig TE, Gertz MA, Kyle RA, Hoyer JD, Jalal SM, Greipp PR . Multiple myeloma and the translocation t(11;14)(q13;q32): a report on 13 cases Br J Haematol 1998 101: 296–301
Troussard X, Avet-Loiseau H, Macro M, Mellerin MP, Malet M, Roussel M, Sola B . Cyclin D1 expression in patients with multiple myeloma Hematology J 2000 1: 181–185
Gernone A, Iolascon A, Pietrafesa A, Dammacco F . p16 gene analysis in multiple myeloma (MM) Leukemia 1996 10: 1401
Tasaka T, Berenson J, Vescio R, Hirama T, Miller CW, Nagai M, Takahara J, Koeffler HP . Analysis of the p16INK4A, p15INK4B, and p18INK4C genes in multiple myeloma Br J Haematol 1997 96: 98–102
Dilworth D, Liu L, Stewart K, Berenson JR, Lassam N, Hogg D . Germline CDKN2A mutation implicated in predisposition to multiple myeloma Blood 2000 95: 1869–1871
Ng MHL, Chung YF, Lo KW, Wickham NWR, Lee JCK, Huang DP . Frequent hypermethylation of the p16 and p15 genes in multiple myeloma Blood 1997 89: 2500–2506
Tasaka T, Asou H, Munker R, Said JW, Berenson J, Vescio RA, Nagai M, Takahara J, Koeffler HP . Methylation of the p16INK4A gene in multiple myeloma Br J Haematol 1998 101: 558–564
Urashima M, Teoh G, Ogata A, Chauhan D, Treon SP, Sugimoto Y, Kaihara C, Matsuzaki M, Hoshi Y, DeCaprio JA, Anderson KC . Characterization of p16INK4A expression in multiple myeloma and plasma cell leukemia Clin Cancer Res 1997 3: 2173–2179
Uchida T, Kinoshita T, Ohno T, Ohashi H, Nagai H, Saito H . Hypermethylation of the p16INK4A gene promoter during the progression of plasma cell dyscrasia Leukemia 2001 15: 157–165
Akiyama N, Tsuruta H, Sasaki H, Sakamoto H, Hamaguchi M, Ohmura Y, Seto M, Ueda R, Hirai H, Yazaki Y . Messenger RNA levels of five genes located at chromosome 11q13 in B-cell tumors with chromosome translocation t(11;14)(q13;q32) Cancer Res 1994 54: 377–379
Shaughnessy J, Tian E, Sawyer J, Bumm K, Landes R, Badros A, Morris C, Tricot G, Epstein J, Barlogie B . High incidence of chromosome 13 deletion in multiple myeloma detected by mutliprobe interphase FISH Blood 2000 96: 1505–1511
Corcoran MM, Rasool O, Liu Y, Iyengar A, Grander D, Ibbotson RE, Merup M, Wu X, Brodyansky V, Gardiner AC, Juliusson G, Chapman RM, Ivanova G, Tiller M, Gahrton G, Yankovsky N, Zabarovsky E, Oscier DG, Einhorn S . Detailed molecular delineation of 13q14.3 loss in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia Blood 1998 91: 1382–1390
Shaughnessy J Jr, Gabrea A, Qi Y, Brents L, Zhan F, Tian E, Sawyer J, Barlogie B, Bergsagel PL, Kuehl M . Cyclin D3 at 6p21 is dysregulated by recurrent chromosomal translocations to immunoglobulin loci in multiple myeloma Blood 2001 98: 217–223
Lovec H, Grzeschiczek A, Kowalski MB, Möröy T . Cyclin D1/bcl-1 cooperates with the myc genes in the generation of B-cell lymphoma in transgenic mice EMBO J 1994 13: 3487–3495
Bodrug SE, Warner BJ, Bath ML, Lindemann GJ, Harris AW . Cyclin D1 transgene impedes lymphocyte maturation and collaborates in lymphogenesis with the myc gene EMBO J 1994 13: 2124–2130
Lukas J, Aagaard L, Strauss M, Bartek J . Oncogenic aberrations of p16INK4/CDKN2 and cyclin D1 cooperate to deregulate G1 control Cancer Res 1995 55: 4818–4823
Zhang T, Nanney LB, Luongo C, Lamps L, Heppner KJ, DuBois RN, Beauchamp RD . Concurrent overexpression of cyclin D1 and cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (Cdk4) in intestinal adenomas from multiple intestinal neoplasia (Min) mice and human familial adenomatous polyposis patients Cancer Res 1997 57: 169–175
Stock W, Tsai T, Golden C, Rankin C, Sher D, Slovak ML, Pallavicini MG, Radich JP, Boldt DH . Cell cycle regulatory gene abnormalities are important determinants of leukemogenesis and disease biology in adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia Blood 2000 95: 2364–2371
Kees UR, Burton PR, Lü C, Baker DL . Homozygous deletion of the p16/MTS1 gene in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia is associated with unfavorable clinical outcome Blood 1997 89: 4161–4166
Semenov, Akyuz C, Roginskaya V, Chanhan D, Corey SJ . Growth inhibition and apoptosis of myeloma cells by the CDK inhibitor flavopiridol Leuk Res 2002 26: 271–280
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr Stefan Bohlander, Institute of Human Genetics, University of Göttingen, Germany and Dr Rainer Siebert, Department of Human Genetics, University of Kiel, Germany for kindly providing the cosmids spanning the 14q32 IgH region and the 9p21 p16INK4A/p15INK4B region, respectively. We thank Dr Axel Benner, Department of Biomedical Statistics, German Cancer Research Center, Heidelberg, Germany for help with the statistical analysis. This work was supported by the Deutsche Krebshilfe and the Forschungsfonds, Fakultät für Klinische Medizin Mannheim, Universität Heidelberg, Germany.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krämer, A., Schultheis, B., Bergmann, J. et al. Alterations of the cyclin D1/pRb/p16INK4A pathway in multiple myeloma. Leukemia 16, 1844–1851 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2402609
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2402609
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Discovery of the oncogenic MDM2, a direct binding target of berberine and a potential therapeutic, in multiple myeloma
Functional & Integrative Genomics (2022)
-
Glaucocalyxin A suppresses multiple myeloma progression in vitro and in vivo through inhibiting the activation of STAT3 signaling pathway
Cancer Cell International (2021)
-
Epigenetic strategies to reverse drug resistance in heterogeneous multiple myeloma
Clinical Epigenetics (2017)
-
piRNA-823 contributes to tumorigenesis by regulating de novo DNA methylation and angiogenesis in multiple myeloma
Leukemia (2015)
-
Association of CCND1 overexpression with KRAS and PTEN alterations in specific subtypes of non-small cell lung carcinoma and its influence on patients’ outcome
Tumor Biology (2015)