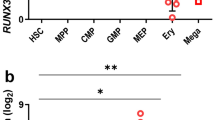
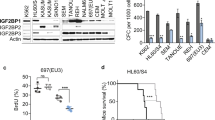
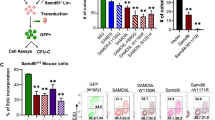
Abstract
The balance between hematopoietic cell viability and apoptosis is regulated by exogenous growth factors, however, the molecular mechanisms by which these trophic factors exert their effects remain obscure. A functional retroviral cDNA library-based screen was employed to identify genes that prevent growth factor withdrawal-mediated apoptosis in the myeloid progenitor cell 32Dcl3. This approach identified three classes of genes: those with known roles in apoptosis (bcl-XL and ornithine decarboxylase); genes previously identified but not linked directly to apoptotic signaling (O-linked N-acetylglucosamine transferase); and a previously uncharacterized gene we termed SPIN-2. In 32Dcl3 cells, expression of exogenous SPIN-2 provides 25% protection from apoptosis following growth factor withdrawal compared to controls which show ∼1–2% survival. SPIN-2 overexpression slows cell growth rates and increases the percentage of cells in G2/M (32% vs control cells at 12%). Immunolocalization studies indicate that myc-epitope tagged SPIN-2 proteins, which retain their anti-apoptotic function, reside in the nucleus, whereas a C-terminal deletion mutant that loses its anti-apoptotic activity is located in the cytoplasm. These studies suggest that SPIN-2 is a novel nuclear protein that functions to regulate cell cycle progression and this activity is related to the inhibition of apoptosis following the removal of essential growth factors.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li J, Eastman A . Apoptosis in an interleukin-2-dependent cytotoxic T lymphocyte cell line is associated with intracellular acidification. Role of the Na(+)/H(+)-antiport J Biol Chem 1995 270: 3203–3211
Askew DS, Ashmun RA, Simmons BC, Cleveland JL . Constitutive c-myc expression in an IL-3-dependent myeloid cell line suppresses cell cycle arrest and accelerates apoptosis Oncogene 1991 6: 1915–1922
van Engeland M, Nieland LJ, Ramaekers FC, Schutte B, Reutelingsperger CP . Annexin V-affinity assay: a review on an apoptosis detection system based on phosphatidylserine exposure Cytometry 1998 31: 1–9
Bojes HK, Feng X, Kehrer JP, Cohen GM . Apoptosis in hematopoietic cells (FL5.12) caused by interleukin-3 withdrawal: relationship to caspase activity and the loss of glutathione Cell Death Differ 1999 6: 61–70
Lilly M, Sandholm J, Cooper JJ, Koskinen PJ, Kraft A . The PIM-1 serine kinase prolongs survival and inhibits apoptosis-related mitochondrial dysfunction in part through a bcl-2-dependent pathway Oncogene 1999 18: 4022–4031
Garland J, Brown G, Beasley J, Brown R . Apoptosis in factor-dependent haematopoietic cells is linked to calcium-sensitive mitochondrial rearrangements and cytoskeletal modulation Br J Haematol 2000 109: 221–234
Wolter KG, Hsu YT, Smith CL, Nechushtan A, Xi XG, Youle RJ . Movement of Bax from the cytosol to mitochondria during apoptosis J Cell Biol 1997 139: 1281–1292
Kluck RM, Bossy-Wetzel E, Green DR, Newmeyer DD . The release of cytochrome c from mitochondria: a primary site for Bcl-2 regulation of apoptosis Science 1997 275: 1132–1136
Liu X, Kim CN, Yang J, Jemmerson R, Wang X . Induction of apoptotic program in cell-free extracts: requirement for dATP and cytochrome c Cell 1996 86: 147–157
Li P, Nijhawan D, Budihardjo I, Srinivasula SM, Ahmad M, Alnemri ES, Wang X . Cytochrome c and dATP-dependent formation of Apaf-1/caspase-9 complex initiates an apoptotic protease cascade Cell 1997 91: 479–489
Hockenbery DM, Oltvai ZN, Yin XM, Milliman CL, Korsmeyer SJ . Bcl-2 functions in an antioxidant pathway to prevent apoptosis Cell 1993 75: 241–251
Hawkins CJ, Vaux DL . Analysis of the role of bcl-2 in apoptosis Immunol Rev 1994 142: 127–139
Kohler T, Leiblein S, Borchert S, Eller J, Rost AK, Lassner D, Krahl R, Helbig W, Wagner O, Remke H . Absolute levels of MDR-1, MRP, and BCL-2 MRNA and tumor remission in acute leukemia Adv Exp Med Biol 1999 457: 177–185
Lauria F, Raspadori D, Rondelli D, Ventura MA, Fiacchini M, Visani G, Forconi F, Tura S . High bcl-2 expression in acute myeloid leukemia cells correlates with CD34 positivity and complete remission rate Leukemia 1997 11: 2075–2078
Yang E, Zha J, Jockel J, Boise LH, Thompson CB, Korsmeyer SJ . Bad, a heterodimeric partner for Bcl-XL and Bcl-2, displaces Bax and promotes cell death Cell 1995 80: 285–291
Lin EY, Orlofsky A, Wang HG, Reed JC, Prystowsky MB . A1, a Bcl-2 family member, prolongs cell survival and permits myeloid differentiation Blood 1996 87: 983–992
Reynolds JE, Yang T, Qian L, Jenkinson JD, Zhou P, Eastman A, Craig RW . Mcl-1, a member of the Bcl-2 family, delays apoptosis induced by c-Myc overexpression in Chinese hamster ovary cells Cancer Res 1994 54: 6348–6352
Deveraux QL, Reed JC . IAP family proteins – suppressors of apoptosis Genes Dev 1999 13: 239–252
LaCasse EC, Baird S, Korneluk RG, MacKenzie AE . The inhibitors of apoptosis (IAPs) and their emerging role in cancer Oncogene 1998 17: 3247–3259
Irmler M, Thome M, Hahne M, Schneider P, Hofmann K, Steiner V, Bodmer JL, Schroter M, Burns K, Mattmann C, Rimoldi D, French LE, Tschopp J . Inhibition of death receptor signals by cellular FLIP Nature 1997 388: 190–195
Hitoshi Y, Lorens J, Kitada SI, Fisher J, LaBarge M, Ring HZ, Francke U, Reed JC, Kinoshita S, Nolan GP . Toso, a cell surface, specific regulator of Fas-induced apoptosis in T cells Immunity 1998 8: 461–471
Kinoshita S, Su L, Amano M, Timmerman LA, Kaneshima H, Nolan GP . The T cell activation factor NF-ATc positively regulates HIV-1 replication and gene expression in T cells Immunity 1997 6: 235–244
Griffiths G, Brands R, Burke B, Louvard D, Warren G . Viral membrane proteins acquire galactose in trans Golgi cisternae during intracellular transport J Cell Biol 1982 95: 781–792
Roth J, Wang Y, Eckhardt AE, Hill RL . Subcellular localization of the UDP-N-acetyl-D-galactosamine: polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase-mediated O-glycosylation reaction in the submaxillary gland Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1994 91: 8935–8939
Blandino G, Scardigli R, Rizzo MG, Crescenzi M, Soddu S, Sacchi A . Wild-type p53 modulates apoptosis of normal, IL-3 deprived, hematopoietic cells Oncogene 1995 10: 731–737
Gaozza E, Baker SJ, Vora RK, Reddy EP . AATYK: a novel tyrosine kinase induced during growth arrest and apoptosis of myeloid cells Oncogene 1997 15: 3127–3135
Greenberger JS, Sakakeeny MA, Humphries RK, Eaves CJ, Eckner RJ . Demonstration of permanent factor-dependent multipotential (erythroid/neutrophil/basophil) hematopoietic progenitor cell lines Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1983 80: 2931–2935
Packham G, Cleveland JL . Ornithine decarboxylase is a mediator of c-Myc-induced apoptosis Mol Cell Biol 1994 14: 5741–5747
Wells L, Vosseller K, Hart GW . Glycosylation of nucleocytoplasmic proteins: signal transduction and O- GlcNAc Science 2001 291: 2376–2378
Oh B, Hwang SY, Solter D, Knowles BB . Spindlin, a major maternal transcript expressed in the mouse during the transition from oocyte to embryo Development 1997 124: 493–503
Deng X, Ito T, Carr B, Mumby M, May WS Jr . Reversible phosphorylation of Bcl2 following interleukin 3 or bryostatin 1 is mediated by direct interaction with protein phosphatase 2A J Biol Chem 1998 273: 34157–34163
Laval SH, Reed V, Blair HJ, Boyd Y . The structure of DXF34, a human X-linked sequence family with homology to a transcribed mouse Y-linked repeat Mamm Genome 1997 8: 689–691
Conway SJ, Mahadevaiah SK, Darling SM, Capel B, Rattigan AM, Burgoyne PS . Y353/B: a candidate multiple-copy spermiogenesis gene on the mouse Y chromosome Mamm Genome 1994 5: 203–210
Reed V, Rider S, Maslen GL, Hatchwell E, Blair HJ, Uwechue IC, Craig IW, Laval SH, Monaco AP, Boyd Y . A 2-Mb YAC contig encompassing three loci (DXF34, DXS14, and DXS390) that lie between Xp11.2 translocation breakpoints associated with incontinentia pigmenti type 1 Genomics 1994 20: 341–346
Quandt K, Frech K, Karas H, Wingender E, Werner T . MatInd and MatInspector: new fast and versatile tools for detection of consensus matches in nucleotide sequence data Nucleic Acids Res 1995 23: 4878–4884
Yoshii T, Fukumori T, Honjo Y, Inohara H, Kim HR, Raz A . Galectin-3 phosphorylation is required for its anti-apoptotic function and cell cycle arrest J Biol Chem 2002 277: 6852–6857
Huang DC, O'Reilly LA, Strasser A, Cory S . The anti-apoptosis function of Bcl-2 can be genetically separated from its inhibitory effect on cell cycle entry EMBO J 1997 16: 4628–4638
Furukawa Y, Iwase S, Kikuchi J, Terui Y, Nakamura M, Yamada H, Kano Y, Matsuda M . Phosphorylation of Bcl-2 protein by CDC2 kinase during G2/M phases and its role in cell cycle regulation J Biol Chem 2000 275: 21661–21667
Pichon B, Mercan D, Pouillon V, Christophe-Hobertus C, Christophe D . A method for the large-scale cloning of nuclear proteins and nuclear targeting sequences on a functional basis Anal Biochem 2000 284: 231–239
Maestro R, Dei Tos AP, Hamamori Y, Krasnokutsky S, Sartorelli V, Kedes L, Doglioni C, Beach DH, Hannon GJ . Twist is a potential oncogene that inhibits apoptosis Genes Dev 1999 13: 2207–2217
Reuther GW, Lambert QT, Caligiuri MA, Der CJ . Identification and characterization of an activating TrkA deletion mutation in acute myeloid leukemia Mol Cell Biol 2000 20: 8655–8666
Ritch PS, Occhipinti SJ, Cunningham RE, Shackney SE . Schedule-dependent synergism of combinations of hydroxyurea with adriamycin and 1-beta-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine with adriamycin Cancer Res 1981 41: 3881–3884
Oh B, Hampl A, Eppig JJ, Solter D, Knowles BB . SPIN, a substrate in the MAP kinase pathway in mouse oocytes Mol Reprod Dev 1998 50: 240–249
Itoh Y, Hori T, Saitoh H, Mizuno S . Chicken spindlin genes on W and Z chromosomes: transcriptional expression of both genes and dynamic behavior of spindlin in interphase and mitotic cells Chromosome Res 2001 9: 283–299
Staub E, Mennerich D, Rosenthal A . The Spin/Ssty repeat: a new motif identified in proteins involved in vertebrate development from gamete to embryo Genome Biol 2001 3: 0003.1–0003.6
O'Connor DS, Grossman D, Plescia J, Li F, Zhang H, Villa A, Tognin S, Marchisio PC, Altieri DC . Regulation of apoptosis at cell division by p34cdc2 phosphorylation of survivin Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000 97: 13103–13107
Li F, Ambrosini G, Chu EY, Plescia J, Tognin S, Marchisio PC, Altieri DC . Control of apoptosis and mitotic spindle checkpoint by survivin Nature 1998 396: 580–584
Acknowledgements
We thank Alan Friedman for the 32Dcl3 cells, Vijay Antharam for technical assistance and Drs Stratford May and Steven Baker for critical reading of the manuscript. The nucleotide sequence for the SPIN-2 gene has been submitted to the GenBank database under the Accession Number AF356353. A portion of this work was supported by a grant to BSF from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Postdoctoral Research Fellowship for Physicians.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fletcher, B., Dragstedt, C., Notterpek, L. et al. Functional cloning of SPIN-2, a nuclear anti-apoptotic protein with roles in cell cycle progression. Leukemia 16, 1507–1518 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2402557
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2402557
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
O-GlcNAc in cancer: An Oncometabolism-fueled vicious cycle
Journal of Bioenergetics and Biomembranes (2018)
-
O-GlcNAc transferase and O-GlcNAcase: achieving target substrate specificity
Amino Acids (2014)
-
Elevated O-GlcNAc-dependent signaling through inducible mOGT expression selectively triggers apoptosis
Amino Acids (2011)
-
Production of complex nucleic acid libraries using highly parallel in situ oligonucleotide synthesis
Nature Methods (2004)