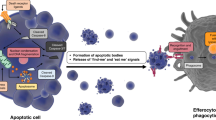
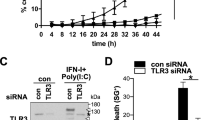
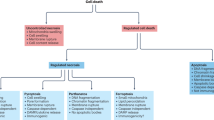
Abstract
Though the term apoptosis was originated in pathology and developmental biology as an alternative to necrosis, the tissue necrosis with inflammation is irrelevant to cell culture conditions where apoptosis is mostly studied. Furthermore, no one single morphological feature is either necessary or sufficient to define apoptosis. The emerging biochemical definition, a cell death with caspase activation, allows the distinction of alternative forms of cell death. Thus, inhibition of caspases delays but does not prevent cell death. Slow cell death without caspase activation may nevertheless be associated with DNA fragmentation. Oncogenic Ras, Raf, and mitogen-activated kinases inhibit apoptosis by affecting the cytochrome C/caspase-9 pathway but may arrest growth and cause slow cell death with delayed DNA fragmentation. Such ‘slow’ cell death without caspase activation is often caused by chemotherapeutic drugs. Whether a cell will undergo apoptosis or slow death depends not only on a chemotherapeutic agent but also on the readiness of cellular caspases. Therefore, one can distinguish apoptosis-prone (eg leukemia) vs apoptosis-resistant cells. Cell susceptibilities to spontaneous, starvation-induced and drug-induced apoptosis are correlated and characterize an apoptosis-prone phenotype. Finally, distinction of slow cell death allows rephrasing of a question regarding the goal of cancer therapy: apoptosis vs slow cell death, or cancer cell-selectivity regardless of the mode of cell death.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kerr JFR, Wyllie AH, Currie AR . Apoptosis: a basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics Br J Cancer 1972 26: 239–257
Vaux DL . Caspases and apoptosis – biology and terminology Cell Death Differ 1999 6: 493–494
Saunders JJW . Death in embryonic systems Science 1966 154: 604–612
Kitanaka C . Kuchino Y. Caspase-independent programmed cell death with necrotic morphology Cell Death Differ 1999 6: 508–515
Martin SJ . Protein or RNA synthesis inhibition induces apoptosis of mature human CD4+ T cell blasts Immunol Lett 1993 35: 125–134
Solary E, Bertrand R, Kohn KW, Pommier Y . Differential induction of apoptosis in undifferentiated and differentiated HL-60 cells by DNA topoisomerase I and II inhibitors Blood 1993 81: 1359–1368
Borner MM, Myers CE, Sartor O, Sei Y, Toko T, Trepel JB, Schneider E . Drug-induced apoptosis is not necessarily dependent on macromolecular synthesis or proliferation in the p53-negative human prostate cancer cell line PC-3 Cancer Res 1995 55: 2122–2128
Weil M, Jacobson MD, Coles HSR, Davies TJ, Gardner RL, Raff KD, Raff MC . Constitutive expression of the machinery for programmed cell death J Cell Biol 1996 133: 1053–1059
Wesselborg S, Engels IH, Rossmann E, Los M, Schulze-Osthoff K . Anticancer drugs induce caspase-8/FLICE activation and apoptosis in the absence of CD95 receptor/ligand interaction Blood 1999 93: 3053–3063
Li YZ, Li CJ, Pinto AV, Pardee AB . Release of mitochondrial cytochrome C in both apoptosis and necrosis induced by beta-lapachone in human carcinoma cells Mol Med 1999 5: 232–239
Nagata S . Apoptosis by death factor Cell 1997 88: 355–365
Ashkenasi A, Dixit VM . Death receptors: signaling and modulation Science 1998 281: 1305–1308
Thornberry NA, Lazebnik Y . Caspases: enemies within Science 1998 281: 1312–1316
Green DR . Apoptotic pathways: the roads to ruin Cell 1998 94: 695–698
Kumar S . Mechanisms mediating caspase activation in cell death Cell Death Differ 1999 6: 1060–1066
Green DR, Reed JC . Mitochondria and apoptosis Science 1998 281: 1309–1312
Lazebnik YA, Kaufmann SH, Desnoyers S, Poirier GG, Earnshaw WC . Cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase by a proteinase with properties like ICE Nature 1994 371: 346–347
Liu X, Zou H, Slaughter C, Wang X . DFF, a heterodimeric protein that functions downstream of caspase-3 to trigger DNA fragmentation during apoptosis Cell 1997 89: 175–184
Janicke RU, Sprengart ML, Wati MR, Porter AG . Caspase-3 is required for DNA fragmentation and morphological changes associated with apoptosis J Biol Chem 1998 273: 9357–9360
Enari M, Sakahira H, Yokoyama H, Okawa K, Iwamatsu A, Nagata S . A caspase-activated DNase that degrades DNA during apoptosis, and its inhibitor ICAD Nature 1998 391: 43–50
McIlroy D, Sakahira H, Talanian RV, Nagata S . Involvement of caspase 3-activated DNase in internucleosomal DNA cleavage induced by diverse apoptotic stimuli Oncogene 1999 18: 4401–4408
Mills JC, Stone NL, Pittman RN . Extranuclear apoptosis: the role of the cytoplasm in the execution phase J Cell Biol 1999 146: 703–707
Martin SJ, Finucance DM, Amarante-Mendes GP, O'Brien GA, Green DR . Phosphatidylserine externalization during CD95-induced apoptosis of cells and cytoplasts requires ICE/CED-3 protease activity J Biol Chem 1996 271: 28753–28756
Samali A, Zhivotovsky B, Jones D, Nagata S, Orrenius S . Apoptosis: cell death defined by caspase activation Cell Death Differ 1999 6: 495–496
Oberhammer F, Wilson JW, Dive C, Morris ID, Hickman JA, Wakeling AE, Walker PR, Sikorska M . Apoptotic death in epithelial cells: cleavage of DNA to 300 and/or 50kb fragments prior to or in the absence of internucleosomal fragmentation EMBO J 1993 12: 3679–3684
Ormerod MG, Oneill CF, Robertson D, Harrap KR . Cisplatin induces apoposis in a human ovarian-carcinoma cell-line without concomitant internucleosomal degradation of DNA Exp Cell Res 1994 211: 231–237
Rasola A, Farahi Far D, Hofman P, Rossi B . Lack of internucleosomal DNA fragmentation is related to Cl(−) efflux impairment in hematopoietic cell apoptosis FASEB J 1999 13: 1711–1723
Dong Z, Saikumar P, Weinberg JM, Venkatachalam MA . Internucleosomal DNA cleavage triggered by plasma membrane damage during necrotic cell death. Involvement of serine but not cystein proteases Am J Pathol 1997 151: 1205–1213
Khodarev NN, Sokolova IA, Vaughan AT . Mechanisms of induction of apoptotic DNA fragmentation Int J Radiat Biol 1998 73: 455–467
Chautan M, Chazal G, Cecconi F, Gruss P, Golstein P . Interdigital cell death can occur through a necrotic and caspase-independent pathway Curr Biol 1999 9: 967–970
Shimizu T, Pommier Y . Camptothecin-induced apoptosis in p53-null human leukemia HL60 cells and their isolated nuclei: effects of the protease inhibitors Z-VAD-fmk and dichloroisocoumarin suggest an involvement of both caspases and serine proteases Leukemia 1997 11: 1238–1244
Zeuner A, Eramo A, Peschle C, De Maria R . Caspase activation without death Cell Death Differ 1999 6: 1075–1080
Hirsch T, Marchetti P, Susin SA, Dallaporta B, Zamzami N, Marzo I, Geuskens M, Kroemer G . The apoptosis-necrosis paradox. Apoptogenic proteases activated after mitochondrial premeability transition determine the mode of cell death Oncogene 1997 15: 1573–1581
Amarante-Mendes GP, Finucane DM, Martin SJ, Cotter TG, Salvesen GS, Green DR . Anti-apoptotic oncogenes prevent caspase-dependent and independent commitment for cell death Cell Death Differ 1998 5: 298–306
Borner C, Monney L . Apoptosis without caspases: an inefficient molecular guillotine Cell Death Differ 1999 6: 497–507
Kolenko V, Uzzo RG, Bukowski R, Bander NH, Novick AC, Hsi ED, Finke JH . Dead or dying: necrosis vs apoptosis in caspase-deficient human renal cell carcinoma Cancer Res 1999 59: 2838–2842
Houghton JA . Apoptosis and drug response Curr Opin Oncol 1999 11: 475–481
Reed JC . Double identity for proteins of the Bcl-2 family Nature 1997 387: 773–776
Shinoura N, Yoshida Y, Nishimura M, Muramatsu Y, Asai A, Kirino T, Hamada H . Expression level of Bcl-2 determines anti- or proapoptotic function Cancer Res 1999 59: 4119–4128
Cheng EH, Kirsch DG, Clem RJ, Ravi R, Kastan MB, Bedi A, Ueno K, Hardwick JM . Conversion of Bcl-2 to a Bax-like death effector by caspases Science 1997 278: 1966–1968
Fadeel B, Hassan Z, Hellstrom-Lindberg M, Henter J-I, Orrenius S, Zhivotovsky B . Cleavage of bcl-2 is an early event in chemotherapy-induced apoptosis of human myeloid leukemia cells Leukemia 1999 13: 719–728
Blagosklonny MV, Chuman Y, Bergan RC, Fojo T . Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway is dispensible for microtubule-active drug-induced Raf-1/Bcl-2 phosphorylation and apoptosis in leukemia cells Leukemia 1999 13: 1028–1036
Lassus P, Ferlin M, Piette J, Hibner U . Anti-apoptotic activity of low levels of wild-type p53 EMBO J 1996 15: 4566–4573
Evan G, Littlewood T . A matter of life and cell death Science 1998 281: 1317–1322
Blagosklonny MV . A node between proliferation, apoptosis, and growth arrest Bioessays 1999 21: 704–709
Kauffman-Zeh A, Rodriguez-Viciana P, Ulrich E, Gilbert C, Coffer P, Downward J, Evan G . Suppression of c-myc-induced apoptosis by Ras signalling through PI(3)K and PKB Nature 1997 385: 544–548
Erhardt P, Schremser EJ, Cooper GM . B-Raf inhibits programmed cell death downstream of cytochrome c release from mitochondria by activating the MEK/Erk pathway Mol Cell Biol 1999 19: 5308–5315
Bonni A, Brunet A, West AE, Datta SR, Takasu MA, Greenberg ME . Cell survival promoted by the Ras-MAPK signaling pathway by transcription-dependent and -independent mechanisms Science 1999 286: 1358–1362
Dubrez L, Eymin B, Sordet O, Droin N, Turhan AG, Solary E . BCR-ABL delays apoptosis upstream of procaspase-3 activation Blood 1998 91: 2415–2422
Amarante-Mendes GP, Naekyung Kim C, Liu L, Huang Y, Perkins CL, Green DR, Bhalla K . Bcr-Abl exerts its antiapoptotic effect against diverse apoptotic stimuli through blockage of mitochondrial release of cytochrome C and activation of caspase-3 Blood 1998 91: 1700–1705
Cardone MH, Roy N, Stennicke HR, Salvesen GS, Franke TF, Stanbridge E, Frisch S, Reed JC . Regulation of cell death protease caspase-9 by phosphorylation Science 1998 282: 1318–1321
Zhu J, Woods D, McMahon M, Bishop JM . Senescence of human fibroblasts induced by oncogenic Raf Genes Dev 1998 12: 2997–3007
Arber N . Janus faces of ras: anti or pro-apoptotic? Apoptosis 1999 4: 383–388
Rak J, Mitsuhashi Y, Erdos V, Huang SN, Filmus J, Kerbel RS . Massive programmed cell death in intestinal epithelial cells induced by three-dimensional growth conditions: suppression by mutant c-H-ras oncogene expression J Cell Biol 1995 131: 1587–1598
Serrano M, Lin AW, McCurrach ME, Beach D, Lowe SW . Oncogenic ras provokes premature cell senescence associated with accumulation of p53 and p16INK4a Cell 1997 88: 593–602
Chi S, Kitanaka C, Noguchi K, Mochizuki T, Nagashima Y, Shirouzu M, Fujita H, Yoshida M, Chen W, Asai A, Himeno M, Yokoyama S, Kuchino Y . Oncogenic Ras triggers cell suicide through the activation of a caspase-independent cell death program in human cancer cells Oncogene 1999 18: 2281–2290
Chen CY, Liou J, Forman LW, Faller DV . Differential regulation of discrete apoptotic pathways by Ras J Biol Chem 1998 273: 16700–16709
Miranda EI, Santana C, Rojas E, Hernandez S, Ostrosky-Wegman P, Garcia-Carranca A . Induced mitotic death of HeLa cells by abnormal expression of c-H-ras Mutat Res 1996 349: 173–182
Blagosklonny MV, Wu GS, Omura S, El-Deiry WS . Proteasome-dependent regulation of p21WAF1/CIP1 expression Biochem Biophys Res Comm 1996 227: 564–569
Canman CE, Gilmer TM, Coutts SB, Kastan MB . Growth factor modulation of p53-mediated growth arrest versus apoptosis Genes Dev 1995 9: 600–611
McCubrey JA, Steelman LS, Hoyle PE, Blalock WL, Weinstein-Oppenheimer C, Franklin RA, Cherwinski H, Bosch E, McMahon M . Differential abilities of activated Raf oncoproteins to abrogate cytokine dependency, prevent apoptosis and induce autocrine growth factor synthesis in human hematopoietic cells Leukemia 1998 12: 1903–1929
El-Ashry D, Miller DL, Kharbanda S, Lippman ME, Kern FG . Constitutive Raf-1 kinase activity in breast cancer cells induces both estrogen-independent growth and apoptosis Oncogene 1997 15: 423–435
Hall-Jackson CA, Jones T, Eccles NG, Dawson TP, Bond JA, Gescher A, Wynford-Thomas D . Induction of cell death by stimulation of protein kinase C in human epithelial cells expressing a mutant ras oncogene: a potential therapeutic target Br J Cancer 1998 78: 641–651
Solary E, Bertrand R, Pommier Y . Apoptosis of human leukemic HL-60 cells induced to differentiate by phorbol ester treatment Leukemia 1994 8: 792–797
Blagosklonny MV . The mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway mediates growth arrest or E1A-dependent apoptosis in SKBr3 human breast cancer cells Int J Cancer 1998 78: 511–517
McCubrey JA, Steelman LS, Sandlin G, Riddle RS, Ways DK . Effects of phorbol esters on an interleukin-3-dependent cell line Blood 1990 76: 63–72
Chang B-D, Xuan Y, Broude EV, Zhu H, Schott B, Fang J, Roninson IB . Role of p53 and p21 waf1/cip1 in senescence-like terminal proliferation arrest induced in human cells by chemotherapeutic drugs Oncogene 1999 18: 4808–4818
Chang B-D, Broude EV, Dokmanovic M, Zhu H, Ruth A, Xuan Y, Kandel ES, Lausch E, Christov K, Roninson IB . A senescence-like phenotype distinguishes tumor cells that undergo terminal proliferation arrest after exposure to anticancer drugs Cancer Res 1999 59: 3761–3767
Kravtsov VD, Greer JP, Whitlock JA, Koury MJ . Use of the microculture kinetic assay of apoptosis to determine chemosensitivities of leukemias Blood 1998 92: 968–980
Classen CF, Fulda S, Friesen C, Debatin KM . Decreased sensitivity of drug-resistant cells towards T cell cytotoxicity Leukemia 1999 13: 410–418
Friesen C, Fulda S, Debatin KM . Deficient activation of the CD95 (APO-1/Fas) system in drug-resistant cells Leukemia 1997 11: 1833–1841
Antoku K, Liu Z, Johnson DE . Inhibition of caspase proteases by CrmA enhances the resistance of human leukemic cells to multiple chemotherapeutic agents Leukemia 1997 11: 1665–1672
Bullock G, Ray S, Reed JC, Krajewski S, Ibrado AM, Huang Y, Bhalla K . Intracellular metabolism of Ara-C and resulting DNA fragmentation and apoptosis of human AML HL-60 cells possessing disparate levels of Bcl-2 protein Leukemia 1996 10: 1731–1740
Turnbull KJ, Brown BL, Dobson PR . Caspase-3-like activity is necessary but not sufficient for daunorubicin-induced apoptosis in Jurkat human lymphoblastic leukemia cells Leukemia 1999 13: 1056–1061
Kawabata Y, Hirokawa M, Kitabayashi A, Horiuchi T, Kuroki J, Miura AB . Defective apoptotic signal transduction pathway downstream of caspase-3 in human B-lymphoma cells: a novel mechanism of nuclear resistance Blood 1999 94: 3523–3530
Roberts JR, Allison DC, Donehower RC, Rowinsky EK . Development of polyploidization in taxol resistant human leukemia cells in vitro Cancer Res 1990 50: 710–716
Martins LM, Mesner PW, Kottke Tj, Basi GS, Sinha S, Tung JS, Svingen PA, Madden BJ, Takahashi A, McCormick DJ, Earnshaw WC, Kaufmann SH . Comparison of caspase activation and subcellular localization in HL-60 and K562 cells undergoing etoposide-induced apoptosis Blood 1997 90: 4283–4296
An WG, Hwang SG, Trepel JB, Blagosklonny MV . Protease inhibitor-induced apoptosis: accumulation wt p53, p21WAF1/CIP1, and induction of apoptosis are independent markers of proteasome inhibition Leukemia 2000 14: 1276–1283
Smith BD, Bambach BJ, Vala MS, Barber JP, Enger C, Brodsky RA, Burke PJ, Gore SD, Jones RJ . Inhibited apoptosis and drug resistance in acute myeloid leukaemia Br J Haematol 1998 102: 1042–1049
Efferth T, Fabry U, Osieka R . Apoptosis and resistance to daunorubicin in human leukemic cells Leukemia 1997 11: 1180–1186
Blagosklonny MV, Somasundaram K, Wu GS, El-Deiry WS . Wild-type p53 is not sufficient for serum starvation-induced apoptosis in cancer cells but accelerates apoptosis in sensitive cells Int J Oncol 1997 11: 1165–1170
Wuchter C, Karawajew L, Ruppert V, Buchner T, Schoch C, Haferlach T, Ratei R, Dorken B, Ludwig WD . Clinical significance of CD95, Bcl-2 and Bax expression and CD95 function in adult de novo acute myeloid leukemia in context of P-glycoprotein function, maturation stage, and cytogenetics Leukemia 1999 13: 1943–1953
Kakihara T, Fukuda T, Kamishima T, Naito M, Tanaka A, Uchiyama M, Kishi K . Resistance to apoptosis induced by serum depletion and all-trans retinoic acid in drug-resistant leukemic cell lines Leuk Lymphoma 1997 26: 369–376
Nieves-Neira W, Pommier Y . Apoptotic response to camptothecin and 7-hydroxystaurosporine (UCN-01) in the 8 human breast cancer cell lines of the NCI Anticancer Drug Screen: multifactorial relationships with topoisomerase I, protein kinase C, Bcl-2, p53, MDM-2 and caspase pathways Int J Cancer 1999 82: 396–404
Los M, Herr I, Friesen C, Fulda S, Schulze-Osthoff K, Debatin KM . Cross-resistance of CD95- and drug-induced apoptosis as a consequence of deficient activation of caspases (ICE/Ced-3 proteases) Blood 1997 90: 3118–3129
Meinhardt G, Roth J, Totok G, Auner H, Emmerich B, Hass R . Signaling defect in the activation of caspase-3 and PKCdelta in human TUR leukemia cells is associated with resistance to apoptosis Exp Cell Res 1999 247: 534–542
Sane AT, Bertrand R . Distinct steps in DNA fragmentation pathway during camptothecin-induced apoptosis involved caspase-, benzyloxycarbonyl- and N-tosyl-L-phenylalanylchloromethyl ketone-sensitive activities Cancer Res 1998 58: 3066–3072
Lorenzo HK, Susin SA, Penninger J, Kroemer G . Apoptosis inducing factor (AIF): a phylogenetically old, caspase-independent effector of cell death Cell Death Differ 1999 6: 516–524
Kataoka A, Kubota M, Wakazono Y, Okuda A, Bessho R, Lin YW, Usami I, Akiyama Y, Furusho K . Association of high-molecular-weight DNA fragmentation with apoptotic or non-apoptotic cell-death induced by calcium ionophore FEBS Lett 1995 364: 264–267
Simm A, Bertsch G, Frank H, Zimmermann U, Hoppe J . Cell death of AKR-2B fibroblasts after serum removal: a process between apoptosis and necrosis J Cell Sci 1997 110: 819–828
Gorczyca W, Bigman K, Mittelman A, Ahmed T, Gong JP, Melamed MR, Darzynkiewicz Z . Induction of DNA strand breaks associated with apoptosis during treatment of leukemias Leukemia 1993 7: 659–670
Stoetzer OJ, Pogrebniak A, Scholz M, Pelka-Fleischer R, Gullis E, Darsow M, Nussler V, Wilmanns W . Drug-induced apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia Leukemia 1999 13: 1873–1880
Ibrado AM, Liu L, Bhalla K . Bcl-xL overexpression inhibits progression of molecular events leading to paclitaxel-induced apoptosis of human AML HL-60 cells Cancer Res 1997 57: 1109–1115
Datta R, Banach D, Kojima H, Talanian RV, Alnemri ES, Wong WW, Kufe DW . Activation of the CPP32 protease in apoptosis induced by 1-b-D arabinofuranosylcytosine and other DNA-damaging agents Blood 1996 88: 1936–1943
Fisher DE . Apoptosis in cancer therapy: crossing the threshold Cell 1994 78: 539–542
Shao RG, Shimizu T, Pommier Y . 7-Hydroxystaurosporine (UCN-01) induces apoptosis in human colon carcinoma and leukemia cells independently of p53 Exp Cell Res 1997 234: 388–397
Senderowicz AM, Headlee D, Stinson SF, Lush RM, Kalil N, Villalba L, Hill K, Steinberg SM, Figg WD, Tompkins A, Arbuck SG, Sausville EA . Phase I trial of continuous infusion flavopiridol, a novel cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, in patients with refractory neoplasms J Clin Oncol 1998 16: 2986–2999
Parker BW, Kaur G, Nieves-Neira W, Taimi M, Kohlhagen G, Shimizu T, Losiewicz MD, Pommier Y, Sausville EA, Senderowicz AM . Early induction of apoptosis in hematopoietic cell lines after exposure to flavopiridol Blood 1998 91: 458–465
Akiyama T, Yoshida T, Tsujita T, Shimizu M, Mizukami T, Okabe M, Akinaga S . G1 phase accumulation induced by UCN-01 is associated with dephosphorylation of Rb and CDK2 proteins as well as induction of CDK inhibitor p21/Cip1/WAF1/Sdi1 in p53-mutated human epidermoid carcinoma A431 cells Cancer Res 1997 57: 1495–1501
Sugiyama K, Akiyama T, Shimizu M, Tamaoki T, Courage C, Gescher A, Akinaga S . Decrease in susceptibility toward induction of apoptosis and alteration in G1 checkpoint function as determinants of resistance of human lung cancer cells against the antisignaling drug UCN-01 (7-hydroxystaurosporine) Cancer Res 1999 59: 4406–4412
Kruger EA, Blagosklonny MV, Dixon SC, Figg WD . UCN-01, a protein kinase C inhibitor, inhibits endothelial proliferation and angiogenic hypoxic response Invas Metast 2000 18: 209–218
Patel V, Senderowicz AM, Pinto DJ, Igishi T, Raffeld M, Quintanilla-Martinez L, Ensley JF, Sausville EA, Gutkind JS . Flavopiridol, a novel cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, suppresses the growth of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas by inducing apoptosis J Clin Invest 1998 102: 1674–1681
Drexler HC . Activation of the cell death program by inhibition of proteasome function Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997 94: 855–860
Orlowski RZ . The role of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in apoptosis Cell Death Differ 1999 6: 303–313
Chandra J, Niemer I, Gilbreath J, Kliche KO, Andreeff M, Freireich EJ, Keating M, McConkey DJ . Proteasome inhibitors induce apoptosis in glucocorticoid-resistant chronic lymphocytic leukemic lymphocytes Blood 1998 92: 4220–4229
Adams J, Palombella VJ, Sausville EA, Johnson J, Destree A, Lazarus DD, Maas J, Pien CS, Prakash S, Elliott PJ . Proteasome inhibitors: a novel class of potent and effective antitumor agents Cancer Res 1999 59: 2615–2622
An B, Goldfarb RH, Siman R, Dou QP . Novel dipeptidyl proteasome inhibitors overcome Bcl-2 protective function and selectively accumulate the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27 and induce apoptosis in transformed, but not normal, human fibroblasts Cell Death Differ 1998 5: 1062–1075
Squier MK, Sehnert AJ, Cohen JJ . Apoptosis in leukocytes J Leuk Biol 1995 57: 2–10
Metcalfe A, Streuli C . Epithelial apoptosis Bioessays 1997 19: 711–720
Reed JC . Dysregulation of apoptosis in cancer J Clin Oncol 1999 17: 2941–2954
Schmitt CA, Lowe SW . Apoptosis and therapy J Pathol 1999 187: 127–137
Kastan MB, Canman CE, Leonard CJ . P53, cell cycle control and apoptosis: implications for cancer Cancer Metast Rev 1995 14: 3–15
Darzynkiewicz Z . Apoptosis in antitumor strategies – modulation of cell-cycle or differentiation J Cell Biochem 1995 58: 151–159
Fadeel B, Orrenius S, Zhivotovsky B . Apoptosis in human disease: a new skin for the old ceremony Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1999 266: 699–717
Kitada S, Andersen J, Akar S, Zapata JM, Takayama S, Krajewski S, Wang HG, Zhang X, Bullrich F, Croce CM, Rai K, Hines J, Reed JC . Expression of apoptosis-regulating proteins in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: correlations with in vitro and in vivo chemoresponses Blood 1998 91: 3379–3389
Hannun YA . Apoptosis and the dilemma of cancer chemotherapy Blood 1997 89: 1845–1853
Martin SJ, Green DR . Apoptosis as a goal of cancer therapy Curr Opin Oncol 1994 6: 616–621
Soignet SL, Maslak P, Wang ZG, Jhanwar S, Calleja E, Dardashti LJ, Corso D, DeBlasio A, Gabrilove J, Scheinberg DA, Pandolfi PP, Warrell RPJ . Complete remission after treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia with arsenic trioxide New Engl J Med 1998 339: 1341–1348
Pardee AB, James LJ . Selective killing of transformed baby hamster kidney (BHK) cells Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1975 72: 4994–4998
Pardee AB . A restriction point for control of normal animal cell proliferation Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1974 71: 1286–1290
Komarov PG, Komarova EA, Kondratov RV, Christov-Tselkov K, Coon JS, Chernov MV, Gudkov AV . A chemical inhibitor of p53 that protects mice from the side-effects of cancer therapy Science 1999 285: 1733–1737
Blagosklonny MV, Robey R, Bates S, Fojo T . Pretreatment with DNA-damaging agents permits selective killing of checkpoint-deficient cells by microtubule-active drugs J Clin Invest 2000 105: 533–539
Blagosklonny MV . Drug-resistance enables selective killing of resistant leukemia cells: exploiting of drug resistance instead of reversal Leukemia 1999 13: 2031–2035
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blagosklonny, M. Cell death beyond apoptosis. Leukemia 14, 1502–1508 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2401864
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2401864
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Targeting of apoptosis gene loci by reprogramming factors leads to selective eradication of leukemia cells
Nature Communications (2019)
-
Two coffins and a funeral: early or late caspase activation determines two types of apoptosis induced by DNA damaging agents
Apoptosis (2017)
-
Differences in osteogenic and apoptotic genes between osteoporotic and osteoarthritic patients
BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2013)
-
Ganglioside Biosynthesis in Developing Brains and Apoptotic Cancer Cells: X. Regulation of Glyco-genes Involved in GD3 and Sialyl-Lex/a Syntheses
Neurochemical Research (2012)